Social norms shape behavior by establishing unwritten rules that guide interactions within communities. These collective expectations influence your decisions and help maintain order and predictability in social settings. Discover how social norms impact daily life and affect personal and group dynamics throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
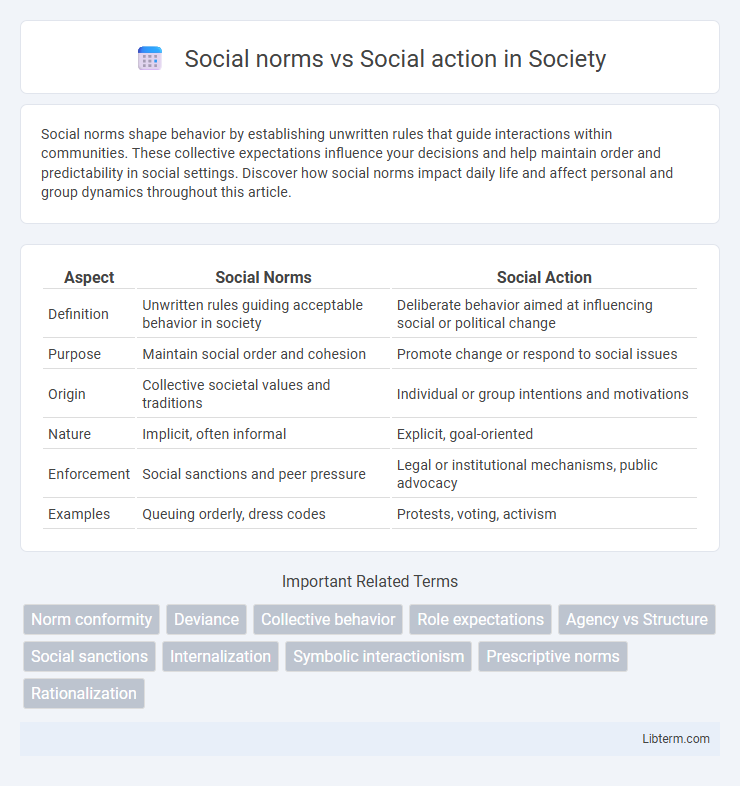
| Aspect | Social Norms | Social Action |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwritten rules guiding acceptable behavior in society | Deliberate behavior aimed at influencing social or political change |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and cohesion | Promote change or respond to social issues |
| Origin | Collective societal values and traditions | Individual or group intentions and motivations |
| Nature | Implicit, often informal | Explicit, goal-oriented |
| Enforcement | Social sanctions and peer pressure | Legal or institutional mechanisms, public advocacy |
| Examples | Queuing orderly, dress codes | Protests, voting, activism |
Understanding Social Norms: Definition and Importance
Social norms are unwritten rules that govern individual behavior within a society, shaping expectations and promoting social order. These collective standards influence social action by guiding individuals on acceptable conduct, reinforcing conformity, and facilitating cooperation. Understanding social norms is vital for analyzing how cultural values and social structures impact behavior and maintain social cohesion.
Social Action: Exploring Its Meaning and Types
Social action refers to behaviors consciously oriented toward others, driven by meanings and intentions within a social context. Max Weber categorized social action into four types: instrumental-rational, value-rational, affectual, and traditional, each reflecting different motivations behind human conduct. Understanding these types helps analyze how individuals shape society through purposeful, meaningful interactions beyond mere adherence to social norms.
How Social Norms Shape Human Behavior
Social norms significantly influence human behavior by establishing shared expectations and rules within a group, guiding individuals toward conforming actions that maintain social harmony. These unwritten standards affect decision-making processes, promoting behaviors that align with societal values and discouraging deviance through social sanctions. The dynamic interaction between internalized norms and external social pressures shapes patterns of social action, reinforcing collective identity and stability.
The Relationship Between Social Norms and Social Action
Social norms serve as implicit rules guiding individual behavior within a society, shaping expectations and influencing decision-making processes. Social actions emerge as responses to these norms, either conforming to, modifying, or challenging them, thereby facilitating dynamic social interactions. The interplay between social norms and social action drives social change, as collective behaviors reinforce existing norms or catalyze new patterns of societal conduct.
Historical Evolution of Social Norms and Actions
Social norms have historically evolved through collective behaviors and moral codes that guided societies from tribal communities to complex civilizations, reflecting shared values and expectations. Social actions, driven by individual agency and context-specific decisions, have often challenged or reinforced these norms, leading to significant cultural and institutional transformations over time. The dynamic interplay between evolving social norms and diverse social actions has shaped legal systems, social movements, and governance structures throughout history.
Factors Influencing Social Action in Different Cultures
Social action is profoundly shaped by cultural values, belief systems, and historical contexts that define societal norms. Variables such as power distribution, economic conditions, and social institutions create diverse motivations and constraints influencing individual and collective behaviors across cultures. Understanding these factors illuminates how social norms translate into concrete actions uniquely within varied cultural frameworks.
Deviance: When Social Action Challenges Social Norms
Deviance occurs when social actions directly challenge established social norms, disrupting expected behaviors within a community or society. Such actions highlight discrepancies between individual or group conduct and collective standards, often prompting social reactions ranging from sanctions to reform. Understanding the dynamics of deviance reveals how societal norms evolve through conflict and negotiation between conformity and resistance.
The Role of Social Norms in Promoting Social Order
Social norms are unwritten rules that guide individual behavior within a community, shaping expectations and maintaining predictability in social interactions. These norms reinforce social order by promoting conformity, reducing conflicts, and enabling cooperation among group members. Social action, driven by personal motives and goals, often aligns with these norms to sustain harmony and collective well-being in society.
Case Studies: Social Change Driven by Collective Action
Case studies of social change driven by collective action reveal how social norms serve as both barriers and catalysts for transformation. For instance, the Civil Rights Movement in the United States reshaped racial equality norms through sustained protests and legal challenges, demonstrating the power of collective agency to redefine societal expectations. Similarly, the #MeToo movement illustrates how digital activism can disrupt entrenched gender norms by mobilizing global conversations on sexual harassment and violence.
Balancing Tradition and Transformation: Navigating Social Norms Today
Balancing tradition and transformation requires understanding the influence of social norms on individual and collective social actions, where deeply ingrained customs often guide behavior while evolving values prompt shifts. Social norms act as unwritten rules that maintain societal cohesion, yet social action embodies the dynamic responses challenging or reinforcing these norms in diverse contexts. Navigating this tension involves critically analyzing cultural expectations alongside emerging social movements to foster progress without eroding foundational community identities.
Social norms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com