Grassroots activism empowers local communities to drive social and political change by mobilizing individuals at the neighborhood level. This form of activism often focuses on issues directly affecting people's daily lives, making it a powerful tool for fostering democratic participation and accountability. Explore how grassroots movements can transform your community and inspire meaningful reforms in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
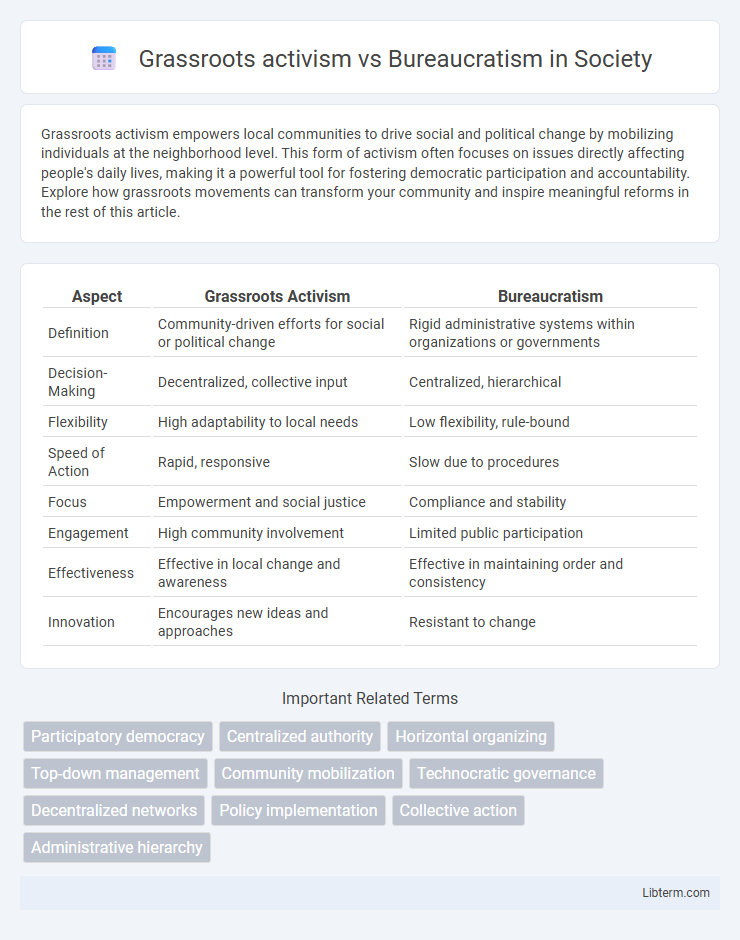
| Aspect | Grassroots Activism | Bureaucratism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Community-driven efforts for social or political change | Rigid administrative systems within organizations or governments |
| Decision-Making | Decentralized, collective input | Centralized, hierarchical |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to local needs | Low flexibility, rule-bound |
| Speed of Action | Rapid, responsive | Slow due to procedures |
| Focus | Empowerment and social justice | Compliance and stability |
| Engagement | High community involvement | Limited public participation |
| Effectiveness | Effective in local change and awareness | Effective in maintaining order and consistency |
| Innovation | Encourages new ideas and approaches | Resistant to change |
Understanding Grassroots Activism
Grassroots activism drives social change through the direct involvement of community members, emphasizing local knowledge and collective action to address specific issues. This bottom-up approach contrasts with bureaucratism, which often relies on hierarchical structures and rigid protocols that can limit responsiveness and innovation. Understanding grassroots activism requires recognizing its power in mobilizing citizens, fostering democratic participation, and creating sustainable, community-centered solutions.
Defining Bureaucratism
Bureaucratism refers to a rigid organizational structure characterized by fixed rules, hierarchical authority, and an emphasis on procedural correctness, often leading to inefficiency and resistance to change. Unlike grassroots activism, which thrives on community-driven participation and flexible strategies, bureaucratism prioritizes standardized processes and control mechanisms that can stifle innovation. This system's dominance in large institutions frequently results in slow decision-making and limited responsiveness to public needs.
Historical Contexts of Both Approaches
Grassroots activism historically emerged as a bottom-up approach during pivotal movements like the Civil Rights Movement and anti-colonial struggles, emphasizing community-driven change and direct participation. Bureaucratism developed alongside modern state institutions, characterized by hierarchical authority and formalized procedures evident in 19th-century European governance and post-World War II administrative expansion. Both approaches reflect contrasting responses to social organization and policy implementation shaped by their unique historical contexts.
Key Differences in Organizational Structure
Grassroots activism relies on decentralized, community-based participation where decision-making is often horizontal and inclusive, empowering individuals at the local level. Bureaucratism features a hierarchical, top-down organizational structure with rigid rules and formal procedures controlling actions and communications. The key difference lies in grassroots activism's flexibility and adaptability versus bureaucratism's emphasis on control, uniformity, and efficiency through established authority levels.
Community Engagement and Participation
Grassroots activism fosters direct community engagement by empowering local residents to actively participate in decision-making processes, enhancing democratic legitimacy and social cohesion. Bureaucratism often imposes top-down regulations that can limit community involvement, creating barriers to meaningful participation and reducing responsiveness to local needs. Effective community engagement thrives when grassroots initiatives influence or collaborate with bureaucratic structures to ensure inclusive and participatory governance.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Grassroots activism emphasizes decentralized decision-making through collective input and community engagement, fostering rapid responses and adaptive strategies aligned with local needs. Bureaucratism relies on hierarchical, formalized procedures with standardized protocols, which can slow decision-making but ensures consistency and accountability across large organizations. The contrast lies in flexibility and responsiveness in grassroots movements versus rigidity and control in bureaucratic structures, impacting the effectiveness and inclusiveness of policy implementation.
Impact and Effectiveness on Social Change
Grassroots activism drives social change through community engagement and direct action, often resulting in rapid, culturally resonant impact by mobilizing local resources and voices. Bureaucratism, characterized by hierarchical structures and procedural frameworks, tends to slow decision-making but ensures policy stability and scalability through institutionalized processes. The effectiveness of grassroots initiatives is frequently measured by immediate community outcomes and awareness, while bureaucratic approaches rely on long-term policy implementation and systemic reform.
Challenges Faced by Grassroots Movements
Grassroots activism often encounters significant challenges such as limited funding, lack of institutional support, and difficulties in gaining media coverage, which hinder its ability to influence policy compared to entrenched bureaucratic systems. These movements struggle with organizational capacity and sustaining momentum while navigating complex legal and political frameworks dominated by bureaucratism. Despite these obstacles, grassroots initiatives drive social change by mobilizing community engagement and leveraging local knowledge to challenge rigid bureaucratic processes.
Critiques and Limitations of Bureaucratic Systems
Bureaucratic systems often face critiques for their rigid hierarchical structures that hinder flexibility and responsiveness in decision-making processes. The emphasis on standardized procedures and numerous formalities can lead to inefficiency, slowing down innovation and grassroots initiatives. Such limitations frequently alienate community-driven efforts by prioritizing control over collaboration, thereby stifling local engagement and adaptive problem-solving.
Navigating Synergy Between Grassroots and Bureaucracy
Navigating the synergy between grassroots activism and bureaucratism requires aligning community-driven initiatives with institutional frameworks to enhance policy impact and operational efficiency. Effective collaboration leverages grassroots insights to inform bureaucratic decision-making while utilizing administrative structures to scale local efforts. This dynamic balance fosters adaptive governance, ensuring responsive public services and sustained social innovation.
Grassroots activism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com