Informal networks play a crucial role in the flow of information and collaboration within organizations by connecting individuals through personal relationships rather than formal structures. These networks often enhance innovation, problem-solving, and employee engagement by facilitating open communication and trust. Explore the rest of the article to discover how you can leverage informal networks for greater workplace success.
Table of Comparison
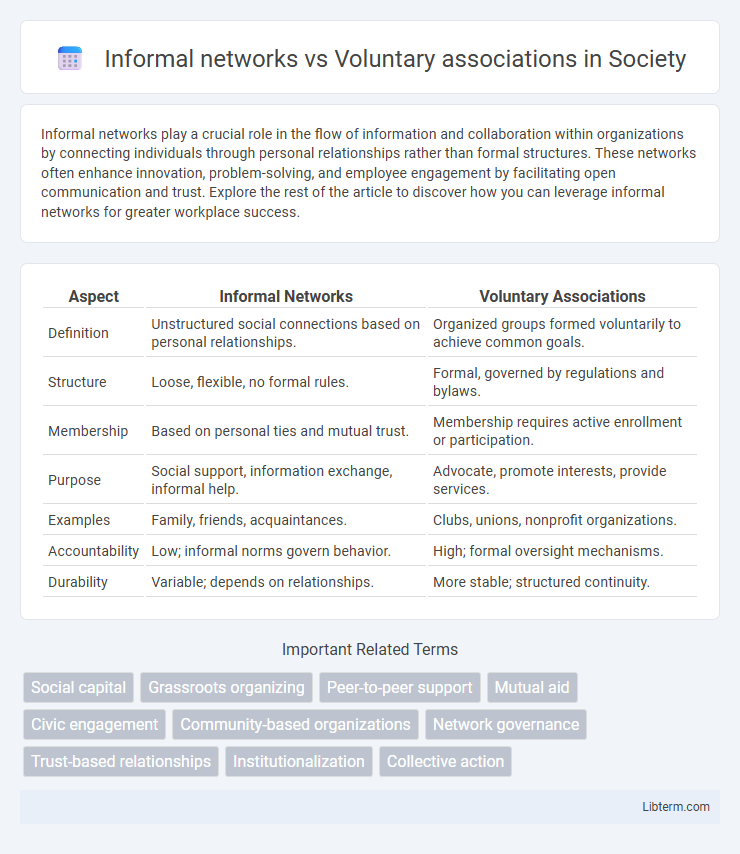
| Aspect | Informal Networks | Voluntary Associations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unstructured social connections based on personal relationships. | Organized groups formed voluntarily to achieve common goals. |
| Structure | Loose, flexible, no formal rules. | Formal, governed by regulations and bylaws. |
| Membership | Based on personal ties and mutual trust. | Membership requires active enrollment or participation. |
| Purpose | Social support, information exchange, informal help. | Advocate, promote interests, provide services. |
| Examples | Family, friends, acquaintances. | Clubs, unions, nonprofit organizations. |
| Accountability | Low; informal norms govern behavior. | High; formal oversight mechanisms. |
| Durability | Variable; depends on relationships. | More stable; structured continuity. |
Understanding Informal Networks
Informal networks are organic, unstructured connections between individuals based on trust, shared interests, or social interactions that facilitate information flow and collaboration beyond formal organizational boundaries. These networks often influence decision-making and problem-solving through personal relationships and informal communication channels. Understanding informal networks is crucial for identifying key influencers, enhancing knowledge sharing, and driving innovation within groups or organizations.
Defining Voluntary Associations
Voluntary associations are formally organized groups created by individuals who share common interests, goals, or values and choose to collaborate to achieve them. These associations possess defined membership criteria, governance structures, and often engage in collective actions or advocacy, distinguishing them from informal networks that rely on personal relationships and lack formal organization. Emphasizing voluntary participation, they foster social capital and community engagement through structured activities and shared commitments.
Key Differences Between Informal Networks and Voluntary Associations
Informal networks consist of spontaneous, organic relationships based on personal connections and social interactions without formal structure or membership requirements. Voluntary associations are formally organized groups with defined goals, membership protocols, and leadership roles designed to achieve common interests or objectives. Key differences include the level of organization, purpose clarity, and mechanisms for coordination and accountability.
Social Dynamics in Informal Networks
Informal networks comprise spontaneous, trust-based relationships that facilitate rapid information flow and social support within communities or organizations, enhancing collaboration and adaptability. These networks often emerge through shared interests, social interactions, and mutual assistance, influencing decision-making processes and group cohesion. Understanding the social dynamics in informal networks is crucial for leveraging social capital and fostering innovation beyond the structured framework of voluntary associations.
Governance Structures in Voluntary Associations
Governance structures in voluntary associations typically involve formalized roles such as elected boards, committees, and constitutions that outline decision-making processes and accountability measures. These frameworks enable transparent leadership, member participation, and systematic policy implementation, distinguishing voluntary associations from informal networks that operate through flexible, unstructured interactions. The presence of bylaws and regular meetings ensures organizational stability and responsive governance in voluntary associations.
The Role of Trust and Reciprocity
Informal networks rely heavily on trust and reciprocity to facilitate social interactions and resource exchanges without formal agreements, strengthening interpersonal bonds and enabling flexible support systems. Voluntary associations, while also built on trust, formalize commitments through membership rules and shared goals, providing structured opportunities for reciprocal actions and collective cooperation. Trust in both contexts enhances cooperation, but informal networks depend on personal relationships whereas voluntary associations institutionalize reciprocal obligations.
Impact on Community Engagement
Informal networks foster spontaneous and flexible interactions among community members, enhancing trust and rapid information exchange that boosts grassroots participation. Voluntary associations provide structured frameworks with clear goals and organized activities, leading to sustained community engagement through coordinated efforts and resource mobilization. Both mechanisms complement each other by balancing organic social bonds with formalized strategies to strengthen community cohesion and collective action.
Flexibility and Adaptability: A Comparative View
Informal networks exhibit high flexibility and adaptability by evolving spontaneously to meet immediate social or professional needs without rigid structures. Voluntary associations maintain flexibility through formal membership rules and organizational frameworks but adapt more slowly due to decision-making processes and established goals. The dynamic nature of informal networks allows rapid response to changes, whereas voluntary associations balance adaptability with stability and long-term objectives.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Case studies reveal that informal networks, such as employee grapevines in corporations like Google, foster rapid information flow and innovation through trust-based, unstructured connections. Voluntary associations like Rotary International demonstrate formalized membership and goal-oriented collaboration, enabling community service projects and leadership development on a global scale. Comparative analyses emphasize informal networks' agility contrasted with voluntary associations' strategic resource mobilization and sustained civic engagement.
Which Model Best Suits Modern Societies?
Informal networks, characterized by spontaneous, flexible connections, excel in fostering rapid information flow and adaptability essential for dynamic modern societies. Voluntary associations, with structured organizations and defined goals, provide stability and organized civic engagement, supporting democratic participation and social cohesion. Modern societies benefit most from hybrid models that blend informal networks' agility with voluntary associations' accountability to address complex social challenges effectively.
Informal networks Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com