Multiculturalism fosters a rich blend of diverse cultures coexisting peacefully, enhancing social cohesion and mutual respect. It encourages understanding and acceptance, promoting inclusivity in communities and workplaces. Explore the rest of the article to discover how embracing multiculturalism can positively impact your world.
Table of Comparison
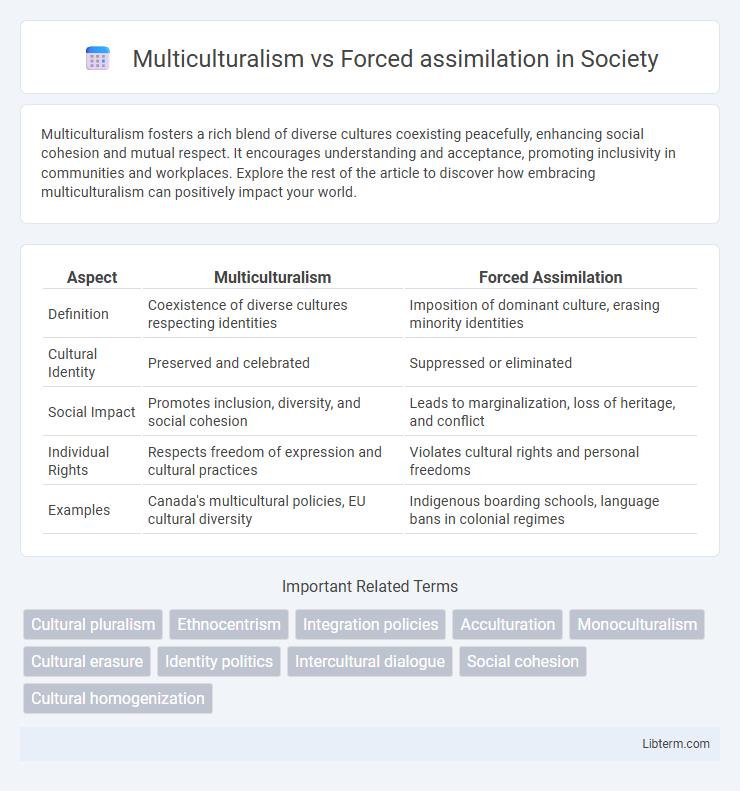
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Forced Assimilation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures respecting identities | Imposition of dominant culture, erasing minority identities |
| Cultural Identity | Preserved and celebrated | Suppressed or eliminated |
| Social Impact | Promotes inclusion, diversity, and social cohesion | Leads to marginalization, loss of heritage, and conflict |
| Individual Rights | Respects freedom of expression and cultural practices | Violates cultural rights and personal freedoms |
| Examples | Canada's multicultural policies, EU cultural diversity | Indigenous boarding schools, language bans in colonial regimes |
Understanding Multiculturalism: Definition and Principles
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence and mutual respect of diverse cultural groups within a society, emphasizing the preservation of unique identities and practices. It is based on principles of equal recognition, inclusion, and cultural pluralism, allowing individuals to maintain their heritage while participating fully in societal life. This approach contrasts with forced assimilation, which demands conformity to a dominant culture, often leading to loss of cultural diversity and social exclusion.
Forced Assimilation: Historical Context and Examples
Forced assimilation refers to policies and practices aimed at eradicating the cultural identity of minority groups to integrate them into a dominant society. Historical examples include the Native American Boarding Schools in the United States, where Indigenous children were compelled to abandon their languages and traditions. Other significant cases are the Australian Stolen Generations and the cultural suppression of Indigenous peoples in Canada through residential schools, both aimed at erasing native identities.
Benefits of Multicultural Societies
Multicultural societies foster creativity and innovation by bringing together diverse perspectives, enhancing problem-solving and economic growth. They promote social cohesion and mutual respect, reducing prejudice and fostering inclusion among different cultural groups. Cultural diversity also enriches educational experiences and broadens individuals' worldviews, contributing to stronger, more adaptable communities.
Consequences of Forced Assimilation Policies
Forced assimilation policies often result in the loss of cultural identity, language extinction, and intergenerational trauma among marginalized communities. These policies disrupt social cohesion by creating resentment and resistance, ultimately weakening national unity and stability. Studies indicate that preserving multiculturalism promotes social inclusion, mental health, and economic contributions from diverse ethnic groups.
Identity Formation in Multicultural Environments
Multiculturalism fosters identity formation by allowing individuals to express diverse cultural heritages within a shared societal framework, promoting inclusivity and psychological well-being. Forced assimilation, in contrast, undermines authentic identity development by suppressing cultural differences and imposing a dominant norm, often leading to identity confusion and social alienation. Research indicates that environments supporting multiculturalism enhance self-esteem and social cohesion by validating multiple cultural identities simultaneously.
Cultural Preservation vs. Homogenization
Multiculturalism promotes cultural preservation by allowing diverse ethnic groups to maintain their unique traditions, languages, and identities within a shared society. Forced assimilation leads to homogenization, often erasing cultural distinctions and imposing a dominant culture's norms and values on minority groups. The tension between these approaches impacts social cohesion, identity politics, and the survival of indigenous languages and customs worldwide.
Social Cohesion: Integration Without Erasure
Multiculturalism fosters social cohesion by promoting integration without erasing cultural identities, allowing diverse communities to maintain their unique traditions while participating fully in society. This approach enhances mutual respect and understanding, reducing social tensions and encouraging collaborative problem-solving across different cultural groups. Forced assimilation, in contrast, often leads to social fragmentation and resentment as it suppresses minority cultures, diminishing trust and undermining collective unity.
Legal Frameworks Supporting Multiculturalism
Legal frameworks supporting multiculturalism emphasize the protection of cultural rights and promote equal recognition of diverse identities, such as Canada's Multiculturalism Act that guarantees cultural preservation and nondiscrimination. International human rights instruments like the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples advocate for the self-determination and cultural autonomy of minority groups. These laws contrast with policies of forced assimilation, which often suppress minority languages and traditions, undermining fundamental human rights protections.
Modern Case Studies: Multiculturalism in Practice
Modern case studies demonstrate multiculturalism's effectiveness in fostering inclusive societies, as seen in Canada's official multiculturalism policy promoting diversity and equal opportunity. In contrast, forced assimilation policies, such as those historically implemented against Indigenous populations in Australia, have led to cultural erasure and social disintegration. Multicultural frameworks support cultural retention, social cohesion, and economic contributions from diverse groups, emphasizing voluntary integration without sacrificing identity.
Moving Forward: Embracing Diversity or Uniformity?
Multiculturalism promotes societal strength through the celebration of diverse cultures, fostering inclusivity, innovation, and mutual respect. Forced assimilation undermines cultural identities and often leads to social fragmentation, loss of heritage, and psychological harm. Moving forward, embracing diversity enhances social cohesion and economic growth by leveraging varied perspectives, while uniformity risks stagnation and cultural erosion.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com