Role overload occurs when you face excessive demands from multiple responsibilities, leading to stress and decreased productivity. Balancing work, family, and personal obligations often intensifies the feeling of being overwhelmed, impacting mental and physical well-being. Explore the rest of the article to discover strategies for managing role overload effectively.
Table of Comparison
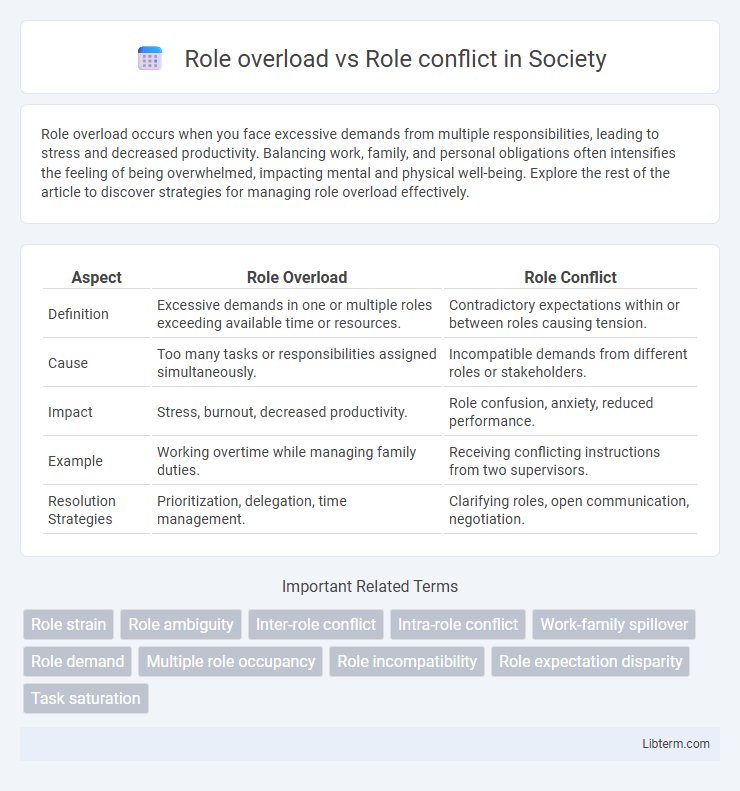
| Aspect | Role Overload | Role Conflict |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive demands in one or multiple roles exceeding available time or resources. | Contradictory expectations within or between roles causing tension. |
| Cause | Too many tasks or responsibilities assigned simultaneously. | Incompatible demands from different roles or stakeholders. |
| Impact | Stress, burnout, decreased productivity. | Role confusion, anxiety, reduced performance. |
| Example | Working overtime while managing family duties. | Receiving conflicting instructions from two supervisors. |
| Resolution Strategies | Prioritization, delegation, time management. | Clarifying roles, open communication, negotiation. |
Understanding Role Overload
Role overload occurs when the demands of multiple roles exceed an individual's available time and resources, leading to stress and decreased performance. This condition contrasts with role conflict, where incompatible expectations from different roles create tension, but role overload centers on sheer volume and intensity of responsibilities. Understanding role overload is essential for effective workload management to prevent burnout and maintain productivity.
Defining Role Conflict
Role conflict occurs when an individual faces incompatible demands from multiple roles, making it difficult to meet expectations simultaneously. It differs from role overload, which involves having too many responsibilities within one or more roles. Defining role conflict centers on the psychological stress caused by contradictory role expectations, leading to tension and impaired performance.
Key Differences Between Role Overload and Role Conflict
Role overload occurs when an individual faces too many tasks or responsibilities simultaneously, leading to stress and reduced performance, whereas role conflict arises from incompatible demands within different roles that create tension and confusion. Role overload emphasizes quantity and capacity limits, while role conflict centers on quality and priority clashes between expectations. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective workload management and interpersonal role negotiations in organizational settings.
Common Causes of Role Overload
Role overload occurs when the demands of multiple roles exceed an individual's time and energy, leading to stress and decreased performance. Common causes of role overload include excessive job responsibilities, unrealistic deadlines, and lack of support or resources in both professional and personal domains. This imbalance often results in reduced job satisfaction and impaired work-life balance.
Typical Sources of Role Conflict
Typical sources of role conflict include incompatible expectations from different social roles, such as conflicting demands between work responsibilities and family obligations. Role conflict often arises when an individual faces contradictory requirements from supervisors, peers, or societal norms, making it difficult to satisfy all expectations simultaneously. Time constraints, resource limitations, and ambiguous job roles further exacerbate these conflicts, leading to stress and decreased performance.
Impact of Role Overload on Well-being
Role overload, characterized by excessive demands exceeding an individual's capacity, significantly impairs well-being by increasing stress levels, exhaustion, and burnout risk. Unlike role conflict, which involves incompatible expectations from multiple roles, role overload primarily leads to decreased job satisfaction and heightened psychological distress. Prolonged exposure to role overload is linked to negative physical health outcomes and reduced overall life satisfaction.
Consequences of Role Conflict in the Workplace
Role conflict in the workplace often leads to decreased job satisfaction, increased stress, and higher absenteeism rates among employees. This conflict arises when incompatible demands from different roles create confusion, resulting in reduced productivity and impaired decision-making. Long-term consequences include burnout, diminished employee engagement, and elevated turnover rates, negatively impacting organizational performance.
Strategies for Managing Role Overload
Role overload occurs when job demands exceed an individual's capacity, leading to stress and burnout, whereas role conflict involves incompatible expectations within or between roles. Effective strategies for managing role overload include prioritizing tasks using time management techniques such as the Eisenhower Matrix, delegating responsibilities to capable team members, and setting clear boundaries to prevent work from encroaching on personal time. Organizations can support employees by promoting flexible work arrangements and providing resources like workload assessments and counseling services to mitigate the impact of role overload.
Solutions to Address Role Conflict
Role conflict arises when incompatible demands from different roles create stress, requiring clear communication and boundary-setting as primary solutions to reduce overlap. Implementing time management techniques and prioritizing tasks can help individuals navigate competing expectations, ensuring each role receives adequate attention. Support from supervisors through role clarification and negotiation further alleviates pressures and enhances role performance.
Comparing the Effects of Role Overload and Role Conflict
Role overload occurs when the demands of multiple roles exceed an individual's capacity, leading to stress and reduced job performance, while role conflict arises from incompatible expectations between roles causing psychological tension and decreased satisfaction. Studies show that role overload primarily impacts employee burnout and physical health, whereas role conflict significantly affects emotional well-being and interpersonal relationships at work. Both factors contribute to decreased organizational commitment but require distinct management strategies targeting workload distribution and role clarity.
Role overload Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com