Libertarianism champions individual freedom, advocating for minimal government interference in personal and economic affairs to maximize autonomy and personal responsibility. This political philosophy emphasizes free markets, private property rights, and voluntary association as the foundations of a just society. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how libertarian principles impact contemporary politics and your daily life.
Table of Comparison
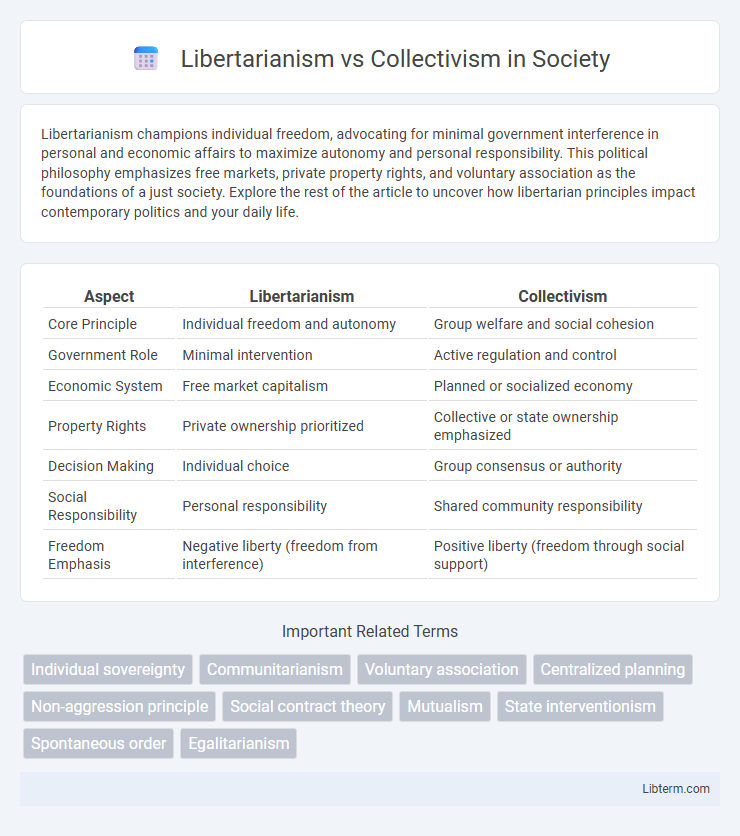
| Aspect | Libertarianism | Collectivism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Individual freedom and autonomy | Group welfare and social cohesion |
| Government Role | Minimal intervention | Active regulation and control |
| Economic System | Free market capitalism | Planned or socialized economy |
| Property Rights | Private ownership prioritized | Collective or state ownership emphasized |
| Decision Making | Individual choice | Group consensus or authority |
| Social Responsibility | Personal responsibility | Shared community responsibility |
| Freedom Emphasis | Negative liberty (freedom from interference) | Positive liberty (freedom through social support) |
Introduction to Libertarianism and Collectivism
Libertarianism emphasizes individual liberty, private property, and minimal government intervention, advocating for free markets and personal autonomy. Collectivism, by contrast, prioritizes group goals, social equality, and often supports government involvement to redistribute resources and promote communal welfare. These contrasting ideologies shape political debates on freedom, responsibility, and the role of the state in society.
Historical Roots and Philosophical Foundations
Libertarianism traces its roots to Enlightenment thinkers such as John Locke and emphasizes individual liberty, property rights, and limited government intervention as foundational principles. Collectivism, influenced by philosophers like Karl Marx and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, prioritizes the group or community's welfare, advocating for shared ownership and centralized control to achieve social equality. The historical development of libertarianism and collectivism reflects a fundamental conflict between individual autonomy and communal responsibility in political philosophy.
Core Principles of Libertarianism
Libertarianism centers on individual liberty, advocating minimal government intervention in personal and economic affairs to maximize freedom and personal responsibility. It emphasizes private property rights, voluntary exchange, and limited state power to protect individual autonomy. The doctrine supports free markets and opposes collectivist policies that prioritize group goals over individual rights.
Fundamental Tenets of Collectivism
Collectivism emphasizes the primacy of the group over the individual, advocating for shared ownership and collective decision-making to achieve social equality and common good. It upholds the belief that individual rights must often be subordinated to the needs of the community or society as a whole. Central tenets include social cooperation, public control of resources, and the pursuit of collective welfare through solidarity and mutual support.
Individual Rights vs Collective Good
Libertarianism emphasizes the primacy of individual rights, advocating minimal state intervention to protect personal freedom and private property. Collectivism prioritizes the collective good, supporting social and economic policies that promote group welfare and equality, sometimes at the expense of individual autonomy. The core tension lies in balancing personal liberty against societal benefits, influencing debates on governance, ethics, and economic systems.
Economic Implications and Property Ownership
Libertarianism emphasizes individual property rights and minimal government intervention, promoting free-market economies where private ownership drives innovation and wealth creation. Collectivism supports communal or state ownership of resources, aiming to reduce economic inequality through centralized planning and redistribution. The economic implications include contrasting incentives: libertarianism fosters competition and personal responsibility, while collectivism prioritizes social welfare and equitable access to resources.
Government Role and Authority in Society
Libertarianism advocates for minimal government intervention, emphasizing individual liberty and personal responsibility as the foundation of a free society. Collectivism supports a stronger government role, prioritizing social equality and collective welfare through policies that regulate economic and social activities. The debate centers on whether authority should protect individual rights or promote communal goals to achieve social justice and stability.
Social Welfare: Personal Responsibility vs Shared Obligation
Libertarianism emphasizes personal responsibility, advocating minimal government intervention in social welfare to encourage individual autonomy and self-reliance. Collectivism supports shared obligation, promoting extensive social safety nets and community-driven programs to ensure equitable access to resources and reduce societal disparities. The debate centers on whether social welfare systems should prioritize individual freedom or collective support to address economic and social challenges.
Success Stories and Critiques: Real-World Examples
Libertarianism thrives in economies like Hong Kong's, where minimal government intervention spurred rapid economic growth and innovation, showcasing the benefits of personal freedom and free markets. Collectivism's success is evident in countries like Sweden, which balance social welfare and economic efficiency, highlighting robust safety nets and low inequality as crucial factors. Critics of libertarianism argue it can lead to significant social inequality and inadequate public services, while collectivism faces criticism for potentially stifling individual initiative and causing bureaucratic inefficiencies.
Conclusion: Finding Balance Between Liberty and Community
Libertarianism emphasizes individual freedom and minimal government interference, while collectivism prioritizes social welfare and communal decision-making. Achieving a balance between liberty and community requires integrating personal rights with social responsibilities to foster both innovation and social cohesion. Sustainable governance models incorporate elements of both ideologies to promote equitable growth and protect individual freedoms.
Libertarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com