Interest groups play a crucial role in shaping public policy by representing the views and concerns of specific segments of society to lawmakers and government officials. They use lobbying, advocacy, and public campaigns to influence decisions that align with their members' interests. Discover how interest groups impact your community and the political landscape by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
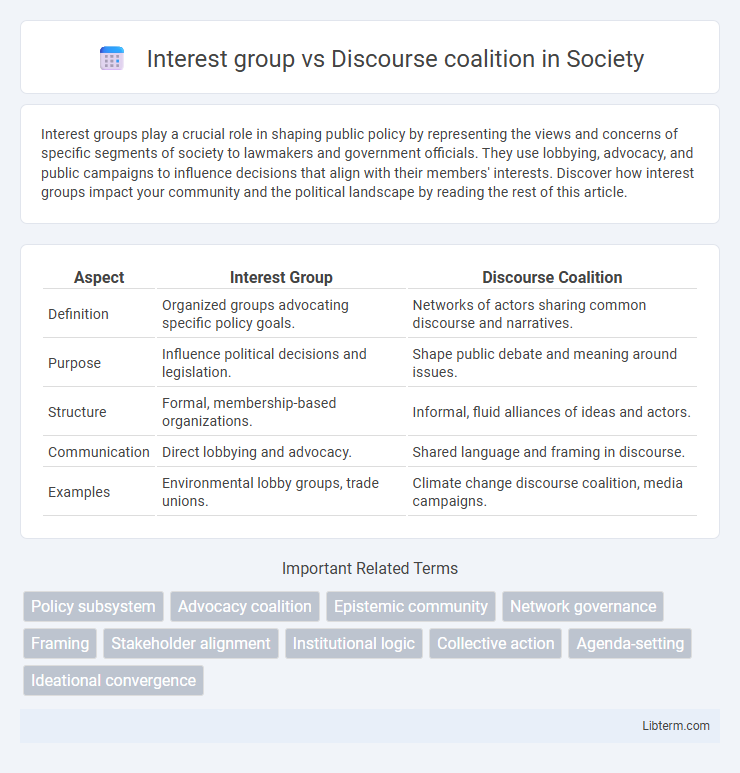
| Aspect | Interest Group | Discourse Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organized groups advocating specific policy goals. | Networks of actors sharing common discourse and narratives. |
| Purpose | Influence political decisions and legislation. | Shape public debate and meaning around issues. |
| Structure | Formal, membership-based organizations. | Informal, fluid alliances of ideas and actors. |
| Communication | Direct lobbying and advocacy. | Shared language and framing in discourse. |
| Examples | Environmental lobby groups, trade unions. | Climate change discourse coalition, media campaigns. |
Introduction to Interest Groups and Discourse Coalitions
Interest groups are organized entities aiming to influence public policy by representing specific interests, often through lobbying and advocacy efforts. Discourse coalitions consist of diverse actors who share common discourses and frame issues in a way that shapes public debate and policymaking. Both play crucial roles in political communication, with interest groups focusing on direct influence and discourse coalitions shaping the narratives within policy discussions.
Defining Interest Groups: Characteristics and Roles
Interest groups are organized entities that seek to influence public policy by representing the interests of specific members or causes, characterized by structured membership, resource mobilization, and targeted lobbying efforts. They play a crucial role in democratic governance by providing expertise, shaping legislation, and amplifying the voices of distinct social, economic, or professional communities. Interest groups differ from discourse coalitions, which are broader, less formal alliances formed around shared narratives rather than defined organizational objectives.
Understanding Discourse Coalitions: Concept and Features
Discourse coalitions are networks of actors linked by shared storylines and narratives that shape public understanding and policy debates, differing from interest groups that primarily pursue specific economic or political goals. These coalitions influence discourse by framing issues, constructing meanings, and mobilizing support through common language and symbols rather than formal organization. Key features include fluid membership, collective identity based on shared discourse, and the capacity to alter policy agendas by shaping societal norms and values.
Historical Development of Both Concepts
Interest groups originated in the early 20th century as organized entities representing specific economic, social, or political interests to influence policy decisions directly. Discourse coalitions emerged later in the 1980s within social constructivist frameworks, emphasizing the role of shared narratives and language in shaping policy debates and knowledge production. The historical development of interest groups focuses on institutional advocacy and lobbying, while discourse coalitions highlight the power of collective meanings and discursive practices in governance.
Objectives and Strategies: A Comparative Analysis
Interest groups pursue specific policy objectives by lobbying, advocacy, and mobilizing members to influence decision-makers directly. Discourse coalitions shape public debate and frame issues through shared narratives, symbols, and language to indirectly impact policy outcomes. While interest groups focus on targeted goals with strategic resources, discourse coalitions rely on constructing dominant meanings to shift societal perspectives and norms.
Membership Structure and Coalitional Dynamics
Interest groups consist of organized members unified by shared goals, often with formal membership and structured leadership, enabling coordinated advocacy efforts. Discourse coalitions feature fluid, informal alliances formed around shared narratives or frames, where participants may come from diverse backgrounds without formal ties. Coalitional dynamics in interest groups emphasize sustained collective action and resource mobilization, while discourse coalitions rely on shifting rhetorical alignments to shape public understanding and influence policy debates.
Influence on Policy-Making Processes
Interest groups exert influence on policy-making processes by directly lobbying legislators, funding campaigns, and providing expert information to shape legislative agendas. Discourse coalitions impact policy by framing issues within public debates, shaping perceptions and norms that indirectly pressure policymakers through media, public opinion, and advocacy networks. The interplay between tangible lobbying efforts of interest groups and the narrative-building role of discourse coalitions creates a multifaceted dynamic influencing policy outcomes.
Examples and Case Studies
Interest groups such as the National Rifle Association (NRA) in the United States lobby directly to influence specific policy outcomes, exemplifying organized advocacy aimed at representing clear, defined member interests. Discourse coalitions, like those studied in climate change debates, consist of diverse actors--including scientists, media, and NGOs--who coalesce around shared narratives and frames to shape public discourse and policy agendas. Case studies in environmental policy reveal how discourse coalitions, such as those formed around the anti-fracking movement, use strategic communication to mobilize support beyond formal interest group boundaries.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Approach
Interest groups wield significant influence through organized lobbying and resource mobilization, enabling targeted policy advocacy but often facing limitations in representing broader public interests. Discourse coalitions excel in shaping public narratives and framing policy debates by uniting diverse actors around shared storylines, yet struggle with measurement challenges and diffuse accountability. Both approaches contribute uniquely to policy processes, with interest groups providing concrete pressure points and discourse coalitions driving ideological resonance.
Conclusion: Implications for Political Advocacy
Interest groups focus on representing specific organizational interests through lobbying and direct policy influence, while discourse coalitions shape broader public narratives by aligning diverse actors around shared ideas and language. Understanding the distinct roles of these entities can enhance political advocacy strategies by integrating targeted lobbying efforts with persuasive communication campaigns to build wider support. Effective advocacy requires blending concrete policy demands of interest groups with the discursive power of coalitions to shift public opinion and political agendas.
Interest group Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com