Social dynamics explores the patterns and changes in interactions within groups, focusing on how relationships, roles, and behaviors influence collective outcomes. Understanding these dynamics enhances your ability to navigate social environments, fostering cooperation and conflict resolution. Dive deeper into this article to uncover key insights and practical strategies for mastering social dynamics.
Table of Comparison
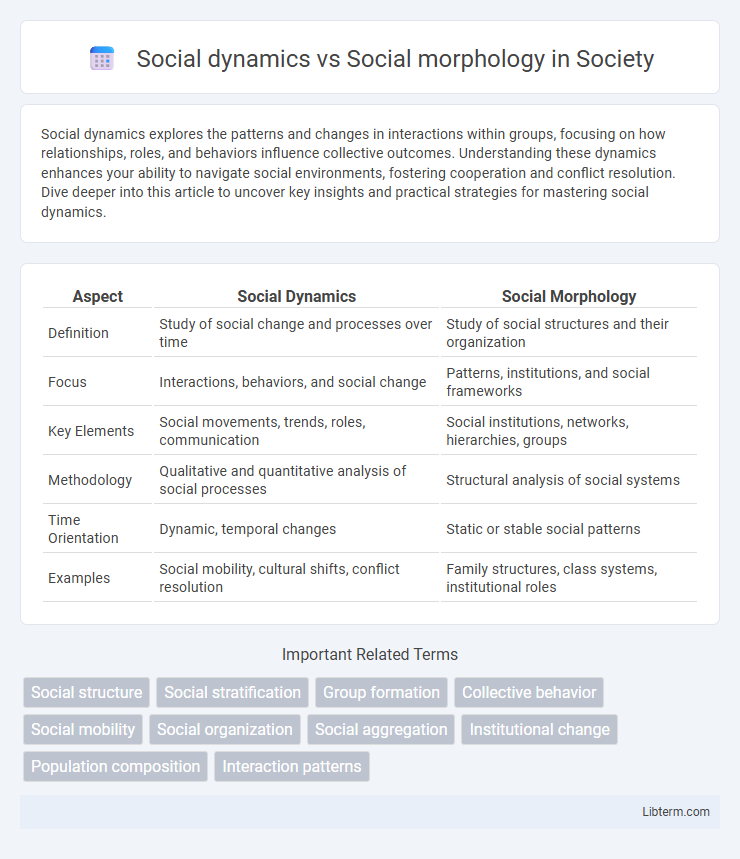
| Aspect | Social Dynamics | Social Morphology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of social change and processes over time | Study of social structures and their organization |
| Focus | Interactions, behaviors, and social change | Patterns, institutions, and social frameworks |
| Key Elements | Social movements, trends, roles, communication | Social institutions, networks, hierarchies, groups |
| Methodology | Qualitative and quantitative analysis of social processes | Structural analysis of social systems |
| Time Orientation | Dynamic, temporal changes | Static or stable social patterns |
| Examples | Social mobility, cultural shifts, conflict resolution | Family structures, class systems, institutional roles |
Introduction to Social Dynamics and Social Morphology
Social dynamics examines the patterns and processes of change within societies, focusing on how social interactions, behaviors, and structures evolve over time. Social morphology, in contrast, analyzes the static aspects of social structures, such as the arrangement and relationships of social groups and institutions at a given point. Understanding both concepts is essential for comprehending the comprehensive nature of societal development, where dynamics emphasize transformation and morphology highlights structural composition.
Defining Social Dynamics
Social dynamics refers to the study of the patterns and processes of change within social systems, emphasizing interactions, behaviors, and relationships over time. It explores how individuals and groups influence social structures, leading to the evolution of norms, roles, and collective actions. This field contrasts with social morphology, which focuses on the static structural features of societies rather than their changing processes.
Understanding Social Morphology
Social morphology examines the structural aspects of society, such as population size, density, and composition, shaping social organization and relationships. It provides essential insights into how physical and demographic patterns influence social behavior and institutional development. Understanding social morphology enables a deeper analysis of how societal changes in form and structure affect social dynamics and collective actions.
Historical Evolution of the Concepts
Social dynamics examines the processes and mechanisms of change within societies over time, focusing on patterns of interaction and collective behavior. Social morphology analyzes the structural organization of societies, including the arrangement of social groups and institutions, emphasizing the static aspects of social structure. Historically, thinkers like Emile Durkheim laid the groundwork for social morphology, while later scholars integrated both perspectives to understand societal evolution comprehensively.
Key Theorists and Their Contributions
Emile Durkheim pioneered social morphology by analyzing social structures and their roles in maintaining societal cohesion, emphasizing institutions and collective norms. Georg Simmel contributed extensively to social dynamics through his exploration of social interactions and the patterns of individual behavior within group contexts. Talcott Parsons developed structural functionalism, integrating social morphology and dynamics by examining how social systems maintain stability and adapt through roles and social processes.
Comparative Analysis: Dynamics vs. Morphology
Social dynamics examines processes of change and interaction patterns within societies, emphasizing behaviors, relationships, and temporal shifts. Social morphology focuses on the structural organization and spatial distribution of social groups, assessing configurations of institutions, roles, and networks at a given time. Comparative analysis reveals that while dynamics capture fluidity and transformation in social life, morphology provides a static framework to understand the underlying social architecture.
Applications in Modern Sociological Research
Social dynamics examines the patterns and processes of change within societies, focusing on interaction, conflict, and transformation over time, which is essential for understanding social movements and network evolution in modern sociological research. Social morphology analyzes the structure and composition of societies, such as population size, distribution, and social institutions, providing critical insights into demographic changes and community organization. Together, these approaches enable sociologists to comprehensively study both the static frameworks and dynamic processes shaping contemporary social phenomena.
Influence on Social Structure and Change
Social dynamics examines the processes and mechanisms driving social change, including conflict, cooperation, and power shifts, directly influencing the evolution of social structures over time. In contrast, social morphology focuses on the static composition and arrangement of social groups, such as class, status, and network patterns, providing a framework to analyze social order and organization. The interplay between social dynamics and morphology shapes how institutions adapt and societies transform, highlighting the continuous interaction between structure and agency in social development.
Case Studies Illustrating Both Concepts
Case studies in urban sociology reveal social dynamics through analyzing patterns of migration, interaction, and cultural exchange within diverse neighborhoods. Social morphology is illustrated by examining the structural composition of communities, such as population density, spatial organization, and institutional frameworks in cities like New York and Tokyo. Comparative studies demonstrate how changes in social morphology influence ongoing social dynamics, shaping residents' behavior and community evolution over time.
Future Directions in Social Analysis
Future directions in social analysis emphasize the integration of social dynamics and social morphology to better understand complex societal changes. Advances in computational modeling and big data analytics enable researchers to capture both the evolving processes (social dynamics) and the structural configurations (social morphology) of social systems. Emphasizing this dual approach promises deeper insights into phenomena such as social networks, cultural shifts, and institutional transformations.
Social dynamics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com