A performance audit evaluates the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of an organization's operations to ensure resources are used optimally. It identifies areas where improvements can enhance your organization's overall productivity and achieve strategic objectives. Explore the rest of this article to understand how a performance audit can drive meaningful change.
Table of Comparison
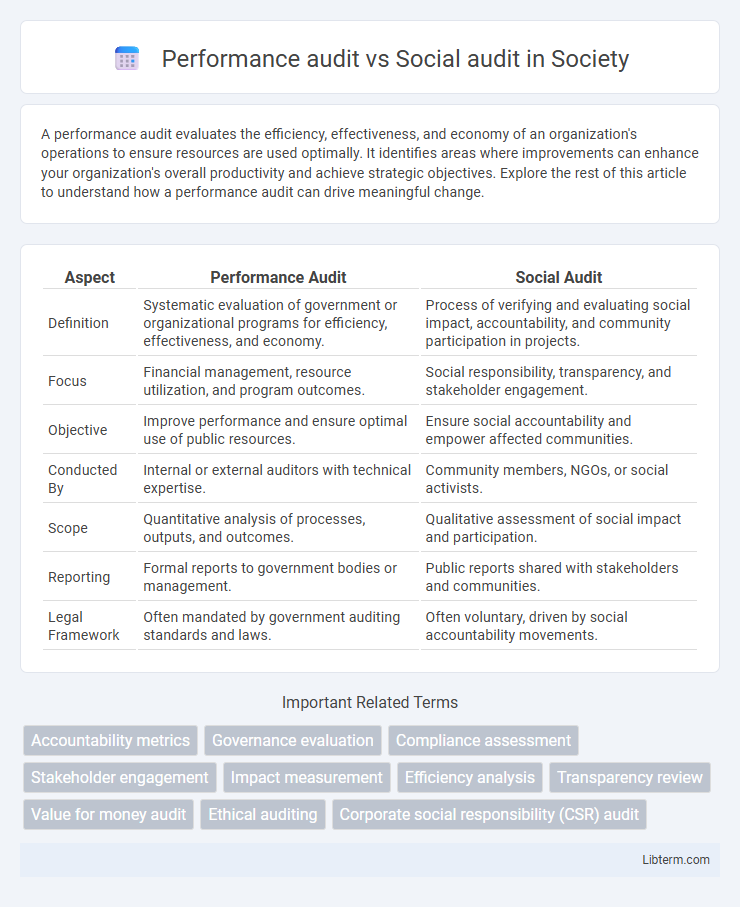
| Aspect | Performance Audit | Social Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic evaluation of government or organizational programs for efficiency, effectiveness, and economy. | Process of verifying and evaluating social impact, accountability, and community participation in projects. |
| Focus | Financial management, resource utilization, and program outcomes. | Social responsibility, transparency, and stakeholder engagement. |
| Objective | Improve performance and ensure optimal use of public resources. | Ensure social accountability and empower affected communities. |
| Conducted By | Internal or external auditors with technical expertise. | Community members, NGOs, or social activists. |
| Scope | Quantitative analysis of processes, outputs, and outcomes. | Qualitative assessment of social impact and participation. |
| Reporting | Formal reports to government bodies or management. | Public reports shared with stakeholders and communities. |
| Legal Framework | Often mandated by government auditing standards and laws. | Often voluntary, driven by social accountability movements. |
Introduction to Performance Audit and Social Audit
Performance audit evaluates the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of government programs by assessing whether resources are being used optimally to achieve intended outcomes. Social audit involves community-led evaluations that verify social welfare projects' transparency and accountability, emphasizing stakeholder participation and societal impact. Both audits enhance public sector governance but differ in scope; performance audit focuses on operational results, while social audit prioritizes social justice and community engagement.
Defining Performance Audit
Performance audit evaluates government programs and operations for efficiency, effectiveness, and economy by examining the use of resources and achievement of objectives. It involves assessing compliance with policies and regulations to ensure accountability and improve management practices. Social audit, in contrast, focuses on evaluating the social impact and community benefits of programs, emphasizing transparency and public participation.
Understanding Social Audit
A social audit evaluates an organization's social impact, community engagement, and adherence to ethical standards by assessing non-financial outcomes and stakeholders' feedback. It prioritizes transparency, accountability, and social responsibility, often involving qualitative data and participatory methods. Unlike performance audits, which focus on efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance of financial and operational activities, social audits emphasize social equity, environmental impact, and the alignment of organizational practices with social goals.
Key Objectives: Performance vs Social Audits
Performance audits primarily focus on evaluating the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of organizational operations, ensuring that resources are being used optimally to achieve intended results. Social audits concentrate on assessing the social impact, accountability, and ethical practices of an organization, emphasizing stakeholder engagement and community welfare. While performance audits aim to improve operational outcomes and compliance, social audits prioritize transparency, social responsibility, and the alignment of activities with societal needs.
Methodologies Used in Performance and Social Audits
Performance audits utilize systematic methodologies such as data analysis, benchmarking, and process evaluations to assess efficiency, effectiveness, and economy in organizations. Social audits employ participatory approaches including community engagement, stakeholder interviews, and qualitative assessments to evaluate social impact and compliance with ethical standards. Both methodologies emphasize evidence-based evaluation but differ in focus, with performance audits centered on operational metrics and social audits prioritizing social accountability and transparency.
Stakeholders Involved in Each Audit Type
Performance audits primarily involve internal stakeholders such as management, auditors, and regulatory bodies focused on efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance of organizational operations. Social audits engage a broader range of stakeholders including community members, beneficiaries, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and sometimes corporate social responsibility (CSR) teams to assess social impact and ethical practices. Both audits rely on stakeholder participation to ensure accountability but differ in scope and emphasis on financial versus social outcomes.
Areas of Application: Where Each Audit is Used
Performance audits are primarily applied in government agencies and public sector organizations to evaluate the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of programs and operations. Social audits are most commonly used in community development projects, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives to assess social impact, transparency, and ethical compliance. Both audits serve distinct purposes, with performance audits focusing on operational outcomes and social audits emphasizing stakeholder engagement and social accountability.
Benefits of Performance and Social Audits
Performance audits provide comprehensive evaluations of an organization's efficiency, effectiveness, and economy in resource utilization, enabling improved decision-making and accountability. Social audits focus on assessing the impact of projects or policies on communities, promoting transparency, community participation, and social responsibility. Both audits enhance organizational performance by identifying areas for improvement and ensuring alignment with social and operational goals.
Differences Between Performance Audit and Social Audit
Performance audit evaluates the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of government programs or organizational operations using financial and operational data. Social audit, on the other hand, focuses on assessing the impact of policies or projects on social outcomes, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and citizen participation. While performance audit is data-driven and quantifiable, social audit relies heavily on community feedback and qualitative social indicators.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Audit for Your Organization
Performance audits evaluate efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of organizational processes to improve operational outcomes, while social audits assess the impact on community welfare and ethical practices. Selecting the appropriate audit depends on organizational goals, with performance audits suited for internal improvements and social audits ideal for stakeholder transparency and corporate social responsibility. Organizations prioritizing accountability and sustainable development often integrate both audits to achieve comprehensive insights and balanced growth.
Performance audit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com