Implicit structure shapes the way information is organized and understood beneath the surface, influencing perception without explicit cues. Mastering this concept enhances your ability to interpret complex texts and communicate ideas more effectively. Explore the rest of this article to discover how implicit structures impact language and cognition.
Table of Comparison
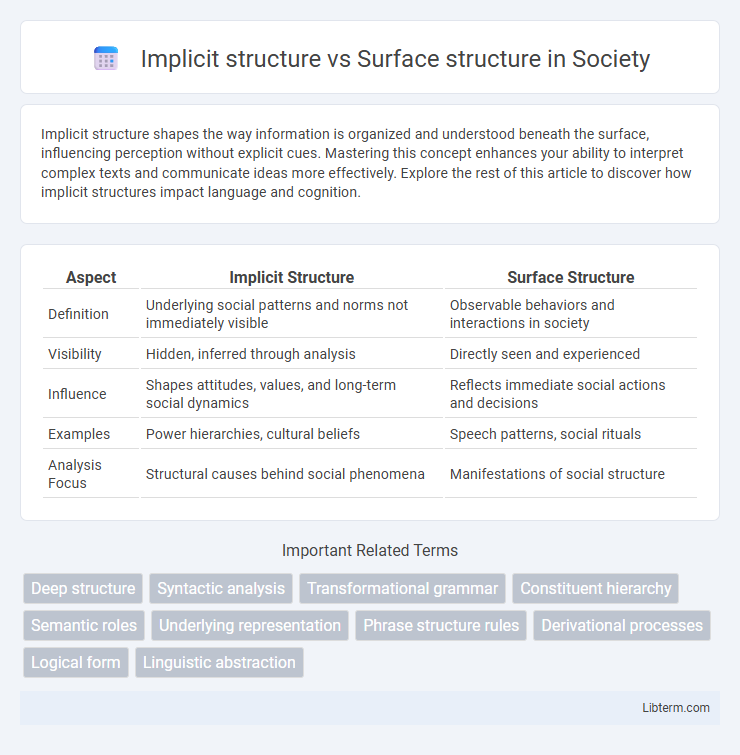
| Aspect | Implicit Structure | Surface Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Underlying social patterns and norms not immediately visible | Observable behaviors and interactions in society |
| Visibility | Hidden, inferred through analysis | Directly seen and experienced |
| Influence | Shapes attitudes, values, and long-term social dynamics | Reflects immediate social actions and decisions |
| Examples | Power hierarchies, cultural beliefs | Speech patterns, social rituals |
| Analysis Focus | Structural causes behind social phenomena | Manifestations of social structure |
Understanding Implicit Structure: A Conceptual Overview
Implicit structure refers to the underlying, often unspoken, organizational framework that shapes meaning in language, whereas surface structure represents the explicit arrangement of words and phrases. Understanding implicit structure requires analyzing semantic roles, thematic relations, and contextual cues that reveal how ideas are interconnected beyond their syntactic presentation. Psycholinguistic studies highlight implicit structure as crucial for interpreting ambiguous sentences and grasping deeper levels of meaning in discourse.
Defining Surface Structure in Language and Communication
Surface structure in language and communication refers to the literal arrangement of words and phrases in a sentence as it appears or is spoken, representing the explicit syntax that conveys immediate meaning. It differs from implicit structure, which involves the underlying, abstract grammatical relationships and deeper meanings not immediately visible in the sentence's form. Understanding surface structure is crucial for parsing sentence construction, enabling initial comprehension before interpreting the implicit nuances embedded within communication.
Key Differences Between Implicit and Surface Structures
Implicit structure refers to the underlying, often hidden, organizational patterns that govern meaning and relationships within a system, whereas surface structure is the explicit, observable arrangement of elements as they appear. Key differences include that implicit structures operate beneath the visible layer influencing interpretation and coherence, while surface structures are the literal form such as syntax in language or layout in design. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in fields like linguistics and data analysis, where meaning derives from both the overt presentation and the covert framework.
The Role of Implicit Structure in Meaning Construction
Implicit structure plays a crucial role in meaning construction by organizing underlying relationships between linguistic elements beyond their explicit, surface-level arrangement. This deeper syntactic and semantic framework enables speakers to infer intended meanings, resolve ambiguities, and understand context-dependent nuances. By encoding information that is not overtly stated, implicit structure supports efficient communication and enriches interpretative processes in language comprehension.
How Surface Structure Shapes Interpretation
Surface structure determines the literal arrangement of words and phrases in a sentence, directly influencing how meaning is initially perceived. Variations in surface structure can lead to different interpretations by altering emphasis, focus, or the relationships between sentence elements. Understanding surface structure is essential for analyzing how syntactic choices affect semantic clarity and ambiguity.
Cognitive Processes Involved in Implicit and Surface Structures
Implicit structure engages deep cognitive processes such as inferencing, schema activation, and implicit memory, allowing individuals to extract meaning beyond explicit language cues. Surface structure processing relies on syntactic parsing and phonological decoding to understand the literal arrangement of words and grammatical forms. These distinct cognitive mechanisms highlight how implicit comprehension integrates contextual knowledge, while surface structure focuses on linguistic form and immediate linguistic input.
Implications for Linguistics and Language Learning
Implicit structure refers to the underlying, abstract grammatical relationships within a sentence, while surface structure denotes the actual spoken or written form. Understanding the distinction is crucial in linguistics for parsing meaning beyond literal word order, affecting syntax analysis and semantic interpretation. In language learning, grasping implicit structures enhances comprehension and production of complex sentences, facilitating deeper proficiency beyond memorization of surface patterns.
Applications in Artificial Intelligence and Natural Language Processing
Implicit structure captures underlying relationships and meanings within data, enabling AI systems to understand context beyond explicit word arrangements. Surface structure represents the literal syntactic form, which NLP models often parse for initial language processing tasks. Leveraging implicit structure enhances applications like semantic analysis, machine translation, and sentiment detection by improving AI's grasp of nuanced human language.
Common Misconceptions about Structural Levels
Common misconceptions about implicit structure and surface structure often confuse their roles in sentence interpretation; surface structure represents the literal arrangement of words, while implicit structure captures the underlying meaning or deep syntax. Many mistakenly assume that changes in surface structure always alter meaning, ignoring that different surface forms can share the same implicit structure. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate linguistic analysis, as implicit structures reveal semantic relationships obscured by variable surface expressions.
Future Directions in Research on Language Structures
Future research on language structures should delve deeper into the interplay between implicit structure, representing underlying grammatical relationships, and surface structure, capturing the observable syntactic form. Advances in computational linguistics and neural network models offer promising tools for uncovering latent hierarchical patterns that govern language processing and acquisition. Emphasizing cross-linguistic analyses and integrating cognitive neuroscience insights will enhance understanding of how implicit and surface structures interact within the human brain during real-time language comprehension.
Implicit structure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com