Effective stakeholder engagement ensures your project aligns with the needs and expectations of all parties involved, fostering collaboration and trust. Identifying key stakeholders early and maintaining transparent communication channels helps mitigate risks and enhances decision-making processes. Continue reading to discover practical strategies for optimizing stakeholder engagement in your projects.
Table of Comparison
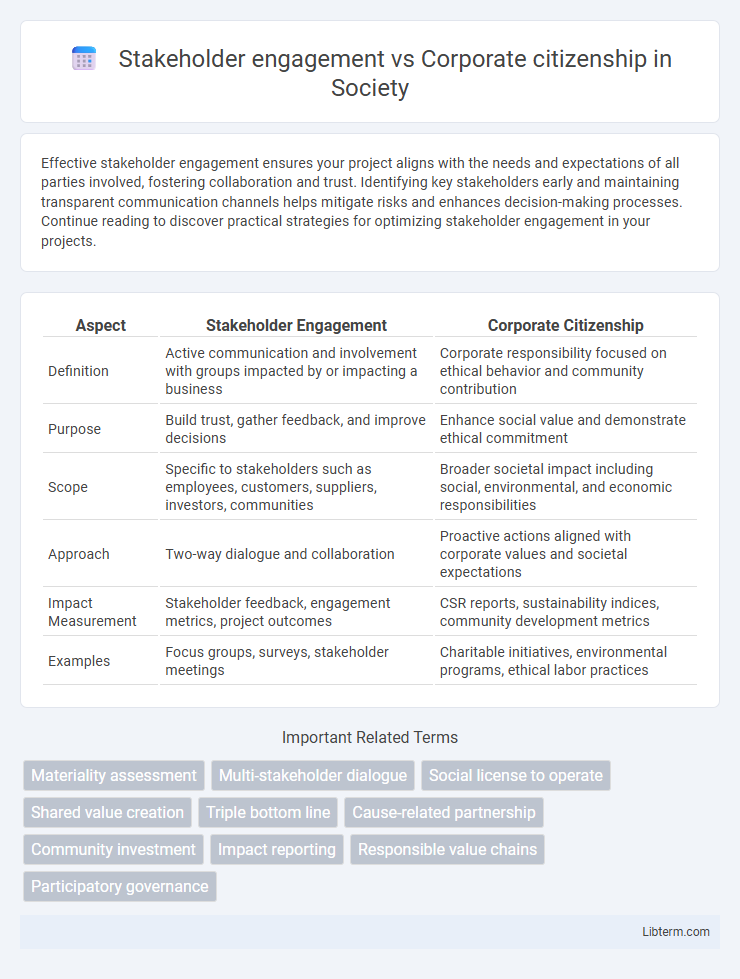
| Aspect | Stakeholder Engagement | Corporate Citizenship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active communication and involvement with groups impacted by or impacting a business | Corporate responsibility focused on ethical behavior and community contribution |
| Purpose | Build trust, gather feedback, and improve decisions | Enhance social value and demonstrate ethical commitment |
| Scope | Specific to stakeholders such as employees, customers, suppliers, investors, communities | Broader societal impact including social, environmental, and economic responsibilities |
| Approach | Two-way dialogue and collaboration | Proactive actions aligned with corporate values and societal expectations |
| Impact Measurement | Stakeholder feedback, engagement metrics, project outcomes | CSR reports, sustainability indices, community development metrics |
| Examples | Focus groups, surveys, stakeholder meetings | Charitable initiatives, environmental programs, ethical labor practices |
Understanding Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement involves actively communicating and collaborating with individuals or groups affected by a company's operations to address their concerns and expectations. This process enhances transparency, builds trust, and aligns business strategies with stakeholder interests. Corporate citizenship, by contrast, encompasses broader responsibilities including ethical behavior, community involvement, and sustainable practices beyond stakeholder dialogue.
Defining Corporate Citizenship
Corporate citizenship refers to a company's responsibility to operate ethically, contribute to economic development, and improve the quality of life for employees, the local community, and society at large. Unlike stakeholder engagement, which centers on actively involving groups such as customers, suppliers, and investors in decision-making processes, corporate citizenship encompasses broader commitments to social, environmental, and economic sustainability. Defining corporate citizenship highlights a corporation's role as an accountable member of society, integrating corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and sustainable business practices into its core operations.
Key Differences Between Stakeholder Engagement and Corporate Citizenship
Stakeholder engagement focuses on actively involving individuals or groups affected by a company's operations to influence decision-making and improve outcomes, while corporate citizenship emphasizes a company's broader commitment to ethical behavior, social responsibility, and sustainable development. Stakeholder engagement is a strategic process targeting specific stakeholder interests and feedback, whereas corporate citizenship reflects an overarching philosophy guiding a company's impact on society and the environment. The key difference lies in stakeholder engagement's interactive dialogue versus corporate citizenship's holistic responsibility and values-driven approach.
The Role of Stakeholder Engagement in Modern Business
Stakeholder engagement plays a critical role in modern business by fostering transparent communication and collaboration between companies and their diverse stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, suppliers, and communities. This process enhances corporate decision-making, drives sustainable business practices, and builds long-term trust, distinguishing it from broader corporate citizenship efforts that encompass overall social responsibility initiatives. Effective stakeholder engagement results in improved risk management, innovation, and alignment of business goals with societal expectations, making it a strategic imperative in today's competitive market.
Corporate Citizenship: Principles and Practices
Corporate citizenship refers to a company's responsibility to contribute positively to society through ethical practices, environmental sustainability, and community involvement, reflecting principles like accountability, transparency, and social equity. Effective corporate citizenship requires integrating these principles into business strategies and operations, ensuring long-term value creation for both stakeholders and society. Organizations practicing strong corporate citizenship often implement community development programs, sustainable resource management, and stakeholder-inclusive governance to demonstrate commitment beyond profit maximization.
Benefits of Effective Stakeholder Engagement
Effective stakeholder engagement enhances corporate transparency, fosters trust, and aligns business strategies with community needs, promoting long-term sustainability. Companies that actively involve stakeholders experience improved risk management, increased innovation, and stronger brand reputation. This engagement drives higher employee morale and customer loyalty, ultimately boosting financial performance and corporate citizenship impact.
Measuring Corporate Citizenship Impact
Measuring corporate citizenship impact involves assessing how a company's social, environmental, and economic initiatives create value for communities and stakeholders. Stakeholder engagement provides critical qualitative and quantitative data by involving employees, customers, investors, and local communities in feedback and performance evaluation processes. Effective measurement combines stakeholder insights with key performance indicators such as sustainability metrics, social return on investment (SROI), and environmental impact assessments to gauge true corporate citizenship effectiveness.
Integrating Stakeholder Engagement with Corporate Citizenship Strategies
Integrating stakeholder engagement with corporate citizenship strategies enhances organizational accountability and drives sustainable business practices by aligning stakeholder interests with social and environmental goals. Effective collaboration with stakeholders, including employees, communities, and investors, fosters transparency and builds trust, which strengthens corporate reputation and long-term value creation. Embedding stakeholder perspectives into corporate citizenship initiatives ensures responsive and inclusive strategies that address societal challenges and promote shared value.
Challenges in Balancing Stakeholder Expectations and Corporate Responsibilities
Balancing stakeholder engagement and corporate citizenship presents challenges such as conflicting expectations between profit-driven investors and socially-conscious communities demanding sustainable practices. Companies often struggle to align short-term financial goals with long-term corporate social responsibility commitments, leading to potential reputational risks and decreased stakeholder trust. Effective communication strategies and transparent governance are essential to harmonize diverse stakeholder interests while fulfilling corporate ethical obligations.
Future Trends: Evolving Stakeholder Engagement and Corporate Citizenship
Future trends in stakeholder engagement emphasize digital platforms enabling real-time dialogue and personalized communication, enhancing transparency and trust. Corporate citizenship is shifting toward integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into core business strategies, reflecting stakeholder demands for sustainable and ethical practices. Emerging technologies like AI and blockchain further facilitate accountability and stakeholder participation in corporate decision-making processes.
Stakeholder engagement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com