Assimilation is a crucial cognitive process in which new information is integrated into existing mental frameworks, enabling individuals to understand and adapt to their environment efficiently. This mechanism plays a significant role in learning, memory retention, and cultural adaptation by allowing your brain to organize and make sense of unfamiliar experiences. Explore the rest of the article to discover how assimilation impacts your daily life and personal growth.
Table of Comparison
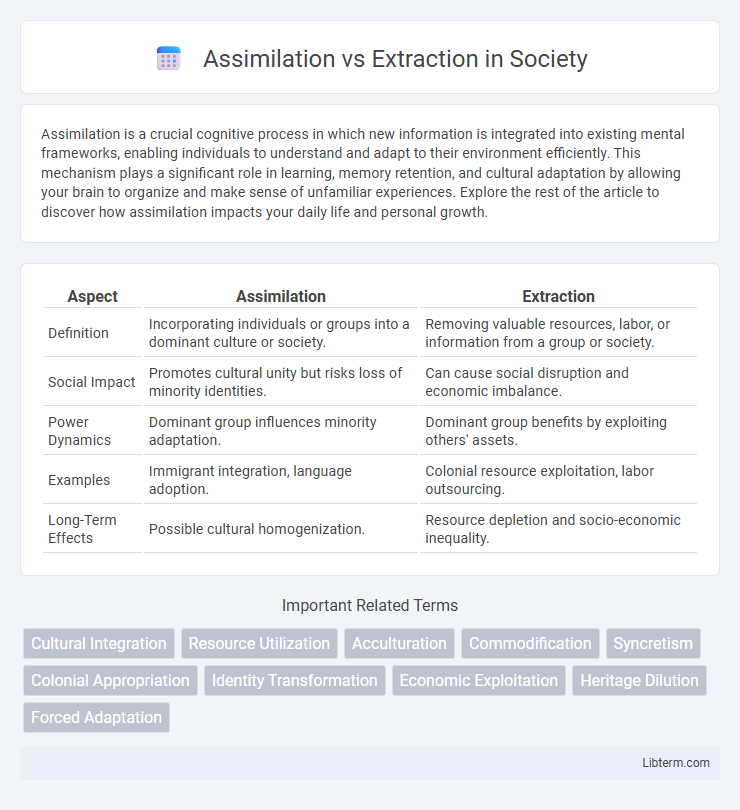
| Aspect | Assimilation | Extraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporating individuals or groups into a dominant culture or society. | Removing valuable resources, labor, or information from a group or society. |
| Social Impact | Promotes cultural unity but risks loss of minority identities. | Can cause social disruption and economic imbalance. |
| Power Dynamics | Dominant group influences minority adaptation. | Dominant group benefits by exploiting others' assets. |
| Examples | Immigrant integration, language adoption. | Colonial resource exploitation, labor outsourcing. |
| Long-Term Effects | Possible cultural homogenization. | Resource depletion and socio-economic inequality. |
Introduction to Assimilation and Extraction
Assimilation refers to the process of integrating new information into existing cognitive frameworks, allowing individuals to interpret experiences based on prior knowledge. Extraction involves selectively identifying and isolating key data points from complex information to facilitate understanding and application. Both processes play crucial roles in knowledge acquisition, with assimilation focusing on adaptation and extraction emphasizing targeted information retrieval.
Defining Assimilation: Meaning and Contexts
Assimilation refers to the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits, behaviors, or social norms of another group, often leading to a blending or integration of identities. In linguistic contexts, assimilation involves the modification of sounds in speech to become more similar to neighboring sounds, enhancing fluency and coherence. This concept is widely applied in sociology, anthropology, and language studies to describe how integration and adaptation occur within social or communicative environments.
Understanding Extraction: Core Concepts
Extraction involves isolating valuable compounds from raw materials using solvents, filtration, or distillation, emphasizing purity and yield optimization. Core concepts include solubility, selectivity, and phase separation, which govern efficient recovery of target substances. Mastery of extraction techniques enables enhanced product quality across pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing industries.
Historical Perspectives on Assimilation and Extraction
Historical perspectives on assimilation and extraction reveal distinct approaches in colonial and economic contexts, where assimilation aimed to integrate indigenous populations into dominant cultures, whereas extraction prioritized the removal of natural resources for metropolitan benefit. Assimilation policies often involved cultural suppression and educational reforms to enforce conformity, while extraction focused on exploiting minerals, agricultural products, and labor, frequently leading to environmental degradation and economic dependency. Key examples include French colonial assimilation practices in Africa and British colonial extraction strategies in India, illustrating contrasting priorities that shaped post-colonial development trajectories.
Key Differences Between Assimilation and Extraction
Assimilation involves the process by which new information is integrated into existing cognitive schemas, enhancing understanding and retention, while extraction refers to identifying and isolating specific data or features from a larger dataset for analysis or decision-making. Assimilation emphasizes cognitive adaptation and learning, whereas extraction prioritizes data retrieval and simplification from complex inputs. Key differences include the focus on internal knowledge restructuring in assimilation versus external information separation in extraction, as well as their applications in psychology and data science respectively.
Advantages of Assimilation Approaches
Assimilation approaches leverage existing knowledge bases to integrate new information seamlessly, enhancing accuracy and consistency in data interpretation. These methods improve adaptability in dynamic environments by updating internal models without discarding prior understanding. This continuous refinement supports more robust decision-making and reduces the risk of information loss compared to extraction techniques.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Extraction Methods
Extraction methods offer precise isolation of specific bioactive compounds from natural sources, enhancing purity and potency for pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic applications. However, these methods can be costly and energy-intensive, sometimes requiring toxic solvents that pose environmental and health risks. Despite these drawbacks, advancements in green extraction technologies like supercritical fluid extraction and ultrasound-assisted extraction are improving efficiency and sustainability.
Real-World Applications: Assimilation vs Extraction
Assimilation in real-world applications involves integrating new information into existing frameworks, enhancing decision-making processes in areas like artificial intelligence and data analytics. Extraction focuses on retrieving specific data from unstructured sources, critical for tasks such as natural language processing and knowledge management. Understanding the distinction between assimilation and extraction improves efficiency in systems ranging from machine learning to business intelligence.
Assimilation and Extraction in Cultural Contexts
Assimilation in cultural contexts involves individuals or groups adopting the customs, values, and norms of a dominant culture, often leading to a loss of original cultural identity. Extraction, by contrast, refers to the selective borrowing or incorporation of specific cultural elements without fully integrating into the dominant culture, preserving distinct cultural traits. Understanding these processes highlights the dynamic interaction between cultural preservation and adaptation within multicultural societies.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Assimilation and Extraction
Choosing between assimilation and extraction hinges on the specific goals of data integration and utilization; assimilation integrates data seamlessly into existing systems for unified analysis, while extraction focuses on isolating relevant information for targeted applications. Organizations prioritizing comprehensive data consistency and real-time synchronization benefit more from assimilation, whereas those requiring flexibility in handling diverse data sources prefer extraction. Evaluating factors like data volume, transformation needs, and system architecture is critical to optimizing the balance between these approaches for effective data management.
Assimilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com