Social integration fosters a sense of belonging and connection within communities, enhancing overall well-being and reducing social isolation. It promotes understanding and cooperation among diverse groups, leading to more cohesive and resilient societies. Explore this article to discover how social integration can impact your life and the community around you.
Table of Comparison
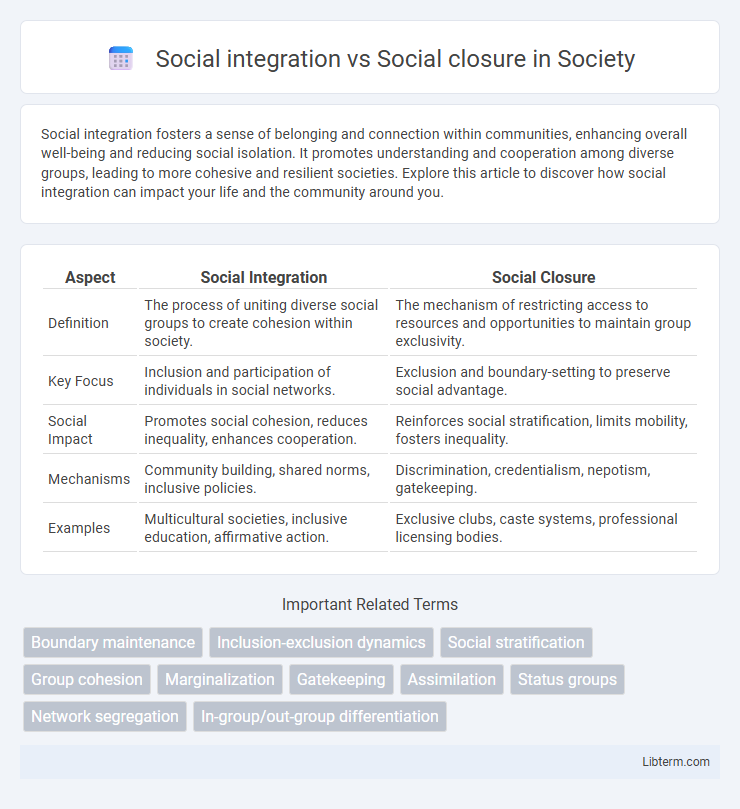
| Aspect | Social Integration | Social Closure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of uniting diverse social groups to create cohesion within society. | The mechanism of restricting access to resources and opportunities to maintain group exclusivity. |
| Key Focus | Inclusion and participation of individuals in social networks. | Exclusion and boundary-setting to preserve social advantage. |
| Social Impact | Promotes social cohesion, reduces inequality, enhances cooperation. | Reinforces social stratification, limits mobility, fosters inequality. |
| Mechanisms | Community building, shared norms, inclusive policies. | Discrimination, credentialism, nepotism, gatekeeping. |
| Examples | Multicultural societies, inclusive education, affirmative action. | Exclusive clubs, caste systems, professional licensing bodies. |
Understanding Social Integration
Social integration refers to the process through which individuals and groups are incorporated into the social structure, fostering cohesion and mutual participation by emphasizing shared norms, values, and social networks. It promotes equal access to social resources and opportunities, enabling diverse groups to function harmoniously within a society. Understanding social integration highlights its role in reducing social exclusion and fostering collective well-being through inclusive interaction.
Defining Social Closure
Social closure refers to the process by which groups maintain exclusive control over resources, opportunities, or privileges by restricting access to outsiders through mechanisms such as education, credentialing, or social networks. This concept emphasizes boundaries and exclusion, ensuring that members of a group preserve their social advantages and limit competition. In contrast to social integration, which promotes inclusion and cohesion, social closure highlights the strategies used to enforce social inequality and sustain hierarchical power structures.
Historical Contexts of Social Integration
Historical contexts of social integration reveal the process by which diverse groups have merged into cohesive societies through shared norms, values, and institutions. Examples include the post-World War II era when social integration was essential for rebuilding and fostering national unity in Europe and the United States. This contrasts with social closure, which historically functioned to maintain privilege by restricting access to resources and social mobility based on race, class, or ethnicity.
Mechanisms of Social Closure
Mechanisms of social closure operate by restricting access to resources, opportunities, and social positions through exclusionary practices such as credentialism, monopolization, and social networks, which enforce group boundaries and maintain privileges. These mechanisms contrast with social integration, which emphasizes inclusivity and the blending of diverse groups within society. By controlling membership and access, social closure effectively preserves power and inequality, reinforcing existing hierarchies.
Key Differences Between Social Integration and Closure
Social integration promotes inclusion by fostering open networks and cooperation across diverse social groups, enhancing social cohesion and collective identity. Social closure involves restricting access to resources or opportunities through exclusionary practices, maintaining power and privileges within selected groups. The key difference lies in integration's emphasis on bridging social divides versus closure's focus on creating social boundaries and limiting interaction.
Benefits of Social Integration in Society
Social integration fosters cohesion by promoting inclusion, trust, and cooperation among diverse groups, which enhances social stability and collective well-being. It enables equitable access to resources, opportunities, and social networks, facilitating economic growth and reducing inequalities. This inclusive environment supports mental health and civic engagement, strengthening societal resilience and harmony.
Social Closure and Its Impact on Inequality
Social closure refers to the process by which groups maintain exclusivity by restricting access to resources, opportunities, and privileges, thereby consolidating power within a select circle. This mechanism significantly contributes to social inequality by limiting upward mobility for marginalized groups and perpetuating disparities in wealth, education, and employment. Discriminatory practices, legal barriers, and social networks often reinforce social closure, intensifying structural inequality across societies.
Factors Influencing Social Integration
Factors influencing social integration include shared cultural values, communication networks, and social institutions that promote inclusion and participation within a community. Access to education, economic opportunities, and equitable policies significantly enhance individuals' ability to connect and collaborate across social boundaries. Conversely, social closure arises when exclusive groups restrict membership and resources, limiting social mobility and integration through mechanisms like discrimination or nepotism.
Case Studies: Integration vs Closure in Practice
Case studies examining social integration and social closure reveal contrasting mechanisms shaping group dynamics and resource access. In urban neighborhoods, integration fosters diverse interactions and reduces socioeconomic disparities, exemplified by mixed-income housing projects increasing social mobility. Conversely, social closure practices in elite educational institutions reinforce exclusivity through legacy admissions and networking, preserving privilege and limiting broader social participation.
Strategies to Promote Social Integration and Reduce Closure
Promoting social integration involves implementing inclusive policies such as equitable access to education, community engagement programs, and fostering cross-cultural dialogue to build trust and shared values among diverse groups. Reducing social closure requires dismantling systemic barriers like discriminatory hiring practices and social networks that exclude outsiders, enabling equal opportunities in employment, housing, and social resources. Strategies such as affirmative action, anti-segregation laws, and diversity training contribute to creating an open social environment that counteracts exclusionary mechanisms and enhances social cohesion.
Social integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com