Demystification involves breaking down complex concepts to make them more understandable and accessible. By clarifying confusing ideas, it empowers you to grasp essential knowledge with confidence and ease. Explore this article to uncover how demystification can simplify your learning process.
Table of Comparison
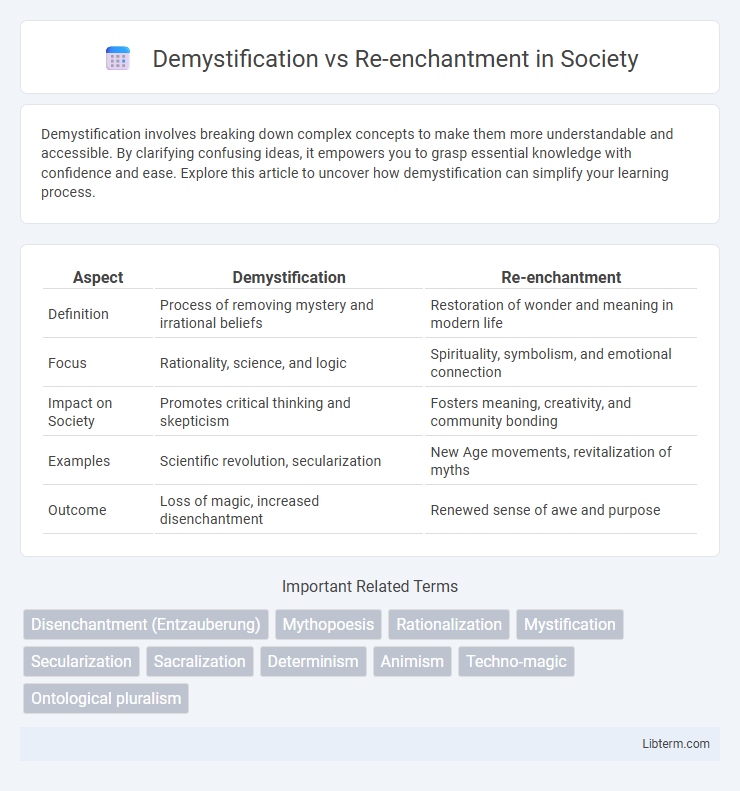
| Aspect | Demystification | Re-enchantment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of removing mystery and irrational beliefs | Restoration of wonder and meaning in modern life |
| Focus | Rationality, science, and logic | Spirituality, symbolism, and emotional connection |
| Impact on Society | Promotes critical thinking and skepticism | Fosters meaning, creativity, and community bonding |
| Examples | Scientific revolution, secularization | New Age movements, revitalization of myths |
| Outcome | Loss of magic, increased disenchantment | Renewed sense of awe and purpose |
Understanding Demystification: Origins and Concepts
Demystification traces its origins to the Enlightenment era, emphasizing reason, scientific inquiry, and the removal of supernatural explanations to reveal the natural laws governing phenomena. This concept underpins modern rationalism, aiming to clarify and simplify complex ideas by stripping away myths and irrational beliefs. Understanding demystification involves recognizing its role in advancing critical thinking and empirical knowledge while challenging traditional, mystical worldviews.
The Rise of Re-enchantment in Modern Discourse
The rise of re-enchantment in modern discourse challenges the secular narrative of demystification by reintroducing wonder, mystery, and spiritual meaning into contemporary cultural and intellectual life. This shift reflects a growing dissatisfaction with purely rational or scientific explanations, fostering renewed interest in symbolism, mythology, and alternative spiritualities. Scholars highlight this trend as a response to globalization and technological advancements that paradoxically create a yearning for deeper connection and transcendence.
Historical Context: From Rationalism to Romanticism
The transition from Rationalism to Romanticism marked a shift in the historical context of demystification versus re-enchantment, as Enlightenment thinkers emphasized reason, scientific inquiry, and skepticism toward traditional myths and religious beliefs, promoting a demystified worldview. Romanticism emerged as a counter-movement, re-enchanting the world by valuing emotion, nature, imagination, and spirituality, challenging the purely rational perspective of the preceding era. This philosophical evolution highlights the tension between a mechanistic universe understood through empirical knowledge and a renewed appreciation for mystery and transcendence in human experience.
Science, Secularism, and the Loss of Mystery
Science and secularism have driven the demystification of the world by explaining phenomena once attributed to supernatural forces, thereby reducing reliance on religious or mystical interpretations. This rational approach fosters technological progress and empirical understanding but often diminishes the sense of wonder and mystery historically associated with human existence. Re-enchantment seeks to restore a sense of awe and spiritual depth by embracing subjective experience and meaning beyond scientific explanations, addressing the existential void created by secular rationalism.
The Cultural Appeal of Re-enchantment
Re-enchantment captivates contemporary culture by revitalizing a sense of wonder and meaning often lost in secular, rational worldviews dominated by demystification. This shift reflects a growing desire to reconnect with spirituality, mysticism, and narrative depth in art, literature, and daily life, which satisfies emotional and psychological needs beyond empirical reality. The cultural appeal of re-enchantment lies in its power to restore mystery and sacredness, offering people a richer, more immersive experience of existence.
Demystification in Philosophy and Sociology
Demystification in philosophy and sociology refers to the process of critically analyzing and breaking down complex social phenomena to reveal underlying structures and power dynamics, often associated with rationalization and secularization theories introduced by Max Weber. This approach emphasizes the removal of myths, superstitions, and illusions to understand social realities through empirical evidence and logical reasoning. By exposing how cultural symbols and social practices are constructed, demystification challenges traditional beliefs and promotes a more scientific perspective on society.
Technology’s Role: Demystification or New Magic?
Technology acts as both a tool of demystification and a source of new enchantment, revealing complex processes through scientific explanations while simultaneously creating experiences that evoke wonder and awe. Innovations like virtual reality and artificial intelligence transform everyday interactions into seemingly magical encounters, reshaping how society perceives reality. This dual role highlights technology's power to dissolve old myths while inspiring new forms of fascination and cultural narratives.
Art, Literature, and the Search for Wonder
Demystification in art and literature seeks to unveil rational explanations behind mysteries, stripping away enchantment to foster critical understanding. Re-enchantment counters this by restoring a sense of wonder and magic, emphasizing symbolic meaning, myth, and emotional resonance to reinvigorate human experience. The ongoing tension between these approaches shapes creative expression, influencing how audiences engage with narratives and perceive the extraordinary in everyday life.
Psychological Impacts of Demystification vs Re-enchantment
Demystification often leads to a perceived loss of wonder and can contribute to feelings of disenchantment or existential emptiness, impacting mental well-being by reducing a sense of meaning and connection. In contrast, re-enchantment fosters psychological resilience and emotional fulfillment by reigniting a sense of awe, purpose, and deep engagement with life's mysteries. This psychological shift influences motivation, stress levels, and overall mental health, highlighting the importance of balancing rational understanding with experiential richness.
Reconciling Rationality and Wonder in Society
Reconciling rationality and wonder in society requires balancing demystification's emphasis on scientific understanding with re-enchantment's celebration of awe and mystery. Demystification promotes clarity and empirical knowledge, fostering progress and innovation, while re-enchantment cultivates creativity, meaning, and emotional depth in human experiences. Integrating these approaches enriches cultural narratives, enabling a society that values both critical thinking and the profound sense of wonder essential to human flourishing.
Demystification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com