Social openness fosters diverse interactions and encourages the exchange of ideas, which enhances creativity and understanding across communities. Embracing social openness can break down barriers and create more inclusive environments where everyone feels valued. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical ways to cultivate social openness in your daily life.
Table of Comparison
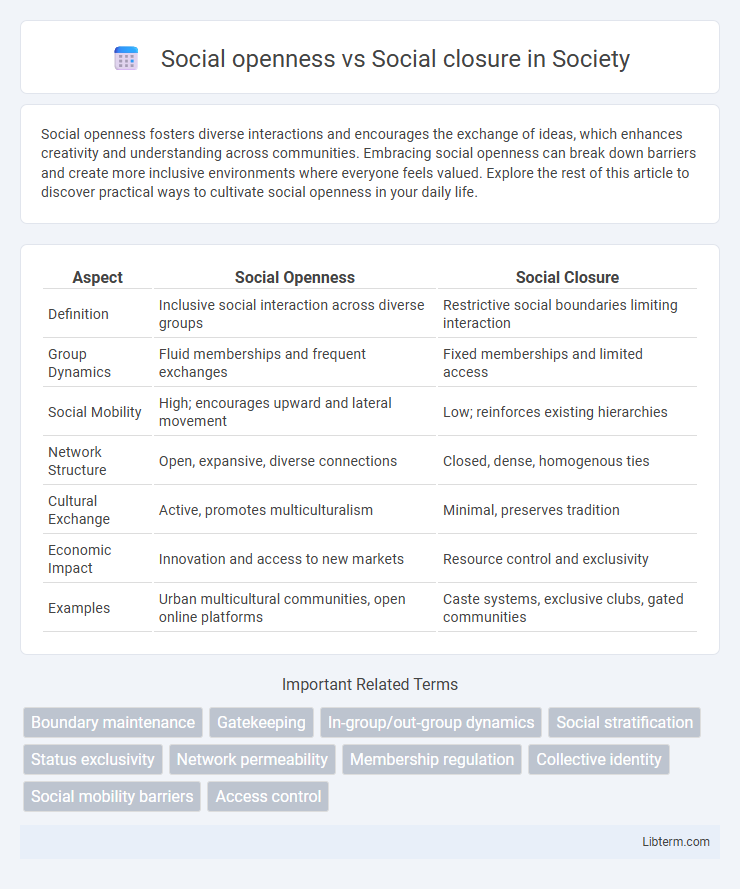
| Aspect | Social Openness | Social Closure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inclusive social interaction across diverse groups | Restrictive social boundaries limiting interaction |
| Group Dynamics | Fluid memberships and frequent exchanges | Fixed memberships and limited access |
| Social Mobility | High; encourages upward and lateral movement | Low; reinforces existing hierarchies |
| Network Structure | Open, expansive, diverse connections | Closed, dense, homogenous ties |
| Cultural Exchange | Active, promotes multiculturalism | Minimal, preserves tradition |
| Economic Impact | Innovation and access to new markets | Resource control and exclusivity |
| Examples | Urban multicultural communities, open online platforms | Caste systems, exclusive clubs, gated communities |
Understanding Social Openness and Social Closure
Social openness refers to a society's willingness to embrace diversity, facilitate social mobility, and promote inclusive interactions across different groups, enhancing cooperation and innovation. Social closure, in contrast, involves mechanisms by which groups maintain exclusive access to resources and opportunities, enforcing boundaries that limit outsider participation and preserve group privileges. Understanding these concepts helps analyze how social structures impact equality, integration, and the distribution of power within communities.
Historical Perspectives on Social Inclusion and Exclusion
Historical perspectives on social inclusion and exclusion reveal how social openness facilitates cultural exchange, economic growth, and political innovation by allowing diverse groups to interact and integrate within societies. Social closure, conversely, enforces boundaries through rigid class structures, discriminatory laws, and exclusionary practices that maintain power within dominant groups and limit access to resources for marginalized communities. Key examples include caste systems, apartheid, and immigration restrictions, which have historically institutionalized social exclusion and shaped societal hierarchies.
Key Theories Explaining Social Openness and Closure
Key theories explaining social openness and closure include Georg Simmel's concept of the "stranger," highlighting how social groups balance inclusion and exclusion dynamics. Pierre Bourdieu's theory of social capital emphasizes how social closure protects group resources and privileges through mechanisms like exclusion and boundary maintenance. Mark Granovetter's strength of weak ties theory illustrates that social openness facilitates access to diverse information and opportunities by bridging structural holes in social networks.
Social Openness: Drivers and Benefits
Social openness, driven by cultural diversity, technological advancements, and globalization, fosters inclusive societies where information exchange and innovation thrive. This approach enhances social capital, promotes economic growth, and supports democratic values through increased participation and transparency. Embracing social openness reduces discrimination, strengthens community resilience, and facilitates adaptive responses to social changes and challenges.
Mechanisms of Social Closure in Modern Societies
Mechanisms of social closure in modern societies include credentialism, exclusionary networks, and regulatory policies that limit access to resources and opportunities for certain groups. Educational requirements and professional certifications serve as tools to maintain social stratification by controlling entry into elite occupations. Legal and institutional barriers reinforce these closures, perpetuating inequality and restricting social mobility.
Impacts of Social Openness on Diversity and Innovation
Social openness fosters diversity by encouraging the inclusion of varied cultural, ethnic, and intellectual backgrounds, which broadens perspectives and drives creative problem-solving. Increased social openness creates environments where innovation flourishes due to the exchange of diverse ideas and collaborative learning. Organizations and societies embracing social openness experience enhanced adaptive capacity and greater resilience in rapidly changing global markets.
Social Closure and Its Role in Inequality
Social closure refers to the process by which groups restrict access to resources and opportunities to maintain power and privilege, reinforcing social stratification. This mechanism often manifests through exclusionary practices based on race, class, gender, or education, exacerbating inequalities by limiting upward mobility for marginalized populations. Understanding social closure is crucial to addressing systemic inequality and promoting equitable social policies.
Factors Influencing Openness or Closure in Communities
Factors influencing social openness or closure in communities include economic diversity, which fosters inclusivity by providing varied opportunities and reducing barriers. Cultural norms and shared values also shape openness, as communities embracing pluralism tend to exhibit greater social integration. Moreover, institutional policies and governance play critical roles in either encouraging interaction among diverse groups or reinforcing social boundaries through exclusionary practices.
Balancing Social Openness and Closure for Social Harmony
Balancing social openness and social closure is essential for maintaining social harmony, as openness promotes inclusivity, diversity, and innovation, while closure fosters group identity, trust, and social order. Effective social systems integrate varying degrees of openness to allow new ideas and members to enter while preserving core cultural values and norms that bind communities together. Achieving this dynamic equilibrium helps prevent social fragmentation and conflict, ensuring sustainable cooperation and cohesion across diverse social groups.
Strategies to Enhance Social Openness and Reduce Closure
Promoting social openness involves implementing inclusive policies that encourage diversity, equitable access, and continuous intercultural dialogue, which foster mutual understanding and collaboration across different social groups. Encouraging community engagement initiatives, educational programs on empathy and inclusion, and transparent communication channels helps break down barriers created by social closure, thereby reducing segregation and prejudice. Facilitating networks that bridge social divides and promoting legal frameworks against discrimination are crucial strategies to sustain openness and dismantle mechanisms of social closure.
Social openness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com