Assimilation is the process by which individuals or groups absorb and integrate cultural traits, language, or customs of another dominant group, often leading to a loss of original identity. Understanding how assimilation impacts social dynamics and personal identity is crucial for recognizing its effects on diversity and inclusion. Explore the rest of the article to discover how assimilation shapes societies and influences your cultural experiences.
Table of Comparison
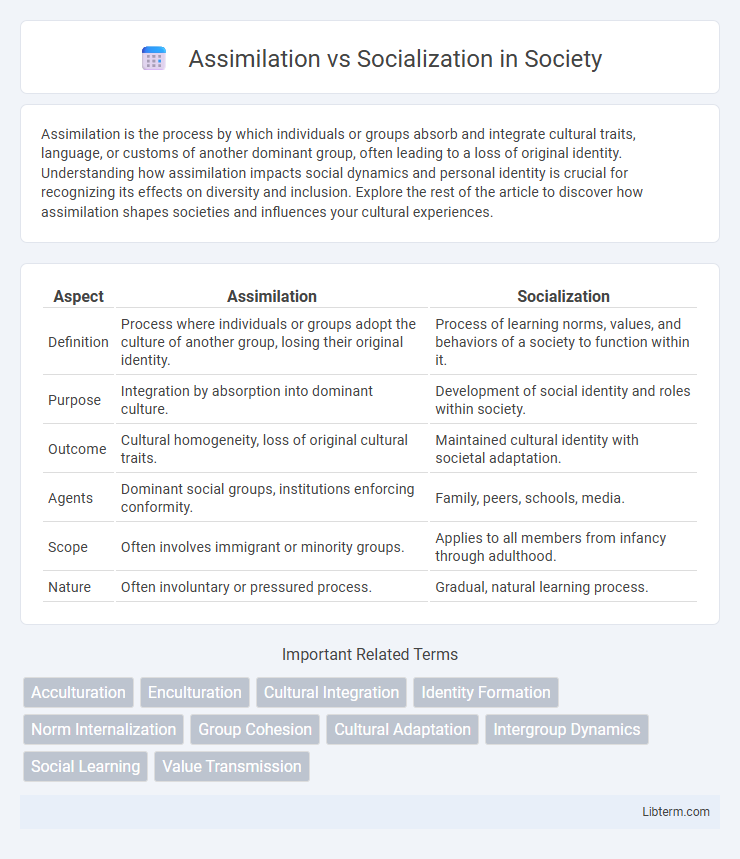
| Aspect | Assimilation | Socialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process where individuals or groups adopt the culture of another group, losing their original identity. | Process of learning norms, values, and behaviors of a society to function within it. |
| Purpose | Integration by absorption into dominant culture. | Development of social identity and roles within society. |
| Outcome | Cultural homogeneity, loss of original cultural traits. | Maintained cultural identity with societal adaptation. |
| Agents | Dominant social groups, institutions enforcing conformity. | Family, peers, schools, media. |
| Scope | Often involves immigrant or minority groups. | Applies to all members from infancy through adulthood. |
| Nature | Often involuntary or pressured process. | Gradual, natural learning process. |
Introduction to Assimilation and Socialization
Assimilation refers to the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits, values, and behaviors of another dominant group, often leading to the erosion of their original identity. Socialization involves the lifelong process through which individuals learn and internalize the norms, customs, and ideologies of their society, shaping their social identity and interactions. Understanding the distinctions between assimilation and socialization is crucial for analyzing cultural integration and identity formation within diverse societies.
Defining Assimilation in Society
Assimilation in society refers to the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural norms, values, and behaviors of a dominant or host society, often leading to the diminishing of their original cultural identities. This process involves the integration of immigrants or minority groups into mainstream social frameworks, influencing language use, customs, and social practices. Unlike socialization, which is the lifelong acquisition of social norms within one's existing culture, assimilation emphasizes the transformation and blending into a new, prevailing cultural context.
Understanding Socialization Processes
Socialization processes involve the ongoing interaction through which individuals learn and internalize the norms, values, behaviors, and social skills necessary to function within their communities, contrasting with assimilation which often implies adopting the dominant culture while losing one's original identity. Understanding socialization highlights how individuals maintain their distinct cultural identities while adapting to diverse social environments, emphasizing the dynamic and reciprocal nature of cultural integration. Studies show that socialization encompasses multiple agents such as family, peers, education, and media, each playing a critical role in shaping social competence and identity development across different stages of life.
Key Differences Between Assimilation and Socialization
Assimilation involves the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits of another group, often losing their original identity, whereas socialization is the lifelong process of learning norms, values, and behaviors necessary for functioning within society. Key differences include assimilation's focus on cultural integration into a dominant group, while socialization encompasses a broader scope of learning social roles across all stages of life. Assimilation often results in cultural absorption, whereas socialization maintains cultural diversity through continuous learning and adaptation.
Historical Perspectives on Assimilation and Socialization
Historical perspectives on assimilation emphasize the process by which minority groups adopt the cultural norms of a dominant society, often resulting in the loss of original cultural identities. In contrast, socialization involves the lifelong process through which individuals learn and internalize the values, behaviors, and social skills necessary to function within their society. The study of these concepts reveals the dynamic interactions between culture, identity formation, and power structures across different historical contexts.
The Role of Culture in Assimilation and Socialization
Culture plays a pivotal role in both assimilation and socialization by shaping individuals' values, norms, and behaviors within a society. Assimilation involves the process where individuals adopt the dominant culture, often leading to the loss or modification of their original cultural identity, while socialization refers to the lifelong process of learning and internalizing cultural norms from family, peers, and institutions. Understanding cultural dynamics in these processes is essential for comprehending how individuals integrate and function within diverse social environments.
Impact on Identity Formation
Assimilation often leads to the erosion of original cultural identity as individuals adopt dominant societal norms, resulting in a loss of heritage and personal uniqueness. Socialization, in contrast, promotes identity formation by allowing individuals to integrate multiple cultural influences while maintaining core aspects of their original identity. The impact on identity formation is significant, as assimilation pressures conformity, whereas socialization fosters a dynamic, multifaceted sense of self.
Socialization Agents vs Assimilation Agents
Socialization agents such as family, peers, schools, and media facilitate the process of acquiring cultural norms, values, and behaviors essential for social integration and identity formation. Assimilation agents, often including government institutions, dominant cultural groups, and educational systems, promote the absorption of minority groups into the prevailing culture, sometimes at the cost of erasing original cultural identities. The distinction lies in socialization supporting cultural diversification and continuity, whereas assimilation drives cultural conformity and homogenization.
Challenges and Controversies
Assimilation often faces challenges related to the loss of cultural identity and resistance from minority groups seeking to preserve their heritage. Socialization controversies arise when dominant cultural norms impose values that marginalize diverse perspectives, leading to tensions in multicultural societies. Both processes can create conflicts over inclusion, power dynamics, and the balance between unity and cultural diversity.
Assimilation and Socialization in Modern Societies
Assimilation in modern societies involves individuals or groups adopting the cultural norms, values, and behaviors of the dominant society, often leading to a loss of their original cultural identity. Socialization is the ongoing process through which individuals learn and internalize the social norms, customs, and ideologies necessary to function effectively within their community. In diverse, multicultural societies, socialization fosters inclusion and identity formation, while assimilation often pressures minorities to conform, highlighting significant dynamics in cultural integration and social cohesion.
Assimilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com