Cultural assimilation involves the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits of another group, often leading to the loss of their original cultural identity. This phenomenon can shape social integration, influence language use, and impact community dynamics significantly. Explore the rest of this article to understand how cultural assimilation affects societies and your role within them.
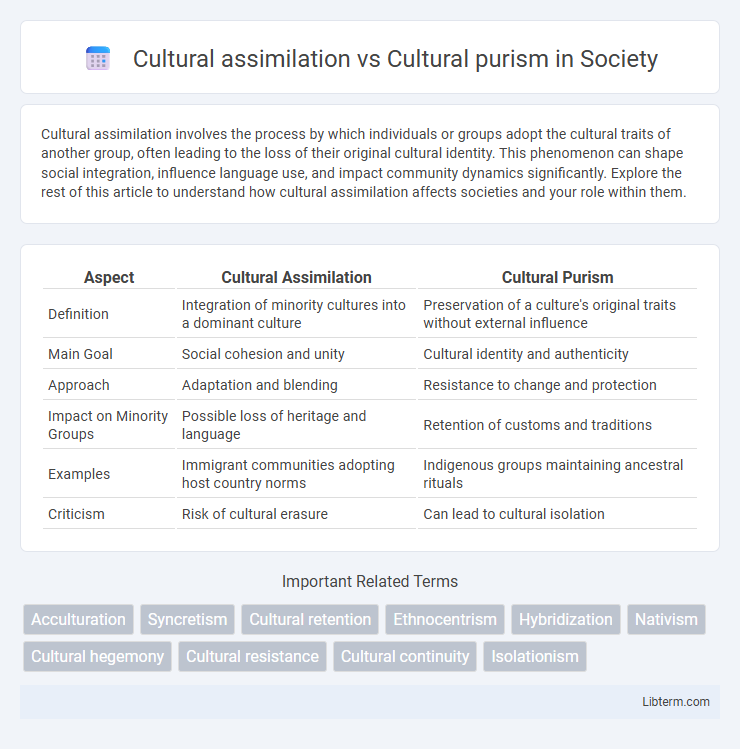
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cultural Assimilation | Cultural Purism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of minority cultures into a dominant culture | Preservation of a culture's original traits without external influence |
| Main Goal | Social cohesion and unity | Cultural identity and authenticity |
| Approach | Adaptation and blending | Resistance to change and protection |
| Impact on Minority Groups | Possible loss of heritage and language | Retention of customs and traditions |
| Examples | Immigrant communities adopting host country norms | Indigenous groups maintaining ancestral rituals |
| Criticism | Risk of cultural erasure | Can lead to cultural isolation |
Defining Cultural Assimilation
Cultural assimilation refers to the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits, values, and behaviors of another dominant culture, often leading to a reduction of their original cultural identity. This process facilitates social integration and can occur through language acquisition, adoption of customs, and changes in social norms. Unlike cultural purism, which emphasizes preserving and maintaining traditional cultural elements, assimilation promotes blending and adaptation within a multicultural society.
Understanding Cultural Purism
Cultural purism emphasizes preserving the original customs, language, and traditions of a community by resisting external influences and avoiding cultural blending. This ideology seeks to maintain cultural identity and heritage, often prioritizing authenticity and continuity over adaptation or change. Understanding cultural purism involves recognizing its role in protecting cultural distinctiveness amid globalization and the pressures of cultural assimilation.
Historical Perspectives on Cultural Change
Historical perspectives on cultural change reveal that cultural assimilation often emerged through colonialism and migration, where dominant groups imposed their values on subcultures, facilitating social cohesion but risking cultural loss. In contrast, cultural purism aimed to preserve ethnic identities by resisting external influences, sometimes leading to cultural revival movements or nationalist ideologies. Key examples include the Americanization policies in the 19th century and the rise of cultural nationalism in postcolonial societies.
Factors Driving Assimilation
Factors driving cultural assimilation include economic opportunities, social integration policies, and the desire for acceptance within a dominant society. Migration patterns, education systems, and media influence also play critical roles by promoting shared values and norms, which encourage minority groups to adopt the prevailing culture. Language acquisition and intermarriage further accelerate assimilation by fostering deeper cultural connections and reducing social barriers.
Motivations Behind Purist Ideologies
Purist ideologies stem from motivations to preserve a perceived authentic cultural identity amid globalization and multicultural influences, often driven by fears of cultural erosion and loss of heritage. These motivations emphasize maintaining traditional customs, language, and values to reinforce community cohesion and resist external cultural dominance. Cultural purism prioritizes protection of cultural integrity over adaptation, contrasting with the assimilation approach that encourages blending and integration.
impacts on Identity and Community
Cultural assimilation often leads to the erosion of distinct cultural identities as individuals adopt dominant societal norms, which can weaken community bonds and diminish cultural diversity. In contrast, cultural purism emphasizes preserving original traditions and values, strengthening group identity and fostering a sense of belonging within the community. Both processes significantly shape social cohesion, influencing how cultural heritage is maintained or transformed across generations.
Case Studies: Assimilation vs. Purism in Practice
Case studies of cultural assimilation demonstrate how immigrant communities adapt language, customs, and social norms to integrate into host societies, often resulting in hybrid identities that blend origin and new cultural traits. In contrast, cultural purism is exemplified by groups like the Amish in the United States or the Basques in Spain, who maintain strict adherence to traditional practices and resist external influences to preserve their unique cultural heritage. Comparative analysis reveals that assimilation promotes social cohesion and economic integration, while purism safeguards cultural continuity and resists homogenization.
Cultural Assimilation in a Globalized World
Cultural assimilation in a globalized world often results in the blending and merging of diverse traditions, languages, and customs, fostering social cohesion and economic integration. This process can enhance cross-cultural understanding and create hybrid identities that reflect interconnected global influences. However, it also poses challenges to preserving unique cultural heritages amid dominant global narratives.
Challenges and Critiques of Cultural Purism
Cultural purism faces challenges such as resisting necessary social integration and fostering exclusion, often leading to cultural stagnation and intolerance. Critics argue that strict adherence to cultural purity ignores the natural evolution and hybridization essential for vibrant, adaptive societies. This rigidity can marginalize minority groups and hinder intercultural dialogue, limiting social cohesion and innovation.
Navigating the Balance: Toward Cultural Harmony
Navigating the balance between cultural assimilation and cultural purism requires understanding the importance of preserving unique cultural identities while embracing shared societal values. Emphasizing mutual respect and open dialogue fosters cultural harmony, allowing diverse traditions to coexist without erasing individual heritages. Promoting inclusive policies that celebrate multiculturalism supports both community integration and the maintenance of distinct cultural practices.
Cultural assimilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com