Economic inequality affects access to resources, education, and healthcare, creating significant gaps between different social groups. Addressing this issue requires comprehensive policies that promote fair wages, equitable taxation, and social safety nets. Discover how economic inequality impacts society and what steps you can take to support a more just economy.
Table of Comparison
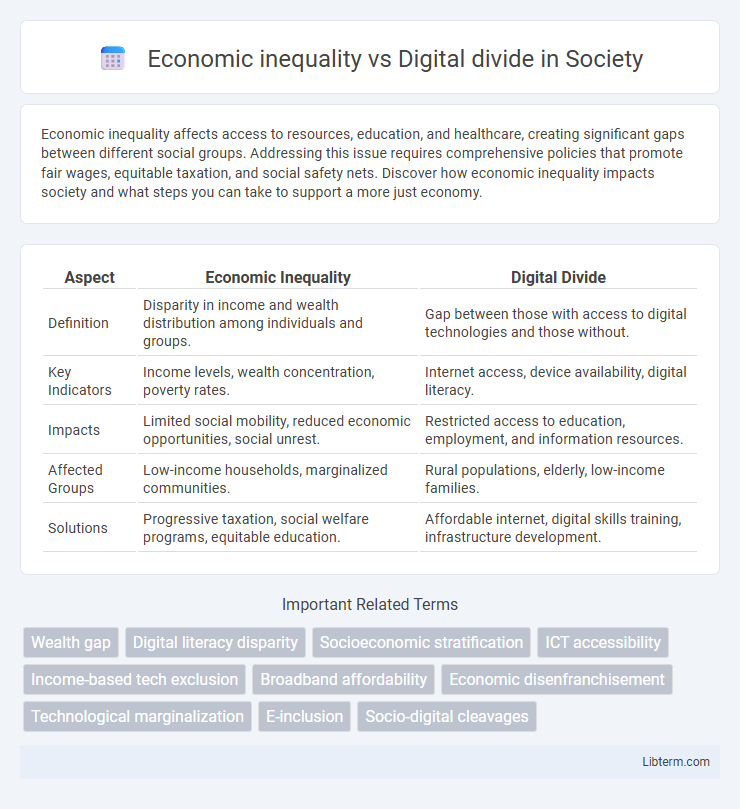
| Aspect | Economic Inequality | Digital Divide |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disparity in income and wealth distribution among individuals and groups. | Gap between those with access to digital technologies and those without. |
| Key Indicators | Income levels, wealth concentration, poverty rates. | Internet access, device availability, digital literacy. |
| Impacts | Limited social mobility, reduced economic opportunities, social unrest. | Restricted access to education, employment, and information resources. |
| Affected Groups | Low-income households, marginalized communities. | Rural populations, elderly, low-income families. |
| Solutions | Progressive taxation, social welfare programs, equitable education. | Affordable internet, digital skills training, infrastructure development. |
Understanding Economic Inequality
Economic inequality refers to the unequal distribution of wealth, income, and access to resources across different socioeconomic groups, significantly impacting opportunities and living standards. Understanding economic inequality is crucial for addressing disparities in education, healthcare, and employment, which consequently influence technological accessibility. Closing the digital divide requires targeted policies that consider these economic disparities to ensure equitable access to digital tools and infrastructure.
Defining the Digital Divide
The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals or communities with adequate access to information and communication technologies (ICT) and those without, significantly influenced by economic inequality. Limited access to high-speed internet, digital devices, and digital literacy disproportionately affects low-income households, exacerbating existing socioeconomic disparities. Bridging the digital divide requires targeted investments in infrastructure, affordable technology, and education to ensure equitable participation in the digital economy.
Interconnectedness of Wealth and Technology Access
Economic inequality and the digital divide are deeply interconnected, with wealth distribution directly influencing access to technology and digital resources. High-income households are more likely to afford advanced devices, reliable internet, and digital skills training, widening the gap between affluent and disadvantaged communities. Bridging the digital divide requires addressing economic disparities to ensure equitable technology access, which is essential for social mobility and inclusive economic growth.
Key Drivers of Economic Inequality
Economic inequality is primarily driven by disparities in income, wealth accumulation, education access, and labor market dynamics, which create significant barriers to economic mobility. Technological advancements exacerbate these inequalities by disproportionately benefiting high-skilled workers and capital owners, leaving low-wage and unskilled labor behind. The digital divide intensifies economic inequality as unequal access to digital technologies and internet connectivity limits educational opportunities, job prospects, and social inclusion for marginalized communities.
Factors Widening the Digital Divide
Economic inequality significantly contributes to the digital divide by limiting access to essential technology and high-speed internet for low-income populations, thereby restricting their educational and economic opportunities. Geographic disparities exacerbate this divide, as rural and underserved urban areas often lack the infrastructure needed for reliable connectivity. Educational disparities further widen the digital gap, as individuals with limited digital literacy skills struggle to utilize online resources effectively, perpetuating cycles of socioeconomic disadvantage.
Societal Impacts of Economic Disparities
Economic inequality exacerbates the digital divide by limiting access to technology, education, and internet connectivity for lower-income populations, which hinders social mobility and economic opportunities. Disparities in digital access reinforce systemic inequities, affecting employment, healthcare, and education outcomes, particularly in underserved communities. Addressing economic disparities is crucial to bridging the digital divide and promoting inclusive societal development.
Consequences of Unequal Digital Access
Unequal digital access exacerbates economic inequality by limiting opportunities for education, employment, and entrepreneurship among underserved populations. Lack of broadband connectivity and digital skills hinders participation in the digital economy, resulting in lower income levels and reduced social mobility. This digital divide creates a feedback loop where marginalized groups remain trapped in poverty, perpetuating systemic disparities in wealth and access to resources.
Bridging the Gap: Policy Initiatives
Bridging the gap between economic inequality and the digital divide requires targeted policy initiatives such as expanding broadband infrastructure in underserved communities and subsidizing access to digital devices. Implementing digital literacy programs alongside financial support policies ensures marginalized populations can participate fully in the digital economy. Governments and private sectors must collaborate to create inclusive frameworks that address both income disparities and technology accessibility simultaneously.
Technology as a Tool for Economic Inclusion
Technology serves as a critical tool for economic inclusion by bridging the digital divide that often exacerbates economic inequality. Access to digital platforms and affordable internet enables marginalized communities to participate in the global economy through remote work, online education, and e-commerce opportunities. Investment in digital infrastructure and digital literacy programs directly correlates with increased economic mobility and reduced income disparities across diverse populations.
Future Outlook: Towards a More Equitable Digital Economy
Bridging the economic inequality and digital divide requires targeted investments in digital infrastructure and inclusive education to ensure equitable access to emerging technologies. Innovations in affordable connectivity and digital literacy programs are projected to empower marginalized communities and foster economic participation. Policies supporting universal broadband access and digital entrepreneurship will be critical in shaping a more inclusive digital economy by 2030.
Economic inequality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com