Effective organization enhances productivity by streamlining workflows and prioritizing tasks. It fosters clear communication, reduces stress, and creates a structured environment for achieving goals. Dive into the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for optimizing your organization's success.
Table of Comparison
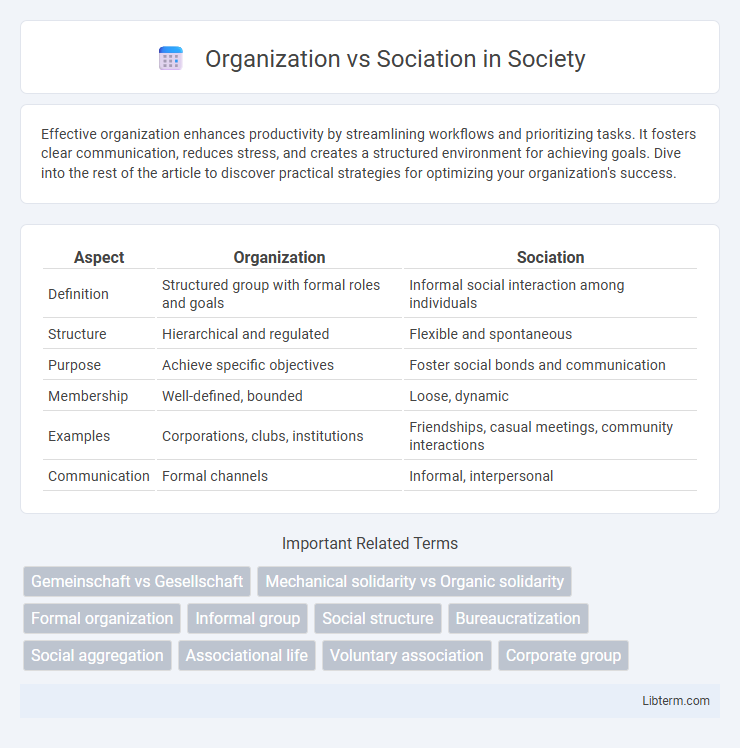
| Aspect | Organization | Sociation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured group with formal roles and goals | Informal social interaction among individuals |
| Structure | Hierarchical and regulated | Flexible and spontaneous |
| Purpose | Achieve specific objectives | Foster social bonds and communication |
| Membership | Well-defined, bounded | Loose, dynamic |
| Examples | Corporations, clubs, institutions | Friendships, casual meetings, community interactions |
| Communication | Formal channels | Informal, interpersonal |
Understanding Organization and Sociation: Definitions
Organization refers to a structured group of individuals working together to achieve common goals through defined roles and coordinated activities. Sociation involves the social interaction and relationships that form between individuals within a community or society, emphasizing social bonds and connections. Understanding these concepts highlights that organizations are formal entities designed for specific purposes, while sociation describes the informal social processes that unite people in shared experiences.
Historical Overview of Organization and Sociation
The historical overview of organization traces back to early human civilizations where structured groups coordinated tasks to achieve common goals, evolving through tribal systems, ancient empires, and industrialization. Sociation, a term introduced by sociologist Georg Simmel, emphasizes the process of interaction and social bonds forming the fabric of society, distinct from formal organizational structures. Understanding the evolution of both concepts reveals their complementary roles: organizations provide structured frameworks while sociation highlights dynamic social relationships and interactions.
Key Differences Between Organization and Sociation
Organizations are structured groups with formal rules, defined roles, and specific goals aimed at achieving collective objectives, whereas sociations are informal social groups formed through voluntary and natural social interactions without rigid structures. Organizations emphasize hierarchy, stability, and accountability, while sociations prioritize social bonds, mutual interests, and shared experiences. The key difference lies in the degree of formalization and purpose: organizations operate through deliberate coordination, whereas sociations emerge spontaneously based on social cohesion.
Structural Elements: Comparing Organization and Sociation
Organizations feature formal structures with defined roles, hierarchies, and rules designed to achieve specific goals efficiently. Sociations, in contrast, possess looser, informal structures characterized by social relationships and shared norms without rigid authority lines. The structural elements of organizations emphasize planned coordination, whereas sociations rely on spontaneous interaction and social cohesion.
Roles and Relationships in Organization vs Sociation
In organizations, roles are formally defined with specific responsibilities and hierarchical relationships, ensuring structured coordination and accountability. Sociations, by contrast, exhibit fluid roles shaped by social interactions and mutual affiliations, emphasizing informal relationships based on shared interests or values. Relationships in organizations are primarily goal-oriented and governed by policies, whereas sociations prioritize cooperative bonds and social cohesion.
Functions and Purposes of Organization and Sociation
Organizations coordinate structured activities and allocate resources to achieve specific goals efficiently, often emphasizing roles, responsibilities, and hierarchical control. Sociations, or social groups, serve to establish and maintain social bonds, shared norms, and collective identities, fostering cooperation and social integration. While organizations primarily focus on task execution and goal accomplishment, sociations prioritize relational functions and the creation of social cohesion among members.
Decision-Making Processes: Organization vs Sociation
Organizations feature structured decision-making processes driven by formal hierarchies and predefined roles, ensuring consistent and efficient outcomes. Sociations, by contrast, rely on informal, fluid interactions where decisions emerge from social norms, collective behavior, and consensus among members. This distinction highlights how organizations prioritize rationalization and control, while sociations emphasize adaptability and social cohesion.
Impact on Social Dynamics and Group Behavior
Organizations shape social dynamics by establishing formal roles, rules, and hierarchies that guide behavior toward specific goals, fostering cooperation and structured interaction within groups. Sociation, characterized by informal social relationships and cultural norms, influences group behavior through shared values, emotional bonds, and spontaneous interactions, which create social cohesion and collective identity. The impact on group behavior varies as organizations drive efficiency and task orientation, while sociation enhances social support and community belonging.
Real-World Examples of Organization and Sociation
Organizations embody structured groups like corporations, governments, and NGOs, designed to achieve specific goals through formal processes and roles. Sociations, exemplified by social networks, clubs, and communities, emphasize informal ties and shared values without strict hierarchical control. For instance, a multinational corporation represents an organization with defined objectives, whereas a neighborhood association reflects a sociation based on social interaction and mutual support.
Future Trends: Organization and Sociation in Modern Society
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain are reshaping organizations by enabling decentralized decision-making and enhanced collaboration, while sociation increasingly relies on digital platforms that foster fluid social interactions beyond traditional institutional boundaries. The future of organizations points toward more adaptive, networked structures that integrate human and machine inputs, whereas sociation evolves with augmented reality and virtual communities facilitating transient, purpose-driven social bonds. These trends highlight a convergence where organizational roles are becoming more dynamic and sociation patterns more digitally mediated, reflecting the complex interplay of technology and human connectivity in modern society.
Organization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com