Government plays a crucial role in shaping economic policies, enforcing laws, and providing public services that maintain societal order and promote national development. Effective governance ensures transparency, accountability, and citizen participation, which are vital for sustainable progress and social stability. Discover how government functions influence your daily life and the broader community by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
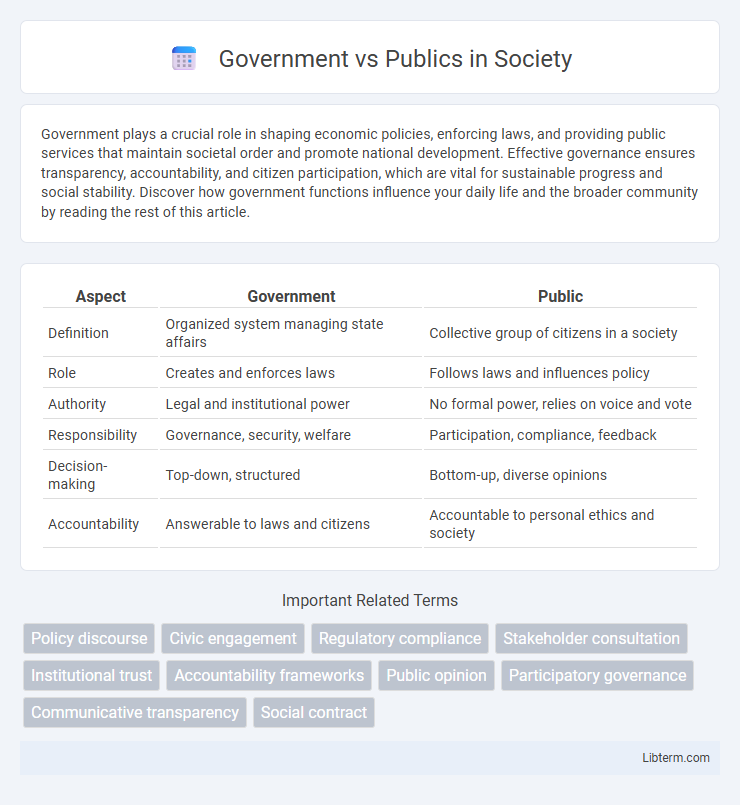
| Aspect | Government | Public |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organized system managing state affairs | Collective group of citizens in a society |
| Role | Creates and enforces laws | Follows laws and influences policy |
| Authority | Legal and institutional power | No formal power, relies on voice and vote |
| Responsibility | Governance, security, welfare | Participation, compliance, feedback |
| Decision-making | Top-down, structured | Bottom-up, diverse opinions |
| Accountability | Answerable to laws and citizens | Accountable to personal ethics and society |
Understanding the Government-Public Relationship
The government-public relationship is characterized by dynamic interactions where government policies and actions directly impact citizens' lives while public opinion influences governance decisions. Understanding this relationship involves analyzing communication channels, trust levels, and the degree of public participation in democratic processes. Effective governance depends on transparency, accountability, and responsiveness to public needs, fostering cooperation and social cohesion.
Historical Context of Government vs Publics
The historical context of government versus publics reveals a dynamic evolution from absolute monarchies to modern democratic systems where citizen participation gained prominence. Early governments exerted centralized control, often limiting public influence, but social movements and revolutions, such as the American and French Revolutions, catalyzed shifts towards representative governance and civil rights. This transformation underscores the ongoing tension and negotiation between state authority and public demands for accountability and transparency.
Key Differences Between Government and Publics
Government refers to the formal institutions and structures responsible for creating and enforcing laws, policies, and regulations within a defined territory. Publics consist of diverse groups of people who share common interests, values, or concerns, influencing or reacting to government actions. Key differences include authority and power held by governments to implement decisions, whereas publics mainly exercise influence through participation, opinion shaping, and collective action.
The Role of Government in Society
Governments establish legal frameworks and enforce laws to maintain order and protect citizens' rights within society. They provide essential public services, including education, healthcare, infrastructure, and national defense, which are critical for societal stability and economic growth. Government intervention regulates markets, mitigates inequalities, and ensures the welfare of vulnerable populations, thereby promoting social cohesion and public trust.
Public Participation in Governance
Public participation in governance enhances transparency and accountability by involving citizens directly in decision-making processes. Governments that prioritize inclusive engagement foster trust, improve policy outcomes, and encourage civic responsibility. Effective public participation mechanisms include public consultations, referenda, and participatory budgeting, which empower communities to influence governance meaningfully.
Conflicts and Challenges: Government vs Public Interests
Conflicts and challenges between government and public interests often arise from differing priorities, such as economic development versus environmental protection or national security versus individual privacy. Government policies may face public resistance when perceived as lacking transparency, inclusiveness, or fairness, thereby eroding trust and social cohesion. Effective governance requires balancing regulatory authority with public accountability to minimize conflicts and foster cooperative problem-solving.
Transparency and Accountability in Government
Transparency in government is essential for fostering public trust and ensuring that citizens have access to information about decision-making processes and resource allocation. Accountability mechanisms such as independent audits, public reporting, and legislative oversight hold government officials responsible for their actions and performance. Public participation enhances transparency by enabling community input and scrutiny, which helps prevent corruption and promotes more responsive governance.
Mechanisms for Public Feedback and Engagement
Governments implement mechanisms such as public consultations, town hall meetings, and digital platforms to facilitate direct public feedback and enhance civic engagement. These tools allow citizens to express opinions, influence policy decisions, and increase government transparency and accountability. Effective public feedback systems integrate surveys, social media interactions, and participatory budgeting to ensure diverse community voices shape governance outcomes.
Case Studies: Government-Public Disputes
Government-public disputes often highlight conflicts over policy implementation, transparency, and civil rights, as seen in landmark cases such as the Boston Tea Party protests and the Tiananmen Square demonstrations. These case studies reveal patterns of public dissent triggered by perceived government overreach, affecting social cohesion and governance legitimacy. Analysis of these disputes underscores the importance of participatory governance and effective communication between authorities and citizens to prevent escalation and ensure accountability.
Future Trends in Government-Public Collaboration
Emerging trends in government-public collaboration highlight increased use of digital platforms and AI-driven tools to enhance transparency and citizen engagement. Governments are investing in open data initiatives and participatory decision-making processes to foster trust and co-create public policies. Enhanced interoperability between government systems and public feedback channels accelerates responsiveness and drives innovation in public service delivery.
Government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com