Voluntary simplicity involves intentionally reducing consumption and focusing on meaningful experiences to enhance personal well-being and environmental sustainability. Embracing minimalist living, mindful spending, and prioritizing relationships can lead to greater life satisfaction and reduced stress. Discover how adopting voluntary simplicity can transform Your lifestyle by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
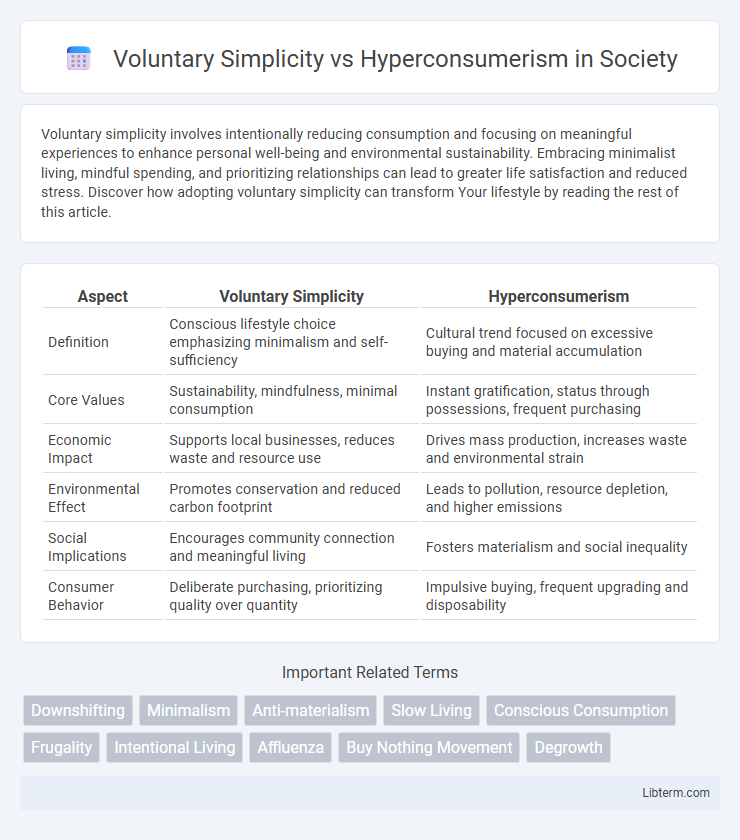
| Aspect | Voluntary Simplicity | Hyperconsumerism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conscious lifestyle choice emphasizing minimalism and self-sufficiency | Cultural trend focused on excessive buying and material accumulation |
| Core Values | Sustainability, mindfulness, minimal consumption | Instant gratification, status through possessions, frequent purchasing |
| Economic Impact | Supports local businesses, reduces waste and resource use | Drives mass production, increases waste and environmental strain |
| Environmental Effect | Promotes conservation and reduced carbon footprint | Leads to pollution, resource depletion, and higher emissions |
| Social Implications | Encourages community connection and meaningful living | Fosters materialism and social inequality |
| Consumer Behavior | Deliberate purchasing, prioritizing quality over quantity | Impulsive buying, frequent upgrading and disposability |
Understanding Voluntary Simplicity
Voluntary simplicity emphasizes mindful consumption and intentional living by reducing material possessions and focusing on personal fulfillment rather than external wealth. This lifestyle encourages sustainable practices, prioritizing environmental conservation and mental well-being over constant acquisition of goods. Understanding voluntary simplicity reveals its role in countering hyperconsumerism trends, promoting a balanced approach to resources and happiness.
Defining Hyperconsumerism
Hyperconsumerism is defined by an excessive preoccupation with purchasing goods and services beyond basic needs, driven by the pursuit of social status and identity through material possessions. This behavior fuels a cycle of continuous consumption, waste generation, and environmental degradation. Corporations leverage marketing strategies to promote hyperconsumerism, encouraging impulse buying and fostering dependency on trends and brand loyalty.
Historical Roots of Simplicity and Consumerism
Voluntary simplicity traces its roots to ancient philosophical traditions such as Stoicism and minimalism, emphasizing intentional living and self-restraint to achieve inner peace and sustainability. In contrast, hyperconsumerism emerged primarily in the post-World War II era, fueled by mass production, advertising innovations, and the rise of a consumer-driven economy promoting material accumulation and instant gratification. These contrasting historical foundations underscore the tension between mindful consumption and relentless consumerism shaping modern societal values.
Psychological Impacts: Simplicity vs Hyperconsumerism
Voluntary simplicity promotes mental clarity, reduced stress, and increased life satisfaction by encouraging mindful consumption and prioritizing intrinsic values over material possessions. Hyperconsumerism often leads to psychological distress, anxiety, and decreased well-being due to constant exposure to advertising, social comparison, and the pursuit of fleeting material gratification. Research indicates that embracing simplicity enhances emotional resilience and long-term happiness, while hyperconsumerism correlates with higher rates of depression and lower self-esteem.
Environmental Consequences
Voluntary simplicity reduces environmental impact by minimizing resource consumption and waste generation, promoting sustainable living and lower carbon emissions. Hyperconsumerism drives overproduction and excessive waste, accelerating resource depletion and contributing significantly to pollution and climate change. Choosing voluntary simplicity supports ecological balance by decreasing demand for energy-intensive goods and encouraging mindful consumption habits.
Financial Implications and Personal Wealth
Voluntary simplicity emphasizes minimizing expenses and prioritizing needs over wants, leading to significant savings and increased personal wealth accumulation over time. Hyperconsumerism drives excessive spending on non-essential goods, often resulting in debt accumulation and financial instability. Adopting voluntary simplicity fosters long-term financial security by reducing reliance on credit and enabling more strategic wealth management.
Social Dynamics and Community Well-being
Voluntary simplicity fosters social dynamics grounded in shared values, cooperation, and local engagement, enhancing community well-being through stronger interpersonal relationships and collective resilience. In contrast, hyperconsumerism often drives social fragmentation and prioritizes individualism, leading to weakened communal bonds and increased social inequality. Communities embracing simplicity typically experience improved mental health, environmental stewardship, and social cohesion, which contrast sharply with the stresses and ecological impacts linked to consumption-driven lifestyles.
Media Influence and Advertising Pressures
Media influence and advertising pressures significantly shape consumer behavior by promoting hyperconsumerism through targeted marketing strategies that encourage constant purchasing and material accumulation. Voluntary simplicity counters these effects by advocating for mindful consumption and rejecting the societal pressures perpetuated by media to acquire excessive goods. The pervasive presence of advertisements in digital and traditional media channels intensifies the pressure to conform to consumerist ideals, making voluntary simplicity a deliberate resistance to these commercial influences.
Practical Steps Toward Voluntary Simplicity
Adopting voluntary simplicity involves practical steps such as minimizing material possessions, reducing consumption, and prioritizing experiences over goods to foster financial independence and environmental sustainability. Implementing mindful spending, decluttering regularly, and choosing quality over quantity can counteract the pressures of hyperconsumerism and promote a fulfilling lifestyle. Embracing habits like growing personal food, using public transportation, and practicing digital detoxes further support a simpler, more intentional way of living.
Future Trends: Embracing Sufficient Living
Future trends indicate a growing shift towards voluntary simplicity as consumers increasingly prioritize sustainable lifestyles over hyperconsumerism-driven excess. Sufficient living emphasizes mindful consumption, reduction of waste, and valuing quality over quantity, aligning with global movements toward environmental responsibility and minimalism. Businesses are expected to adapt by offering products and services that support durability, repairability, and ethical production, catering to a demographic seeking meaningful consumption patterns.
Voluntary Simplicity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com