Economic boundaries define the limits within which economic activities such as production, trade, and consumption occur, influencing resource allocation and market operations. These boundaries can be shaped by geographical, political, and regulatory factors, affecting how businesses and consumers interact within a specific area. Explore the rest of the article to understand how economic boundaries impact your local and global economic environment.
Table of Comparison
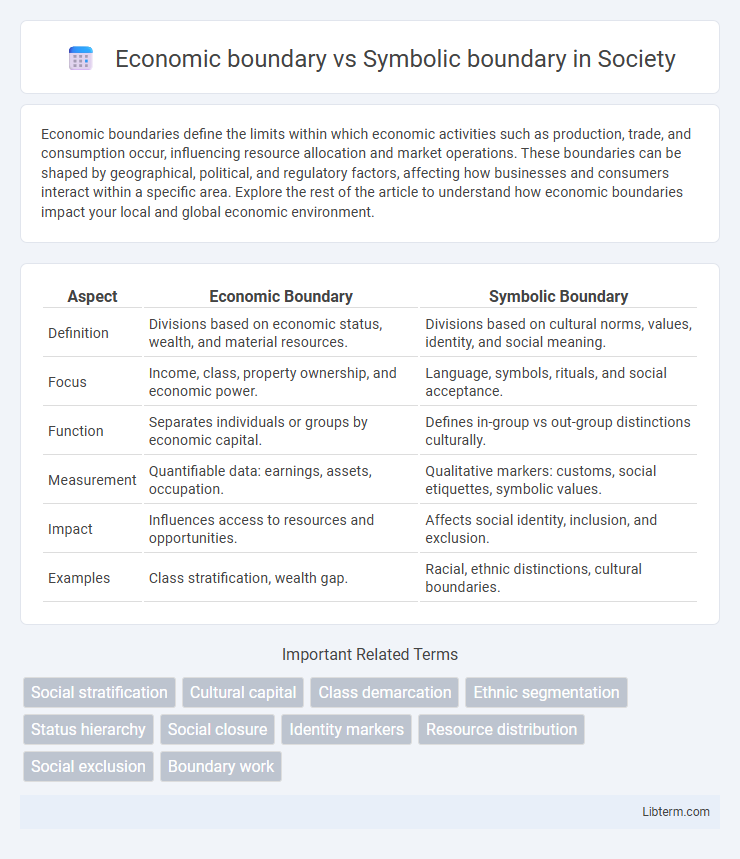
| Aspect | Economic Boundary | Symbolic Boundary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Divisions based on economic status, wealth, and material resources. | Divisions based on cultural norms, values, identity, and social meaning. |
| Focus | Income, class, property ownership, and economic power. | Language, symbols, rituals, and social acceptance. |
| Function | Separates individuals or groups by economic capital. | Defines in-group vs out-group distinctions culturally. |
| Measurement | Quantifiable data: earnings, assets, occupation. | Qualitative markers: customs, social etiquettes, symbolic values. |
| Impact | Influences access to resources and opportunities. | Affects social identity, inclusion, and exclusion. |
| Examples | Class stratification, wealth gap. | Racial, ethnic distinctions, cultural boundaries. |
Introduction to Economic and Symbolic Boundaries
Economic boundaries define divisions based on material resources, exchange, and economic power, shaping access to wealth and opportunities within societies. Symbolic boundaries, in contrast, are social distinctions drawn through cultural markers such as language, religion, or dress, influencing group identity and social inclusion. Understanding these boundaries clarifies how economic status and cultural practices jointly structure social hierarchies and group membership.
Defining Economic Boundaries: Key Features
Economic boundaries delineate the limits of resource allocation, production, and trade activities within or between organizations or markets, emphasizing financial transactions, ownership rights, and legal constraints. Key features include clear demarcation of property rights, control over economic assets, and regulatory frameworks that govern market entry and competition. These boundaries influence economic behavior by restricting or enabling access to resources and shaping market dynamics.
Understanding Symbolic Boundaries: Core Concepts
Symbolic boundaries refer to the conceptual distinctions that individuals or groups create to categorize people, behaviors, or objects, shaping social identities and group memberships. These boundaries often manifest through language, rituals, and cultural practices, reinforcing social hierarchies and inclusion or exclusion within communities. Understanding symbolic boundaries is crucial for analyzing how social cohesion and divisions form beyond economic factors.
Historical Evolution of Economic and Symbolic Boundaries
Economic boundaries historically emerged from tangible divisions in wealth, production, and market access, shaping class structures and trade regulations since the industrial revolution. Symbolic boundaries evolved as social markers based on cultural values, identity, and status distinctions, influencing social inclusion and exclusion across history. The interaction between economic and symbolic boundaries has continuously transformed societal hierarchies by intertwining material resources with cultural meaning.
Comparative Analysis: Economic vs Symbolic Boundaries
Economic boundaries define divisions based on material resources, wealth distribution, and access to economic opportunities, directly affecting social class stratification and mobility. Symbolic boundaries, meanwhile, involve cultural distinctions, norms, and shared meanings that shape group identity and social inclusion or exclusion without necessarily linking to material wealth. Comparative analysis reveals that while economic boundaries manifest in tangible disparities, symbolic boundaries influence social perception and group cohesion, together reinforcing social hierarchies through both financial and cultural mechanisms.
Intersections and Overlaps Between Economic and Symbolic Boundaries
Economic boundaries define access to material resources and market participation, while symbolic boundaries distinguish social groups through cultural norms and identity markers; their intersections occur when economic status influences cultural inclusion or exclusion. Overlaps between these boundaries are evident in phenomena such as consumption patterns signaling class membership and the stigmatization of economic hardship that reinforces social hierarchies. Understanding these overlaps reveals how economic inequalities are both produced and legitimized through symbolic practices and cultural distinctions.
Impact of Economic Boundaries on Social Stratification
Economic boundaries, defined by disparities in income, wealth, and access to resources, significantly influence social stratification by determining individuals' ability to participate in various social and economic activities. These boundaries create distinct social classes, reinforcing inequality through limited upward mobility and restricted access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities. The persistence of economic boundaries perpetuates social divisions and shapes patterns of privilege and disadvantage within societies.
Role of Symbolic Boundaries in Shaping Cultural Identity
Symbolic boundaries play a crucial role in shaping cultural identity by defining group membership through shared values, beliefs, and practices, distinguishing "us" from "them" beyond economic factors. Unlike economic boundaries that separate groups based on material resources or wealth, symbolic boundaries influence social interactions, cultural inclusion, and identity formation within communities. These boundaries help individuals internalize cultural norms and create a sense of belonging that is essential for social cohesion and identity maintenance.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Economic and Symbolic Boundaries
Case studies reveal economic boundaries as tangible divisions rooted in access to resources, income, and market participation, exemplified by the stark financial disparities between urban and rural communities worldwide. Symbolic boundaries manifest through social markers like language, religion, or cultural practices, as seen in caste distinctions in India or racial segregation in the United States, reinforcing social exclusion beyond mere economic factors. Understanding these boundaries highlights their interplay in shaping inequality, where economic barriers often align with symbolic distinctions to perpetuate systemic exclusion and social stratification.
Future Directions in Boundary Research and Social Policy
Future directions in boundary research emphasize integrating economic and symbolic boundaries to better understand social stratification and inequality. Scholars advocate for interdisciplinary approaches combining economic data with cultural analysis to inform social policies that address both material disparities and identity-based exclusion. Policies targeting economic inequities must also consider symbolic boundaries to promote social cohesion and reduce discrimination.
Economic boundary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com