Discrimination undermines equality by unfairly treating individuals based on race, gender, age, or other characteristics, impacting opportunities and mental health. Understanding its forms and consequences is key to fostering inclusive environments and promoting social justice. Explore the rest of this article to learn how you can identify and combat discrimination effectively.
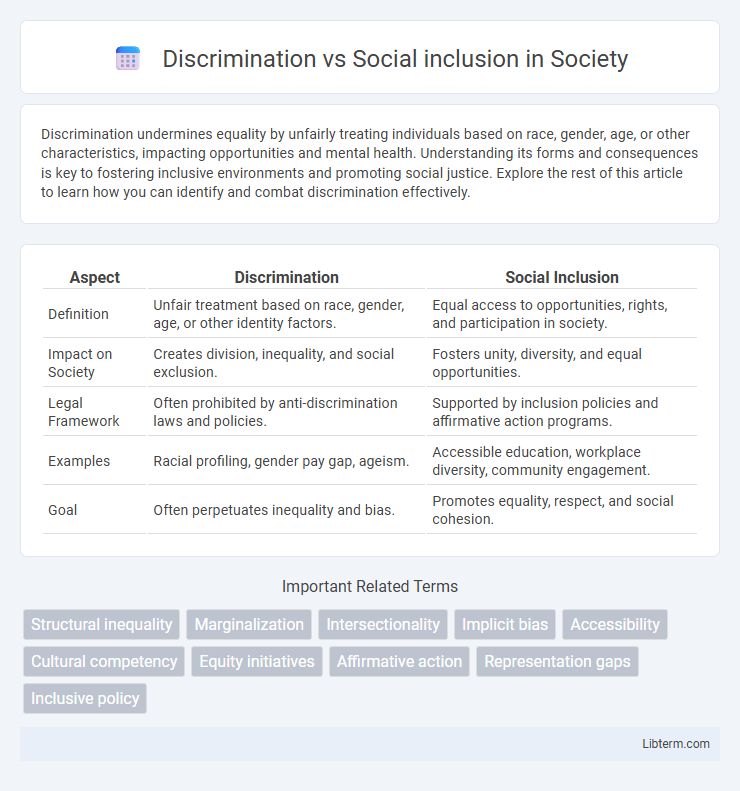
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Discrimination | Social Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unfair treatment based on race, gender, age, or other identity factors. | Equal access to opportunities, rights, and participation in society. |
| Impact on Society | Creates division, inequality, and social exclusion. | Fosters unity, diversity, and equal opportunities. |
| Legal Framework | Often prohibited by anti-discrimination laws and policies. | Supported by inclusion policies and affirmative action programs. |
| Examples | Racial profiling, gender pay gap, ageism. | Accessible education, workplace diversity, community engagement. |
| Goal | Often perpetuates inequality and bias. | Promotes equality, respect, and social cohesion. |
Understanding Discrimination: Definitions and Types
Discrimination involves unfair or prejudicial treatment of individuals based on characteristics such as race, gender, age, or disability, resulting in social exclusion and inequality. Types of discrimination include direct discrimination, where explicit bias is demonstrated, and indirect discrimination, where policies or practices disadvantage certain groups unintentionally. Understanding these definitions is essential for promoting social inclusion, which aims to ensure equal access to opportunities and participation for all individuals regardless of their differences.
The Concept of Social Inclusion Explained
Social inclusion refers to the process of improving the terms of participation in society for marginalized groups by reducing barriers related to race, gender, disability, and socioeconomic status. Unlike discrimination, which excludes individuals based on prejudice or systemic inequality, social inclusion actively promotes equal access to opportunities, resources, and rights. Effective social inclusion strategies involve policies targeting education, employment, healthcare, and community engagement to foster a more equitable and cohesive society.
Historical Context: Discrimination and Inclusion
Historical context reveals systemic discrimination rooted in laws and social norms enforcing racial, gender, and class hierarchies, such as Jim Crow laws and apartheid. Social inclusion emerged as a counter-movement, promoting equality through civil rights legislation, affirmative action, and community-based initiatives. These efforts aim to dismantle structural barriers and foster diverse, equitable societies.
Key Differences Between Discrimination and Social Inclusion
Discrimination involves unfair treatment or exclusion based on characteristics such as race, gender, or religion, resulting in social inequality and marginalization. Social inclusion promotes equal access and participation in society regardless of differences, fostering diversity and equity. The key difference lies in discrimination's perpetuation of barriers, while social inclusion actively removes obstacles to ensure acceptance and belonging.
Impact of Discrimination on Individuals and Communities
Discrimination causes significant psychological distress, lowering self-esteem and increasing anxiety among individuals while restricting access to education, employment, and healthcare, which perpetuates social and economic inequalities. Communities affected by discrimination experience heightened social fragmentation, reduced social cohesion, and limited participation in civic activities, which undermines collective well-being and economic development. Addressing discrimination fosters social inclusion by promoting equal opportunities, enhancing social trust, and improving health and economic outcomes for marginalized groups.
Benefits of Social Inclusion in Society
Social inclusion fosters diversity, equity, and equal opportunities, leading to stronger social cohesion and reduced inequalities. It promotes mental well-being by combating isolation and marginalization, enhancing individual empowerment and participation. Inclusive societies drive economic growth through diverse talent utilization and innovation, creating a more resilient and prosperous community.
Legal Frameworks Addressing Discrimination
Legal frameworks addressing discrimination establish clear prohibitions against unequal treatment based on race, gender, disability, religion, or ethnicity, ensuring protection of fundamental human rights. Key international instruments such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination set standards for member states to implement anti-discrimination laws. National legislation, including the Civil Rights Act in the United States and the Equality Act in the United Kingdom, provide mechanisms for enforcing social inclusion through legal recourse and policy mandates.
Strategies for Promoting Social Inclusion
Strategies for promoting social inclusion emphasize creating equitable access to education, employment, and healthcare for marginalized groups, thereby reducing systemic discrimination. Community engagement initiatives and inclusive policy-making foster environments where diversity is valued and social barriers are dismantled. Implementing targeted awareness campaigns and anti-discrimination laws supports the integration of underrepresented populations into mainstream society.
Case Studies: Overcoming Discrimination Through Inclusion
Case studies highlight the transformative power of social inclusion in overcoming discrimination, demonstrating how inclusive policies foster equal opportunities across race, gender, and disability. Initiatives like the Scandinavian inclusive education model, which integrates children with disabilities into mainstream classrooms, show measurable improvements in social cohesion and academic success. Corporate diversity programs implemented by companies such as Microsoft reveal increased innovation and employee satisfaction when workplace inclusion actively counters discriminatory practices.
Building an Inclusive Future: Action Steps
Building an inclusive future requires implementing policies that promote equal access to education, employment, and healthcare for marginalized groups. Community-based programs fostering intercultural dialogue and empathy reduce barriers created by discrimination. Leveraging technology for accessible communication platforms enhances participation and representation in decision-making processes.
Discrimination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com