Smart growth prioritizes sustainable urban development by promoting walkable neighborhoods, efficient land use, and diverse transportation options. This approach reduces environmental impact while enhancing community livability and economic vitality. Explore how smart growth strategies can transform your city into a thriving, resilient community by reading further.
Table of Comparison
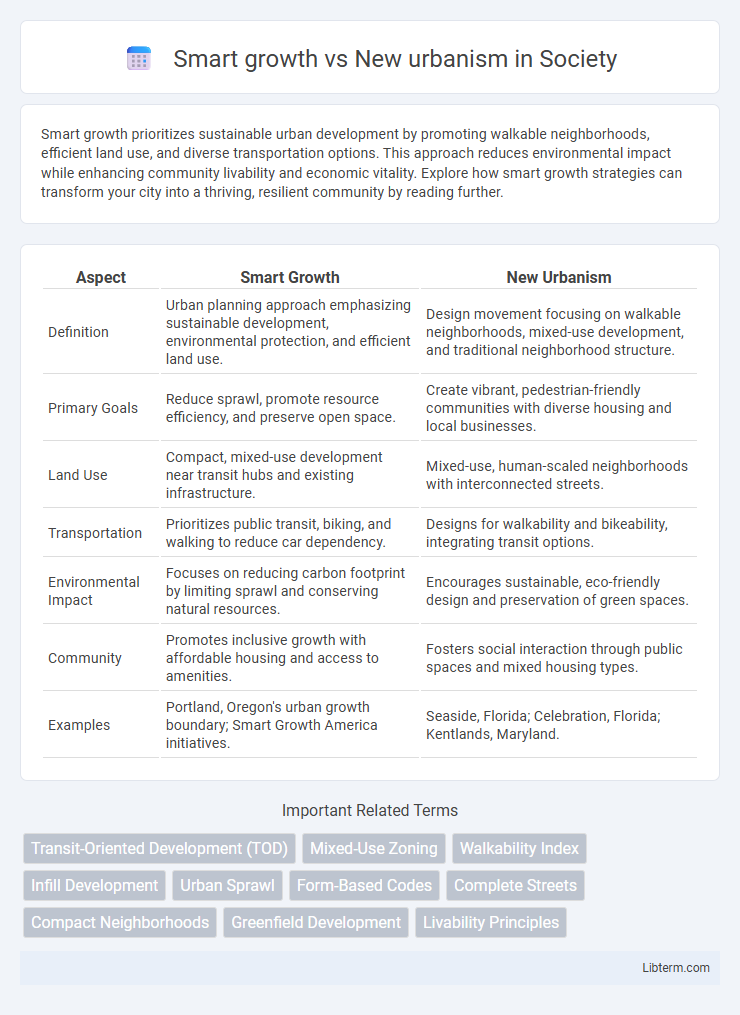
| Aspect | Smart Growth | New Urbanism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Urban planning approach emphasizing sustainable development, environmental protection, and efficient land use. | Design movement focusing on walkable neighborhoods, mixed-use development, and traditional neighborhood structure. |
| Primary Goals | Reduce sprawl, promote resource efficiency, and preserve open space. | Create vibrant, pedestrian-friendly communities with diverse housing and local businesses. |
| Land Use | Compact, mixed-use development near transit hubs and existing infrastructure. | Mixed-use, human-scaled neighborhoods with interconnected streets. |
| Transportation | Prioritizes public transit, biking, and walking to reduce car dependency. | Designs for walkability and bikeability, integrating transit options. |
| Environmental Impact | Focuses on reducing carbon footprint by limiting sprawl and conserving natural resources. | Encourages sustainable, eco-friendly design and preservation of green spaces. |
| Community | Promotes inclusive growth with affordable housing and access to amenities. | Fosters social interaction through public spaces and mixed housing types. |
| Examples | Portland, Oregon's urban growth boundary; Smart Growth America initiatives. | Seaside, Florida; Celebration, Florida; Kentlands, Maryland. |
Introduction: Defining Smart Growth and New Urbanism
Smart Growth and New Urbanism represent influential urban planning approaches aimed at sustainable development and improved community living. Smart Growth emphasizes compact, transit-oriented, and walkable neighborhoods to reduce sprawl, preserve open space, and promote environmental stewardship. New Urbanism focuses on designing traditional neighborhood structures with mixed-use development, diverse housing options, and pedestrian-friendly public spaces to foster social interaction and vibrant communities.
Historical Context and Evolution
Smart growth emerged in the late 20th century as a response to suburban sprawl, emphasizing sustainable development, efficient land use, and environmental stewardship. New urbanism, developing simultaneously in the 1980s and 1990s, focuses on designing walkable neighborhoods, mixed-use communities, and human-scale urban environments. Both movements share roots in earlier urban planning theories but diverge in their approaches, with smart growth stressing regional planning and policy reforms, while new urbanism prioritizes architectural design and community-focused layouts.
Core Principles of Smart Growth
Smart Growth emphasizes efficient land use, mixed land development, and the preservation of open space to create sustainable, walkable communities. It prioritizes compact building design, diverse transportation options, and community engagement in planning processes to reduce urban sprawl and environmental impact. Smart Growth principles foster economic development by promoting healthy neighborhoods with accessible amenities and infrastructure.
Core Principles of New Urbanism
New Urbanism emphasizes walkable neighborhoods, mixed-use development, and diverse housing options to create vibrant, community-oriented environments. Its core principles include compact, pedestrian-friendly layouts, integrated public spaces, and a strong sense of place that fosters social interaction and environmental sustainability. These design strategies contrast with the broader Smart Growth approach by focusing specifically on urban design and architectural details that enhance quality of life.
Key Differences Between Smart Growth and New Urbanism
Smart Growth emphasizes sustainable land use by promoting compact, walkable communities with mixed-use development and efficient public transit systems to reduce urban sprawl. New Urbanism prioritizes designing human-scaled neighborhoods featuring traditional architecture, connected street grids, and public spaces that foster social interaction. While both advocate walkability and environmental stewardship, Smart Growth focuses more on planning policies and regional coordination, whereas New Urbanism centers on architectural design and the physical form of communities.
Overlapping Goals and Shared Strategies
Smart growth and New Urbanism both prioritize sustainable community development, emphasizing walkability, mixed-use neighborhoods, and reduced reliance on automobiles. Their shared strategies include promoting higher density housing, preserving open spaces, and enhancing public transit accessibility to foster vibrant, livable communities. These overlapping goals aim to combat urban sprawl while supporting economic vitality and environmental stewardship.
Urban Design and Land Use Approaches
Smart growth emphasizes compact, transit-oriented development with mixed land uses to reduce sprawl and promote sustainable communities. New urbanism prioritizes walkable neighborhoods, a connected street grid, and diverse housing types to foster social interaction and human-scale urban environments. Both approaches advocate for active transportation and land preservation but differ in design details, with smart growth focusing more on policy frameworks and new urbanism on architectural aesthetics and community form.
Transportation and Mobility Considerations
Smart growth emphasizes reducing automobile dependence through mixed-use development, compact design, and enhanced public transit systems to promote walkability and transit accessibility. New urbanism prioritizes pedestrian-friendly street grids, interconnected sidewalks, and diverse transportation modes including biking and public transit to create human-scale neighborhoods. Both approaches aim to improve mobility while minimizing traffic congestion and environmental impacts by encouraging sustainable transportation options.
Environmental and Social Impact Comparison
Smart growth emphasizes reducing urban sprawl by promoting compact, transit-oriented development that minimizes environmental degradation and preserves open space. New urbanism focuses on designing walkable, mixed-use neighborhoods that enhance social cohesion and reduce reliance on automobiles, contributing to lower carbon emissions and improved public health. Both movements prioritize sustainable land use and community engagement, but smart growth is more policy-driven while new urbanism centers on architectural and neighborhood design principles.
Choosing the Right Approach for Urban Development
Smart growth emphasizes sustainable land use, efficient transportation, and preserving natural resources to foster economically viable and environmentally friendly communities. New urbanism advocates for walkable neighborhoods, mixed-use development, and human-scaled urban design that promotes social interaction and reduces car dependency. Selecting the right approach depends on local context, infrastructure needs, and community priorities to balance growth management with livability goals.
Smart growth Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com