Rapid technological advancement is transforming industries and everyday life, driving innovation and increasing efficiency. Embracing these changes can enhance your productivity and open up new opportunities for growth. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to leverage the latest technologies effectively.
Table of Comparison
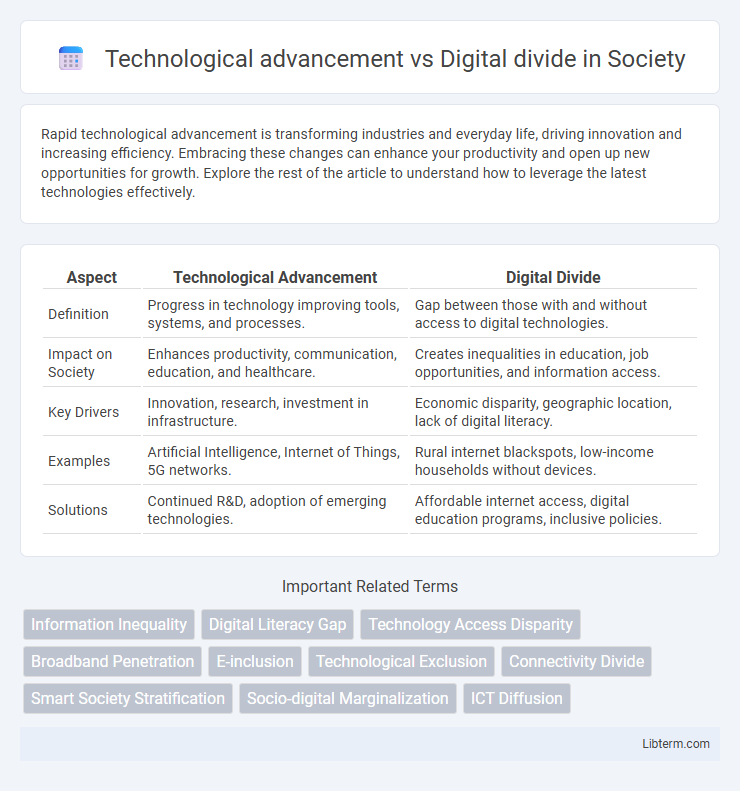
| Aspect | Technological Advancement | Digital Divide |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Progress in technology improving tools, systems, and processes. | Gap between those with and without access to digital technologies. |
| Impact on Society | Enhances productivity, communication, education, and healthcare. | Creates inequalities in education, job opportunities, and information access. |
| Key Drivers | Innovation, research, investment in infrastructure. | Economic disparity, geographic location, lack of digital literacy. |
| Examples | Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, 5G networks. | Rural internet blackspots, low-income households without devices. |
| Solutions | Continued R&D, adoption of emerging technologies. | Affordable internet access, digital education programs, inclusive policies. |
Understanding Technological Advancement
Technological advancement drives innovation across industries, enhancing productivity and enabling new services through developments in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and 5G connectivity. Understanding these advancements requires analyzing how emerging technologies improve infrastructure, access to information, and economic growth. Addressing the digital divide involves ensuring equitable distribution of technological benefits to prevent disparities in education, healthcare, and employment opportunities.
Defining the Digital Divide
The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals or communities with access to modern information and communication technologies and those without, highlighting disparities in internet connectivity, device availability, and digital literacy. Technological advancement often accelerates this divide by rapidly introducing new tools that underserved populations cannot access or afford. Bridging the digital divide requires targeted policies to improve infrastructure, affordable access, and education to ensure equitable participation in the digital economy.
Historical Context of Digital Inequality
The historical context of digital inequality reveals a persistent gap rooted in uneven access to technological advancements since the late 20th century. Early adoption of the internet and computing technologies was heavily concentrated in urban and economically developed regions, leaving rural and underserved populations marginalized. This digital divide has perpetuated disparities in education, economic opportunities, and social inclusion, highlighting the critical need for inclusive policies to bridge access gaps.
Drivers of Rapid Technological Progress
Rapid technological progress is driven by innovations in artificial intelligence, increased investment in research and development, and expanding global internet connectivity. Breakthroughs in machine learning algorithms and 5G infrastructure accelerate adoption and accessibility, yet disparities in digital literacy and infrastructure widen the digital divide. Addressing unequal access to emerging technologies remains crucial for inclusive socio-economic growth.
Impact of Technology on Socioeconomic Gaps
Technological advancements have the potential to bridge socioeconomic gaps by improving access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities through digital tools and platforms. However, the digital divide persists as marginalized communities often lack reliable internet access, digital literacy, and affordable devices, exacerbating existing inequalities. Closing this divide requires targeted policies to enhance infrastructure, promote digital skills training, and ensure equitable technology distribution across socioeconomic groups.
Barriers to Digital Access and Inclusion
Barriers to digital access and inclusion include limited infrastructure, affordability issues, and lack of digital literacy, disproportionately affecting rural and low-income communities. Technological advancements often widen the digital divide as high-speed internet, modern devices, and innovative platforms remain inaccessible to marginalized populations. Addressing these barriers requires targeted policies to improve connectivity, reduce costs, and promote digital education to ensure equitable access to technology benefits.
The Role of Governments in Bridging the Divide
Governments play a crucial role in bridging the digital divide by investing in infrastructure to expand broadband access in underserved and rural areas. They implement policies and funding programs aimed at improving digital literacy and affordability of devices, ensuring equitable access to technology for all socioeconomic groups. Public-private partnerships are often leveraged to accelerate technological advancement while addressing disparities in digital inclusion.
Education and Digital Literacy Challenges
Rapid technological advancement in education enhances learning opportunities but simultaneously widens the digital divide, disproportionately affecting students in underserved and rural areas. Limited access to devices, reliable internet, and digital literacy skills creates significant barriers to equitable education and hampers student engagement in digital classrooms. Addressing these challenges requires targeted investments in infrastructure, teacher training, and inclusive digital literacy programs to bridge gaps and promote educational equity.
Innovations Addressing Digital Inequality
Innovations addressing digital inequality include affordable internet solutions, such as low-cost smartphones and satellite broadband, which expand connectivity in remote areas. Educational platforms leveraging AI and offline capabilities deliver personalized learning experiences to underserved populations. Community-driven tech hubs and digital literacy programs empower users, bridging gaps caused by technological disparities and fostering inclusive access to digital resources.
Future Strategies for Equitable Technological Growth
Future strategies for equitable technological growth emphasize expanding affordable internet access and digital literacy programs in underserved communities. Investment in inclusive infrastructure and policy reforms targeting marginalized populations are essential to bridge the digital divide. Collaboration between governments, private sector, and non-profits can drive innovation that ensures technology benefits are universally accessible.
Technological advancement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com