Civic space refers to the environment that allows individuals and groups to freely express their opinions, assemble, and participate in public decision-making processes. Protecting and expanding civic space is essential for fostering democratic governance and promoting human rights globally. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your involvement can help safeguard and enhance civic space worldwide.
Table of Comparison
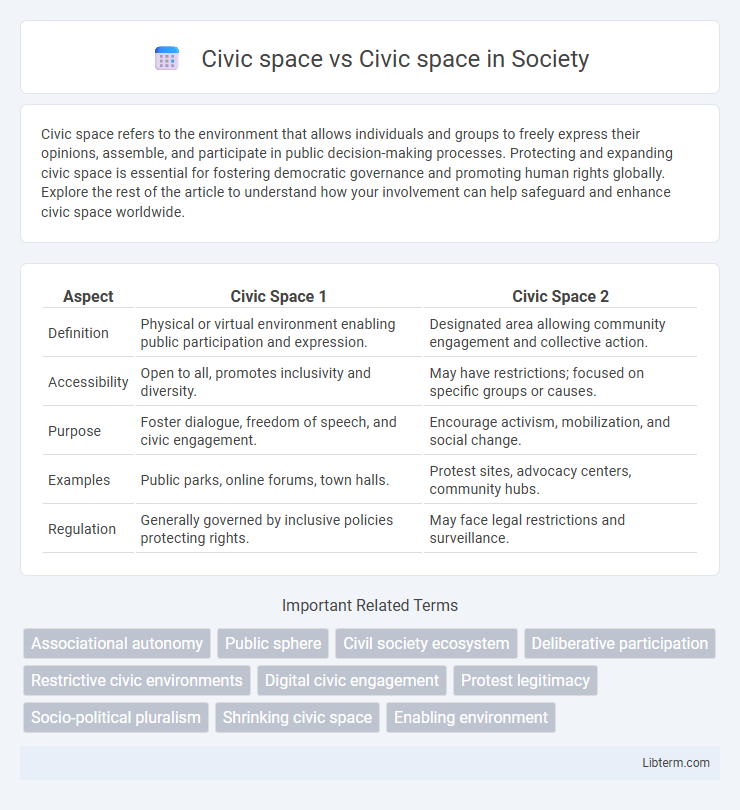
| Aspect | Civic Space 1 | Civic Space 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical or virtual environment enabling public participation and expression. | Designated area allowing community engagement and collective action. |
| Accessibility | Open to all, promotes inclusivity and diversity. | May have restrictions; focused on specific groups or causes. |
| Purpose | Foster dialogue, freedom of speech, and civic engagement. | Encourage activism, mobilization, and social change. |
| Examples | Public parks, online forums, town halls. | Protest sites, advocacy centers, community hubs. |
| Regulation | Generally governed by inclusive policies protecting rights. | May face legal restrictions and surveillance. |
Defining Civic Space: Meanings and Interpretations
Civic space refers to the environment that enables individuals and groups to participate freely in societal, political, and community activities. Definitions vary across contexts, encompassing dimensions such as freedom of expression, assembly, and association, crucial for democracy and social justice. Interpretations of civic space also include legal frameworks, cultural norms, and digital platforms that shape citizens' ability to engage and influence public affairs.
Historical Evolution of Civic Space
Civic space has evolved from ancient agoras and forums, where citizens gathered for public discourse, to modern digital platforms facilitating global participation. Historical shifts such as the Magna Carta, Enlightenment ideals, and civil rights movements have progressively expanded freedoms of assembly, expression, and association, redefining civic engagement boundaries. Contemporary civic spaces integrate both physical and virtual dimensions, reflecting ongoing struggles for inclusive governance and human rights protection.
Legal Frameworks Governing Civic Spaces
Legal frameworks governing civic spaces establish the rights and limitations for public assembly, free speech, and civic participation, shaping how citizens engage with their governments. Variations in these laws often impact the accessibility and protection of civic spaces, influencing the level of civic freedom and democratic practices. Effective legal frameworks balance public order with individual freedoms, ensuring inclusive and safe environments for civic expression.
Civic Space in Physical vs Digital Realms
Civic space in physical realms refers to public areas such as parks, plazas, and streets where citizens gather to express opinions, protest, and engage in community activities. Digital civic space consists of online platforms, social media networks, and virtual forums enabling free speech, mobilization, and civic participation across geographical boundaries. Comparing both, physical civic space offers tangible interaction and local impact, while digital civic space facilitates broader reach, real-time communication, and anonymity that can enhance or complicate democratic engagement.
Key Stakeholders in Civic Spaces
Key stakeholders in civic spaces include government institutions, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), community groups, and private sector actors who influence public participation and policy-making. Civic spaces serve as platforms for citizens to express views, advocate for rights, and engage in democratic processes, with the effectiveness of these spaces often depending on collaboration among these stakeholders. Monitoring how these groups interact and assert power is critical for ensuring an inclusive and vibrant civic environment.
Challenges and Threats to Civic Space
Civic space faces significant challenges such as government crackdowns, restrictive legislation, and surveillance that limit freedom of expression and assembly. Threats include harassment of activists, censorship, and shrinking access to funding for civil society organizations. These factors undermine democratic participation and stifle public debate essential for accountable governance.
Civic Engagement: Opportunities and Barriers
Civic engagement thrives in open civic spaces that facilitate free assembly, dialogue, and access to information, enabling citizens to participate actively in governance and community development. Barriers such as restrictive laws, surveillance, and limited digital access undermine these opportunities by stifling dissent and marginalizing vulnerable groups. Enhancing civic engagement requires safeguarding physical and digital civic spaces to promote inclusivity, transparency, and accountability.
Case Studies: Successes and Setbacks in Civic Space
Case studies in civic space reveal diverse outcomes shaped by political, social, and legal contexts, highlighting notable successes such as grassroots mobilization leading to policy reforms and enhanced public accountability. Conversely, setbacks often stem from government crackdowns, restrictive legislation, and digital surveillance that stifle freedom of assembly and expression. Analyzing these case studies underscores the dynamic interplay between civil society actors, state apparatus, and international norms influencing the resilience or erosion of civic space globally.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Civic Space
Technology transforms civic space by expanding digital platforms that facilitate public participation, enabling diverse communities to engage in governance and social activism more effectively. Online tools such as social media, digital petitions, and virtual town halls empower citizens to voice concerns, mobilize support, and hold authorities accountable in real-time. The integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics further enhances policy-making by providing insights into public opinion and improving transparency within civic processes.
The Future of Civic Space: Trends and Predictions
The future of civic space is shaped by increasing digital activism and the rise of hybrid platforms that combine online and offline engagement. Trends indicate a growing emphasis on decentralized governance models empowering local communities and enhancing participatory democracy. Predictive analyses highlight advancements in AI-driven tools facilitating real-time feedback and data-driven decision-making to strengthen transparency and accountability.
Civic space Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com