Resocialization involves the process of discarding old behaviors and norms to adopt new ones, often essential in transformative life events or institutional settings. This psychological and sociological adjustment helps individuals align with new environments or social roles effectively. Explore the article to discover how resocialization shapes your identity and facilitates personal growth.
Table of Comparison
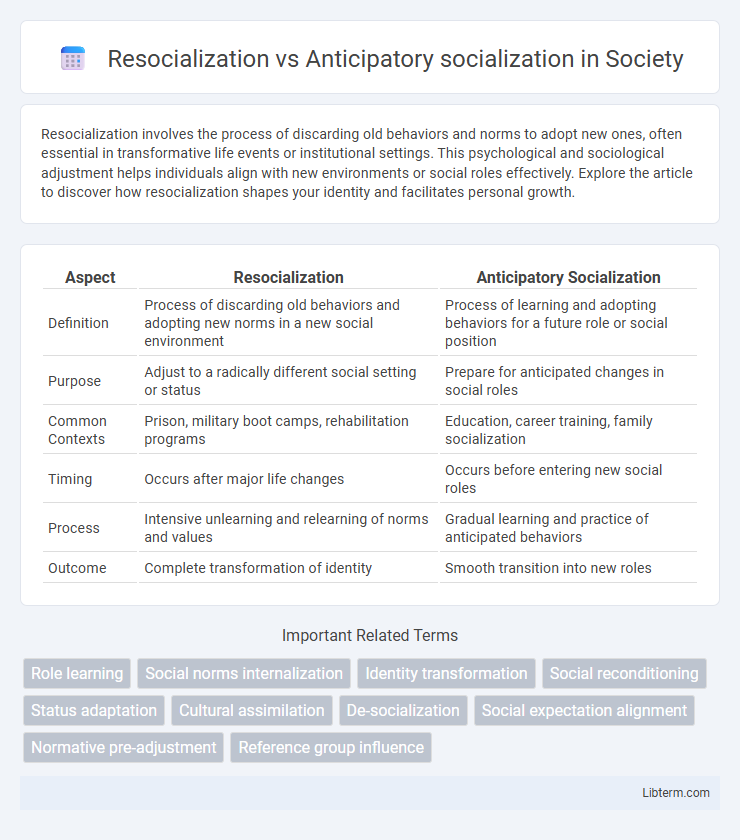
| Aspect | Resocialization | Anticipatory Socialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of discarding old behaviors and adopting new norms in a new social environment | Process of learning and adopting behaviors for a future role or social position |
| Purpose | Adjust to a radically different social setting or status | Prepare for anticipated changes in social roles |
| Common Contexts | Prison, military boot camps, rehabilitation programs | Education, career training, family socialization |
| Timing | Occurs after major life changes | Occurs before entering new social roles |
| Process | Intensive unlearning and relearning of norms and values | Gradual learning and practice of anticipated behaviors |
| Outcome | Complete transformation of identity | Smooth transition into new roles |
Understanding Socialization: Key Concepts
Resocialization involves the process of discarding previous behaviors and adopting new norms when entering a radically different environment, often seen in total institutions like prisons or military boot camps. Anticipatory socialization refers to the proactive learning of new roles and behaviors in preparation for future changes, such as teenagers adopting adult responsibilities before adulthood. Both concepts emphasize the dynamic nature of socialization in shaping identity and facilitating role adaptation across various social contexts.
Defining Resocialization
Resocialization involves the process where individuals undergo a fundamental change in their values, norms, and behaviors to adapt to a new social environment, often seen in contexts such as prison rehabilitation or military training. This process requires unlearning previous social roles and adopting new ones that align with different cultural or organizational expectations. In contrast, anticipatory socialization prepares individuals to assume future roles by learning and adopting behaviors and norms expected in those roles before they are actually experienced.
What is Anticipatory Socialization?
Anticipatory socialization is the process by which individuals adopt behaviors, values, and norms of a group they aspire to join before actually becoming members. This socialization helps prepare individuals for future roles and social settings, facilitating smoother transitions. It contrasts with resocialization, where individuals discard old behaviors and adopt new ones upon entering a new social context.
Major Differences Between Resocialization and Anticipatory Socialization
Resocialization involves discarding previous behaviors and adopting new ones to fully adapt to a new environment, often occurring in total institutions like prisons or the military. Anticipatory socialization, on the other hand, entails preparing and adopting behaviors for a future role or status before actually entering that new phase, common in career training or parenting classes. The major difference lies in timing and context: resocialization replaces old norms after a significant life change, while anticipatory socialization prepares individuals in advance.
Real-Life Examples of Resocialization
Resocialization involves the process where individuals discard old behaviors and adopt new norms to adapt to a significantly different social environment, seen in examples like military boot camps or rehabilitation centers where strict discipline and new routines reshape identity. Anticipatory socialization, by contrast, prepares individuals for future roles by learning norms and behaviors in advance, such as interns adopting professional conduct before entering full-time careers. Real-life resocialization cases, including inmates adjusting to prison culture or immigrants adapting to new countries, highlight the profound transformation required to successfully integrate into altered social settings.
Practical Examples of Anticipatory Socialization
Anticipatory socialization occurs when individuals adopt behaviors, values, and norms of a group they aspire to join, such as a student learning professional etiquette during an internship. This type of socialization helps people prepare for future roles, seen when a teenager imitates adult responsibilities in preparation for adulthood. In contrast, resocialization involves discarding past behaviors to adapt to entirely new environments, like military recruits undergoing basic training.
Psychological Impact of Resocialization
Resocialization involves a significant psychological impact as individuals undergo profound changes in beliefs, values, and behaviors, often triggered by drastic life events or institutional settings such as prisons or military training. This process challenges existing identity structures, causing stress, anxiety, and cognitive dissonance while fostering adaptation and personal growth. In contrast, anticipatory socialization psychologically prepares individuals for future roles by gradually shaping expectations and behaviors, minimizing shock and aiding smoother transitions.
Societal Influence on Anticipatory Socialization
Anticipatory socialization involves individuals adopting behaviors, values, and norms of a group they aspire to join, heavily influenced by societal expectations and cultural standards. This process allows for smoother integration by preparing individuals in advance for future social roles, often shaped by media, family, and peer groups reinforcing societal norms. In contrast, resocialization occurs when a person undergoes a complete transformation in social identity, usually triggered by entering a new and drastically different environment.
Challenges in Resocialization and Anticipatory Socialization
Resocialization involves unlearning previous behaviors and norms to adapt to a new social environment, often posing challenges such as identity conflict and psychological stress due to the abrupt nature of change. Anticipatory socialization requires individuals to prepare for future roles by adopting new norms and behaviors, but it can be hindered by inaccurate expectations and social pressure to conform prematurely. Both processes demand significant cognitive and emotional adjustment, impacting personal identity and social integration.
Importance of Socialization Processes in Modern Society
Resocialization involves discarding old behaviors and norms to adopt new roles in drastically different environments, essential for individuals undergoing significant life transitions such as imprisonment or career changes. Anticipatory socialization prepares individuals to adapt to future roles and social expectations, enhancing their ability to integrate smoothly into new social settings like starting a new job or entering parenthood. These socialization processes are crucial in modern society for fostering adaptability, social cohesion, and continuous personal development amidst rapid social and technological changes.
Resocialization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com