Simplicity enhances clarity by removing unnecessary complexity and focusing on what truly matters. Embracing simplicity can improve productivity and reduce stress in both personal and professional environments. Discover how adopting simplicity can transform your life by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
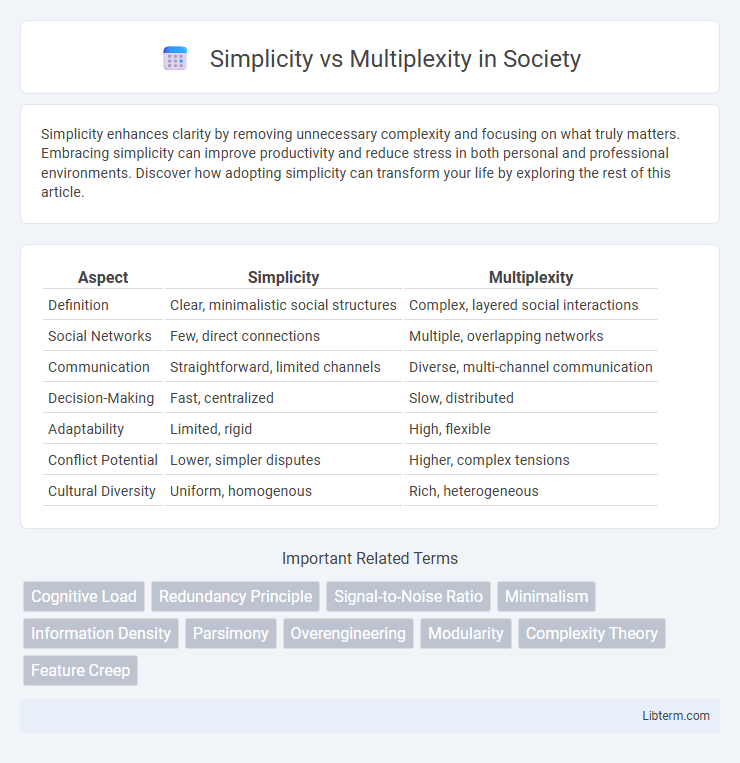
| Aspect | Simplicity | Multiplexity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clear, minimalistic social structures | Complex, layered social interactions |
| Social Networks | Few, direct connections | Multiple, overlapping networks |
| Communication | Straightforward, limited channels | Diverse, multi-channel communication |
| Decision-Making | Fast, centralized | Slow, distributed |
| Adaptability | Limited, rigid | High, flexible |
| Conflict Potential | Lower, simpler disputes | Higher, complex tensions |
| Cultural Diversity | Uniform, homogenous | Rich, heterogeneous |
Understanding Simplicity and Multiplexity
Understanding simplicity involves recognizing the clarity and ease of comprehension that comes from minimalism and straightforward design, which enhances efficiency and reduces cognitive load. Multiplexity refers to the complexity arising from multiple interconnected elements or layers, often requiring deeper analysis and multifaceted problem-solving approaches. Balancing simplicity and multiplexity is crucial in fields like communication, technology, and system design to optimize functionality and user experience.
Historical Perspectives on Complexity
Historical perspectives on complexity trace back to early scientific endeavors where simplicity was often equated with truth, exemplified by Occam's Razor advocating for minimal assumptions. The shift towards recognizing multiplexity emerged in the 20th century with the advent of systems theory and complexity science, revealing that many natural and social phenomena cannot be fully understood through simple models alone. Landmark contributions from figures like Ludwig von Bertalanffy and Edgar Morin emphasized that complex systems exhibit emergent properties, nonlinear interactions, and adaptive behaviors, challenging the primacy of simplicity in explaining reality.
The Psychological Impact of Simple vs. Complex Design
Simple design reduces cognitive load, making users feel more relaxed and focused, which enhances usability and satisfaction. Complex design increases mental effort and can lead to frustration or decision fatigue, negatively impacting user engagement and emotional response. Studies show minimalistic interfaces improve information retention and overall psychological well-being compared to cluttered, multiplex designs.
Simplicity in Communication and Information Processing
Simplicity in communication and information processing enhances clarity by reducing cognitive load and minimizing misunderstandings. Clear, concise messages facilitate faster decision-making and improve retention by focusing on essential information. Efficient information processing relies on straightforward structures that eliminate ambiguity and promote immediate comprehension.
When Multiplexity Adds Value
Multiplexity adds value when complex systems require multiple layers of interaction to enhance adaptability and resilience, such as in ecosystems, social networks, or advanced technological infrastructures. By integrating diverse elements and multifaceted relationships, multiplex structures improve problem-solving capabilities and innovation potential beyond what simple models can achieve. This complexity enables deeper insights and more robust solutions in dynamic environments where single-dimensional approaches fall short.
Case Studies: Successes of Simplicity and Multiplexity
Case studies reveal that simplicity often drives success by enhancing user experience and operational efficiency in products like Apple's iPhone, emphasizing intuitive design and streamlined functionality. Conversely, multiplexity proves advantageous in complex systems such as Google's search algorithms, where multifaceted layers and diverse data integration create robust, adaptive performance. These examples highlight that choosing between simplicity and multiplexity depends on the context and objectives of the system or product.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Complexity
Technology drives the shift from simplicity to multiplexity by enabling intricate systems and interconnected networks through advanced computing power and data analytics. Innovations like artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things increase operational complexity while enhancing efficiency and scalability. These technological advancements transform traditional simple models into multifaceted frameworks capable of addressing dynamic, real-world challenges.
Balancing Simplicity and Multiplexity in Problem-Solving
Balancing simplicity and multiplexity in problem-solving enhances solution effectiveness by integrating straightforward approaches with complex, multifaceted strategies to address various dimensions of challenges. Emphasizing minimalist design when feasible reduces cognitive load and accelerates decision-making, while incorporating layered analysis uncovers hidden variables and interdependencies essential for robust outcomes. Recognizing when to pivot between simple heuristics and complex models optimizes resource use and improves adaptability in dynamic problem-solving contexts.
Simplicity vs. Multiplexity in User Experience (UX)
Simplicity in User Experience (UX) emphasizes intuitive design, clear navigation, and minimal cognitive load to enhance user satisfaction and efficiency. Multiplexity, involving complex interfaces with multifaceted functionalities, aims to cater to diverse user needs but risks overwhelming users and increasing error rates. Balancing simplicity and multiplexity requires adaptive design strategies that prioritize essential features while offering advanced options through progressive disclosure.
Future Trends: Striving for Optimal Complexity
Future trends in system design emphasize balancing simplicity and multiplexity to achieve optimal complexity, enhancing functionality without overwhelming user experience. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning enable adaptive systems that dynamically adjust complexity based on user behavior and context. Embracing modular architectures and scalable solutions supports efficient innovation while maintaining clarity and usability in evolving technologies.
Simplicity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com