Rurality encompasses the characteristics and lifestyle of areas located outside urban centers, often marked by low population density and vast natural landscapes. These regions typically face unique challenges in infrastructure, healthcare, and education while offering a close connection to nature and community traditions. Discover how understanding rurality can enhance your perspective on regional development and social dynamics in the rest of this article.
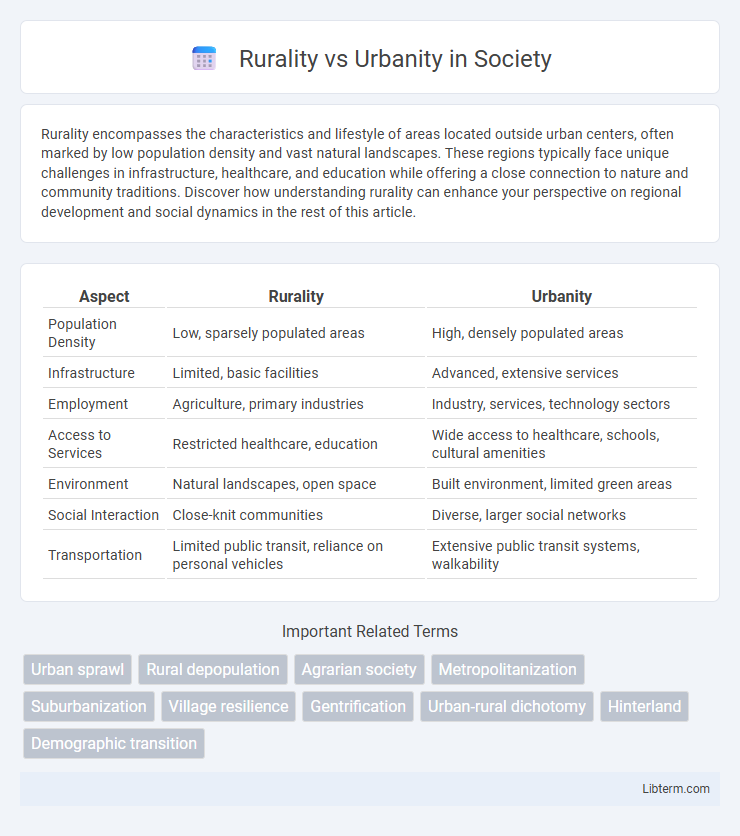
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Rurality | Urbanity |
|---|---|---|
| Population Density | Low, sparsely populated areas | High, densely populated areas |
| Infrastructure | Limited, basic facilities | Advanced, extensive services |
| Employment | Agriculture, primary industries | Industry, services, technology sectors |
| Access to Services | Restricted healthcare, education | Wide access to healthcare, schools, cultural amenities |
| Environment | Natural landscapes, open space | Built environment, limited green areas |
| Social Interaction | Close-knit communities | Diverse, larger social networks |
| Transportation | Limited public transit, reliance on personal vehicles | Extensive public transit systems, walkability |
Defining Rurality and Urbanity
Rurality is defined by low population density, expansive natural landscapes, and limited infrastructure, often characterized by agriculture-based economies and tight-knit communities. Urbanity refers to densely populated areas with advanced infrastructure, diverse economic activities, and complex social dynamics typical of cities and metropolitan zones. Key metrics for distinguishing rurality and urbanity include population thresholds, land use patterns, and availability of services such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
Historical Evolution of Rural and Urban Communities
Rural and urban communities have evolved significantly through history, shaped by agricultural advancements and industrialization. Early rural societies centered on subsistence farming and close-knit social structures, while urban areas expanded with trade, manufacturing, and technological innovation. The Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal shift, driving mass migration from rural to urban settings and altering economic, demographic, and cultural landscapes.
Demographic Differences between Rural and Urban Areas
Rural areas typically exhibit lower population densities with a higher proportion of elderly residents and lower ethnic diversity compared to urban centers, which are characterized by younger populations and greater multiculturalism. Employment sectors also differ significantly, as rural communities rely more heavily on agriculture and resource-based industries, while urban areas boast diversified economies with concentration in services, technology, and manufacturing. Educational attainment levels and access to healthcare services are generally higher in urban environments, influencing migration patterns and demographic profiles.
Economic Opportunities in Rural vs Urban Settings
Economic opportunities in urban settings typically offer greater diversity and higher income potential due to concentrated industries, advanced infrastructure, and access to global markets. Rural areas often face challenges such as limited job availability, lower wages, and dependence on agriculture or resource-based sectors, but they benefit from niche markets like agritourism and local craftsmanship. Technological advancements and improved connectivity are gradually bridging the economic gap by enabling remote work and digital entrepreneurship in rural communities.
Infrastructure and Accessibility: Rural vs Urban
Urban areas typically feature advanced infrastructure, including extensive public transportation networks, high-speed internet, and comprehensive healthcare facilities that enhance accessibility for residents. In contrast, rural regions often face challenges such as limited road connectivity, lower broadband penetration, and fewer medical centers, which restrict mobility and access to essential services. These disparities in infrastructure and accessibility significantly influence economic opportunities and quality of life between rural and urban communities.
Quality of Life: Contrasting Rural and Urban Experiences
Rural areas often offer a higher quality of life through increased access to natural environments, lower pollution levels, and stronger community ties, which contribute to enhanced mental health and well-being. Urbanity provides superior access to healthcare, education, and employment opportunities, but these advantages are frequently offset by higher stress levels, noise pollution, and overcrowded living conditions. The balance between rural tranquility and urban convenience shapes distinct lifestyle experiences, with each environment influencing physical and psychological health outcomes differently.
Education and Healthcare Disparities
Rurality often correlates with limited access to quality education and healthcare, as schools and medical facilities tend to be underfunded and geographically dispersed compared to urban centers. This disparity results in lower graduation rates and higher incidences of chronic diseases in rural populations, exacerbated by shortages of qualified teachers and healthcare professionals. Urbanity provides greater availability of specialized medical services and diverse educational programs, driving improved health outcomes and academic achievement.
Environmental Impact: Rural and Urban Perspectives
Rural areas often generate lower greenhouse gas emissions per capita due to less dense industrial activity, yet face challenges such as deforestation and biodiversity loss from agricultural expansion. Urban environments contribute significantly to air and water pollution through concentrated transportation, energy consumption, and waste production but offer opportunities for sustainable infrastructure and green technologies. Understanding the contrasting environmental impacts of rural and urban settings is essential for developing targeted policies that promote ecological balance and climate resilience.
Social Dynamics and Community Engagement
Rurality fosters close-knit social dynamics with strong community engagement driven by shared traditions and face-to-face interactions, creating robust support networks. Urbanity features diverse social dynamics where engagement often occurs through formal organizations and digital platforms, reflecting heterogeneous populations and faster-paced lifestyles. These contrasting environments shape varying community cohesion, social capital, and participation in local governance.
Future Trends: Bridging the Rural-Urban Divide
Future trends in rurality vs urbanity emphasize the integration of advanced technologies like 5G, artificial intelligence, and remote work to bridge the rural-urban divide. Investments in digital infrastructure, renewable energy, and smart agriculture drive sustainable rural development while enhancing urban connectivity. Emerging policies promote inclusive growth, reducing disparities by fostering collaboration between rural communities and urban centers.
Rurality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com