Regional nationalism emphasizes the unique cultural, linguistic, and historical identity of a specific region within a larger nation, often advocating for greater autonomy or independence. It shapes political movements and social dynamics by fostering a strong sense of belonging and pride tied closely to local traditions and governance. Explore how regional nationalism influences national policies and your community's cultural landscape in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
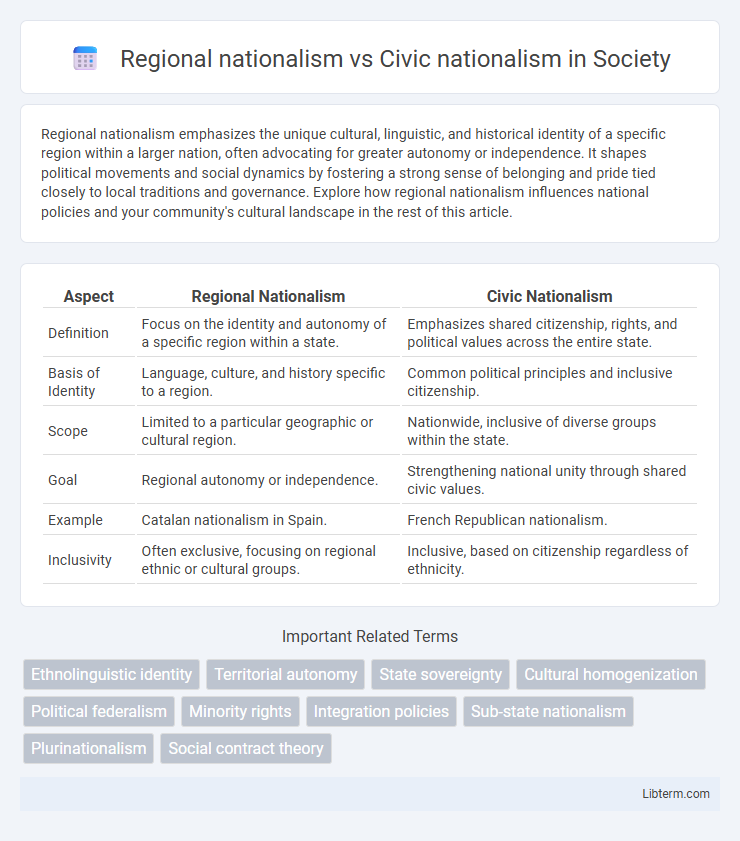
| Aspect | Regional Nationalism | Civic Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on the identity and autonomy of a specific region within a state. | Emphasizes shared citizenship, rights, and political values across the entire state. |
| Basis of Identity | Language, culture, and history specific to a region. | Common political principles and inclusive citizenship. |
| Scope | Limited to a particular geographic or cultural region. | Nationwide, inclusive of diverse groups within the state. |
| Goal | Regional autonomy or independence. | Strengthening national unity through shared civic values. |
| Example | Catalan nationalism in Spain. | French Republican nationalism. |
| Inclusivity | Often exclusive, focusing on regional ethnic or cultural groups. | Inclusive, based on citizenship regardless of ethnicity. |
Defining Regional Nationalism: Roots and Characteristics
Regional nationalism stems from distinct historical, cultural, and linguistic identities within a specific geographic area, emphasizing the preservation of local traditions and autonomy. It often arises in regions with a strong collective memory and social cohesion, seeking recognition or independence from a broader national framework. This form of nationalism contrasts with civic nationalism by prioritizing ethnic or cultural homogeneity over political or civic participation as the basis of national identity.
Civic Nationalism Explained: Principles and Frameworks
Civic nationalism is grounded in shared values, rights, and citizenship rather than ethnic or cultural identity, promoting inclusion and equal participation within a political community. It emphasizes the rule of law, democratic governance, and individual freedoms as foundational principles that unite diverse populations under common institutions. Civic nationalism frameworks prioritize allegiance to a political entity and its constitutional principles, fostering social cohesion through collective commitment rather than ethnic homogeneity.
Historical Origins: Regional vs Civic Nationalism
Regional nationalism traces its historical origins to distinct ethnic, linguistic, or cultural groups seeking political autonomy or independence within existing state boundaries, often rooted in medieval or early modern territorial identities. Civic nationalism emerges from Enlightenment and revolutionary ideals emphasizing shared citizenship, legal equality, and collective political values rather than ethnic or cultural homogeneity. Key examples include Catalan nationalism embodying regional identity and the French Revolution symbolizing the birth of civic nationalism based on universal civic rights.
Cultural Identity and Language in Regional Nationalism
Regional nationalism emphasizes the preservation and promotion of unique cultural identities and languages as core elements of its political agenda, often seeking autonomy or independence to protect these characteristics. Distinct languages and traditions serve as symbols of collective heritage, reinforcing a sense of belonging and differentiating the region from the dominant national culture. This cultural emphasis contrasts with civic nationalism, which prioritizes shared political values and citizenship over ethnic or linguistic distinctions.
Citizenship and Inclusivity in Civic Nationalism
Civic nationalism emphasizes inclusive citizenship based on shared values, legal rights, and active participation in the political community, transcending ethnic or regional identities. This form of nationalism promotes multiculturalism and equal rights for all residents regardless of their birthplace or ethnicity, fostering social cohesion and democratic engagement. In contrast, regional nationalism often prioritizes ethnic heritage, language, or historical ties specific to a region, which can limit inclusivity and citizenship access to those who identify with that particular group.
Political Movements: Regional vs Civic Nationalist Agendas
Political movements rooted in regional nationalism emphasize cultural, linguistic, or historical distinctiveness within a specific territory, often advocating for regional autonomy or independence. Civic nationalist agendas prioritize inclusive governance based on shared citizenship, values, and political rights, promoting unity through legal and institutional frameworks rather than ethnic or cultural identity. The tension between these movements shapes debates on sovereignty, identity, and state structure in diverse societies worldwide.
Economic Factors Driving Regional and Civic Nationalism
Economic disparities often fuel regional nationalism as marginalized areas seek greater autonomy to control local resources and economic policies. Civic nationalism tends to emphasize inclusive economic growth through national institutions and shared citizenship that promote equitable development across regions. Investment in infrastructure and social services frequently acts as a catalyst for civic nationalism by fostering a sense of unity and common economic purpose.
Case Studies: Regional Nationalism in Catalonia and Quebec
Regional nationalism in Catalonia and Quebec emphasizes the preservation of distinct linguistic, cultural, and historical identities within their respective states, often advocating for greater autonomy or independence. Catalonia's independence movement centers on Catalan language rights, economic self-determination, and resistance to Spanish centralism, while Quebec nationalism highlights the protection of French language and culture within Canada, promoting sovereignty to safeguard its unique identity. Both cases illustrate how regional nationalism prioritizes ethnic and cultural homogeneity, contrasting with civic nationalism's focus on inclusive citizenship and shared political values.
Civic Nationalism in Multicultural Societies
Civic nationalism in multicultural societies emphasizes inclusive citizenship based on shared political values and legal equality rather than ethnic or cultural identity, fostering social cohesion among diverse groups. This approach supports democratic principles and individual rights, encouraging participation across ethnic, religious, and cultural lines without privileging any single group. In contrast to regional nationalism, which prioritizes distinct cultural or ethnic identities tied to specific territories, civic nationalism aims to unify diverse populations under common national institutions and civic ideals.
Future Prospects: Balancing Regional and Civic National Identities
Future prospects for balancing regional nationalism and civic nationalism involve fostering inclusive political frameworks that respect regional cultural identities while promoting shared civic values and legal equality. Emphasizing dialogue and decentralization can enable regions to maintain distinct traditions without compromising national unity or democratic governance. Successful models demonstrate that integrating diverse regional aspirations within a unified civic nation-state enhances social cohesion and political stability.
Regional nationalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com