Elite performance and status often result from a combination of exceptional skill, dedication, and strategic thinking. Achieving elite levels in any field requires consistent effort and a commitment to growth and improvement. Discover how you can elevate your own abilities by exploring the insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
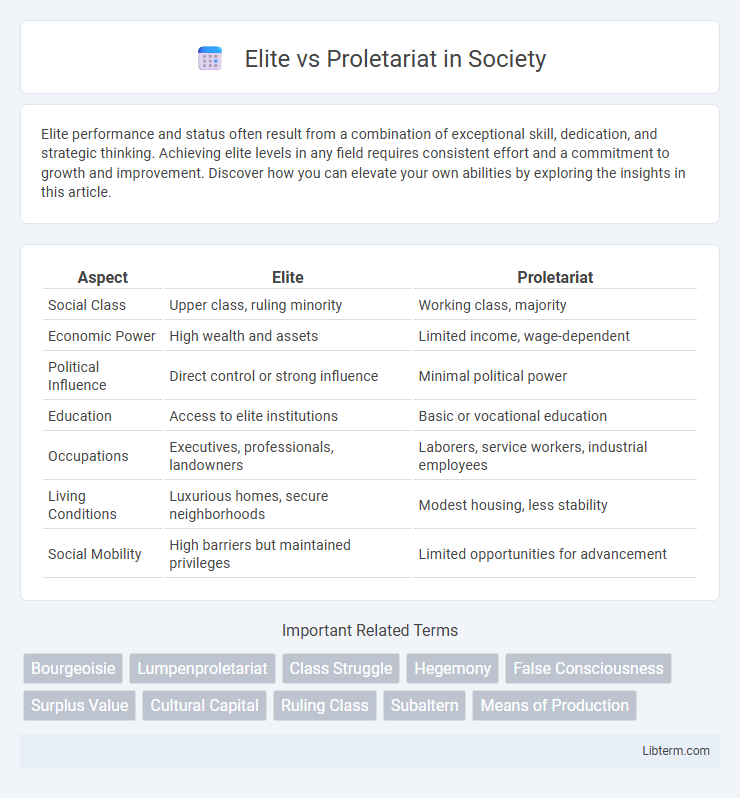
| Aspect | Elite | Proletariat |
|---|---|---|
| Social Class | Upper class, ruling minority | Working class, majority |
| Economic Power | High wealth and assets | Limited income, wage-dependent |
| Political Influence | Direct control or strong influence | Minimal political power |
| Education | Access to elite institutions | Basic or vocational education |
| Occupations | Executives, professionals, landowners | Laborers, service workers, industrial employees |
| Living Conditions | Luxurious homes, secure neighborhoods | Modest housing, less stability |
| Social Mobility | High barriers but maintained privileges | Limited opportunities for advancement |
Understanding the Elite and Proletariat Divide
The elite class controls key economic resources, political power, and cultural influence, shaping societal structures to maintain their dominance. The proletariat, consisting of working-class individuals, provides labor essential for production but lacks control over capital and decision-making. This divide creates systemic inequalities, influencing social mobility, access to education, and political representation.
Historical Roots of Class Distinctions
Class distinctions between the elite and proletariat originate from historical developments in feudal societies where landownership and hereditary privilege established ruling elites. The Industrial Revolution intensified these divisions as capitalist entrepreneurs amassed wealth while laborers faced exploitation and limited social mobility. Marxist theory further analyzed this conflict, highlighting how economic control by elites perpetuates class stratification and systemic inequality.
Power Dynamics: Who Holds Control?
The elite hold dominant power through control of wealth, political institutions, and key resources that shape societal decisions. Proletariat, despite making up the majority, largely operate under the influence and constraints imposed by elite interests. This power imbalance creates structural inequalities that maintain elite dominance and limit proletariat agency in governance and economic opportunities.
Economic Inequality: Wealth Gap Analysis
Economic inequality between the elite and proletariat manifests in a significant wealth gap, with the top 1% owning a substantial portion of global assets while the majority hold minimal financial resources. This disparity limits social mobility and concentrates economic power, reinforcing systemic barriers for the working class. Studies show that wealth accumulation among elites increases through capital gains and inheritance, whereas income stagnation restricts proletariat economic advancement.
Social Mobility: Barriers and Opportunities
Social mobility between the elite and proletariat is often constrained by systemic barriers such as unequal access to quality education, inherited wealth, and social capital limitations. Elite groups typically benefit from exclusive networks, prestigious institutions, and generational advantages that facilitate upward mobility and maintain socioeconomic status. In contrast, proletariat individuals face structural challenges including wage stagnation, limited career advancement, and institutional biases, which obstruct their ability to ascend the social hierarchy despite available opportunities.
Cultural Influence: Shaping Narratives and Values
Elite groups dominate cultural institutions, controlling media, education, and art to shape societal narratives and reinforce values that maintain their power and privilege. Proletariat culture often emerges as a form of resistance, using alternative art, music, and literature to challenge dominant ideologies and promote solidarity and social change. The dynamic between elite cultural production and proletariat counterculture significantly influences public consciousness and ideological frameworks within society.
Political Representation and Exclusion
Political representation often favors the elite class, who control key institutions and resources, enabling them to shape policy decisions to their advantage. The proletariat, by contrast, faces systematic exclusion due to limited access to political networks, financial resources, and media influence, which marginalizes their voices in democratic processes. This imbalance perpetuates social inequality and hinders the equitable distribution of power within governance structures.
Education: Access and Impact on Classes
Elite access to quality education is marked by prestigious institutions, advanced resources, and extensive networks, fundamentally reinforcing socioeconomic advantages. In contrast, the proletariat often faces limited educational opportunities, underfunded schools, and systemic barriers that hamper upward mobility. This disparity in education access perpetuates class divisions by influencing career prospects, income potential, and social capital.
Global Perspectives on Class Structures
Global perspectives on class structures reveal stark contrasts between the elite and proletariat, highlighting systemic inequalities in wealth distribution and power dynamics. In emerging economies, elites often consolidate control over resources and political influence, exacerbating disparities and limiting social mobility for the proletariat. Cross-national studies emphasize the persistence of class stratification, where elite dominance curtails opportunities for the working class, reinforcing entrenched socioeconomic hierarchies worldwide.
Bridging the Divide: Pathways to Equity
Bridging the divide between the elite and proletariat requires targeted policies that promote equitable access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Implementing progressive taxation and social safety nets can reduce income inequality and empower marginalized communities. Strengthening labor rights and fostering inclusive political participation ensures that wealth and power are more evenly distributed across society.
Elite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com