Public space serves as a vital area for community interaction, recreation, and cultural exchange, fostering social cohesion and inclusivity. Effective design and maintenance of these areas enhance urban life by providing accessible environments that encourage physical activity and social engagement. Discover how public spaces can transform your city and enrich daily experiences by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
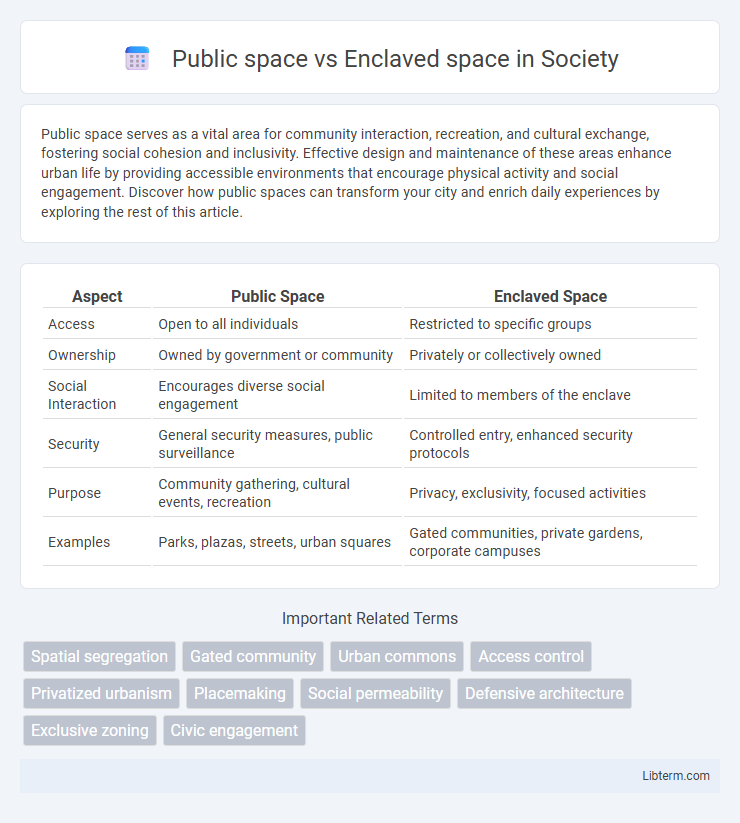
| Aspect | Public Space | Enclaved Space |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Open to all individuals | Restricted to specific groups |
| Ownership | Owned by government or community | Privately or collectively owned |
| Social Interaction | Encourages diverse social engagement | Limited to members of the enclave |
| Security | General security measures, public surveillance | Controlled entry, enhanced security protocols |
| Purpose | Community gathering, cultural events, recreation | Privacy, exclusivity, focused activities |
| Examples | Parks, plazas, streets, urban squares | Gated communities, private gardens, corporate campuses |
Defining Public Space: Concepts and Characteristics
Public space is defined by its accessibility, openness, and inclusiveness, serving as an area where people from diverse backgrounds can gather, interact, and engage in communal activities. Characteristics of public space include transparency, freedom of use, and multifunctionality, often supported by urban design elements such as parks, plazas, and streetscapes that encourage social interaction. In contrast to enclaved space, which is restricted and privately controlled, public space promotes democratic values and social cohesion through its universal availability and lack of physical or social barriers.
Understanding Enclaved Spaces: Private and Exclusive Realms
Enclaved spaces are defined by their private, controlled access, often enclosed physically or symbolically to restrict public entry and maintain exclusivity. These spaces prioritize security, privacy, and identity, serving residential gated communities, corporate campuses, or exclusive clubs that separate inhabitants from broader public interaction. Understanding enclaved spaces involves analyzing their role in urban fragmentation, social segregation, and the implications for accessibility and community cohesion within the larger public spatial network.
Historical Evolution of Urban Spaces
Urban spaces have evolved from open, accessible public squares in ancient cities like Rome and Athens to increasingly segmented and privatized enclaved spaces in modern metropolises. The rise of industrialization and urban planning in the 19th and 20th centuries contributed to the fragmentation of public space through gated communities, shopping malls, and corporate plazas. This historical shift reflects changing social dynamics, economic factors, and governance models influencing spatial accessibility and community interaction in contemporary cities.
Accessibility and Inclusion in Public vs Enclaved Spaces
Public spaces prioritize universal accessibility and inclusion, offering open environments where diverse social interactions and activities can occur without barriers. Enclaved spaces, often characterized by restricted access and controlled entry, limit inclusivity by regulating who can enter and participate in the area. The design and management of public spaces emphasize equitable access for all community members, while enclaved spaces tend to create exclusivity, impacting social cohesion and diversity.
Social Interaction and Community Building
Public spaces encourage social interaction by providing open, accessible areas where diverse groups can gather, fostering inclusivity and spontaneous connections essential for community building. Enclaved spaces offer controlled environments that promote focused interactions among specific groups, enhancing trust and deeper relationships but potentially limiting broader social integration. Balancing both types of spaces is crucial for cultivating a vibrant social fabric, allowing communities to thrive through varied forms of engagement.
Security, Surveillance, and Control
Public spaces often incorporate surveillance technologies such as CCTV cameras and increased police presence to enhance security and deter criminal activities. Enclaved spaces, in contrast, utilize controlled access points, physical barriers, and private security measures to restrict entry and maintain exclusive control. The balance between safety and privacy varies, with public spaces prioritizing openness and visibility, while enclaved spaces emphasize exclusion and monitored environments.
Economic Implications and Land Use
Public spaces enhance urban economic vitality by attracting diverse businesses, increasing foot traffic, and boosting local commerce, while enclaved spaces often limit economic opportunities due to restricted access and reduced customer flow. Efficient land use in public spaces promotes mixed-use developments and communal activities, driving higher property values and sustainable urban growth; enclaved spaces typically result in underutilized land and segregated economic zones. The contrast between open accessibility in public spaces and exclusivity in enclaved spaces influences urban economic integration, impacting investment patterns and long-term land value appreciation.
Aesthetic and Cultural Significance
Public spaces serve as dynamic platforms for communal interaction, showcasing diverse cultural expressions through street art, performances, and architectural design, enhancing urban aesthetics and fostering cultural identity. Enclaved spaces, often characterized by restricted access and homogeneous design, prioritize privacy and exclusivity, which can limit cultural exchange but create distinct aesthetic environments reflective of specific community values. The juxtaposition of open, inclusive public areas with secluded enclaved spaces highlights the varied cultural narratives and aesthetic priorities embedded in urban planning.
Legal Frameworks and Governance
Legal frameworks governing public spaces establish rights of access and use, often emphasizing inclusivity and collective ownership enforced by municipal or state authorities. Enclaved spaces, in contrast, operate under private property laws that restrict access, with governance mechanisms tailored to preserve exclusivity through homeowners' associations or private security. Regulatory distinctions influence urban planning, shaping how public space policies balance community engagement against privatized control within cities.
Future Trends in Urban Space Development
Future trends in urban space development emphasize the integration of public spaces that promote inclusivity, accessibility, and community engagement, contrasting with the increasing prevalence of enclaved spaces that prioritize exclusivity and private control. Smart city technologies and sustainable design principles are driving the transformation of open public areas into multifunctional hubs that support social interaction and environmental resilience. Urban planners are leveraging data analytics and participatory design to balance public access with security, addressing the challenges posed by enclaved developments while fostering vibrant, connected urban environments.
Public space Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com