Cultural preservation safeguards the unique traditions, languages, and heritage of communities, ensuring they are passed down to future generations. It strengthens community identity and promotes diversity in an increasingly globalized world. Explore the rest of this article to discover how you can contribute to preserving cultural heritage.
Table of Comparison
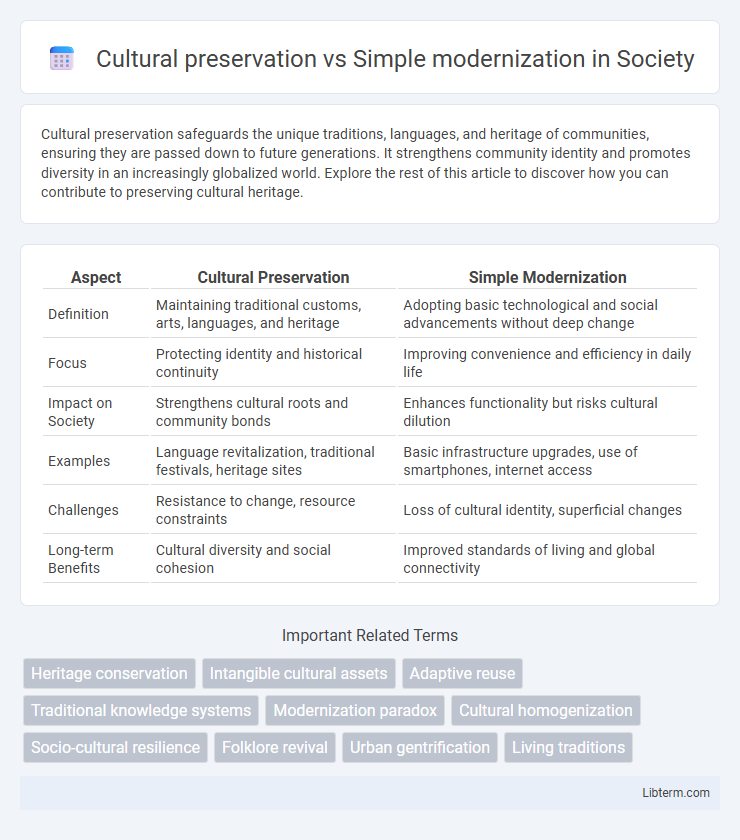
| Aspect | Cultural Preservation | Simple Modernization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintaining traditional customs, arts, languages, and heritage | Adopting basic technological and social advancements without deep change |
| Focus | Protecting identity and historical continuity | Improving convenience and efficiency in daily life |
| Impact on Society | Strengthens cultural roots and community bonds | Enhances functionality but risks cultural dilution |
| Examples | Language revitalization, traditional festivals, heritage sites | Basic infrastructure upgrades, use of smartphones, internet access |
| Challenges | Resistance to change, resource constraints | Loss of cultural identity, superficial changes |
| Long-term Benefits | Cultural diversity and social cohesion | Improved standards of living and global connectivity |
Introduction to Cultural Preservation and Modernization
Cultural preservation involves safeguarding traditions, languages, and heritage to maintain societal identity and historical continuity. Modernization emphasizes adopting new technologies, infrastructure, and social systems to improve economic growth and quality of life. Balancing cultural heritage with progressive development is essential for sustainable and inclusive societal advancement.
Defining Cultural Preservation: Importance and Scope
Cultural preservation involves safeguarding traditions, languages, arts, and heritage to maintain a community's identity amidst rapid modernization. Emphasizing intangible and tangible cultural assets ensures that future generations inherit authentic narratives and practices, enhancing social cohesion and diversity. This process balances respect for historical legacies while navigating technological and infrastructural development pressures.
The Drive for Simple Modernization
The drive for simple modernization prioritizes technological advancements and infrastructure development to boost economic growth and improve living standards. It often emphasizes efficiency, uniformity, and global integration, sometimes at the expense of cultural heritage and traditional practices. This approach can lead to the erosion of local identities, as modernization efforts favor standardized solutions over culturally sensitive adaptations.
Tensions Between Tradition and Progress
Cultural preservation emphasizes safeguarding historical customs, languages, and art forms to maintain a community's identity, while simple modernization prioritizes technological advancements and economic growth. The tension between tradition and progress arises as modernization risks eroding ancestral heritage, causing social fragmentation or loss of cultural diversity. Balancing these forces requires integrative policies that support innovation while respecting ritualistic practices and indigenous knowledge systems.
Societal Benefits of Preserving Culture
Preserving cultural heritage fosters social cohesion by strengthening community identity and transmitting traditional knowledge across generations. It supports sustainable tourism, creating economic opportunities while maintaining unique cultural landscapes and practices. Emphasizing cultural preservation encourages diversity and inclusivity, enriching societal values and promoting intercultural understanding in rapidly modernizing environments.
Challenges Faced in Modernizing Traditional Societies
Modernizing traditional societies encounters challenges such as resistance to change due to deep-rooted cultural beliefs and practices, risking the loss of unique heritage and identity. Economic disparities and lack of technological infrastructure hinder equitable access to modernization benefits, creating social divides. Balancing the integration of innovations with respect for customs requires inclusive policies that engage local communities in decision-making processes.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Balancing Both
Case studies such as Kyoto, Japan, and Charleston, South Carolina, illustrate successful integration of cultural preservation with modern development by maintaining historic architecture while incorporating contemporary infrastructure. In Kyoto, adaptive reuse projects enable the city to retain its traditional wooden machiya houses alongside modern amenities, fostering tourism and local engagement. Charleston balances strict zoning laws and preservation commissions with urban growth, demonstrating how regulatory frameworks can support cultural heritage in evolving cities.
Cultural Identity in a Modernizing World
Cultural identity faces challenges in a modernizing world as rapid urbanization and globalization introduce new values and lifestyles that can erode traditional customs and languages. Preserving cultural heritage through education, local arts, and community engagement strengthens societal roots and fosters a sense of belonging amid change. Balancing modernization with cultural preservation enables societies to innovate while maintaining unique historical and social narratives integral to their identity.
Policy Approaches for Harmonizing Preservation and Modernization
Policy approaches for harmonizing cultural preservation and modernization emphasize integrating heritage conservation within urban development frameworks to maintain historical identity while supporting economic growth. Strategies include adaptive reuse of historic buildings, incentivizing traditional craftsmanship through grants, and implementing regulatory zoning that safeguards cultural landmarks alongside infrastructural upgrades. Collaborative governance involving local communities, heritage experts, and urban planners ensures balanced decision-making that respects cultural significance without hindering technological advancement.
Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Balancing cultural preservation with simple modernization requires integrating traditional values into contemporary development to maintain identity while promoting progress. Emphasizing adaptive reuse of heritage sites and incorporating cultural narratives in urban planning ensures sustainable growth that respects historical significance. Future perspectives highlight the need for collaborative policies that empower communities to safeguard intangible cultural assets amid technological advancements and globalization.
Cultural preservation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com