Social exile involves the intentional or forced removal of an individual from their community, leading to feelings of isolation and disconnection. This phenomenon can significantly impact mental health, causing loneliness, anxiety, and depression. Explore the rest of this article to understand the causes, effects, and ways to cope with social exile.
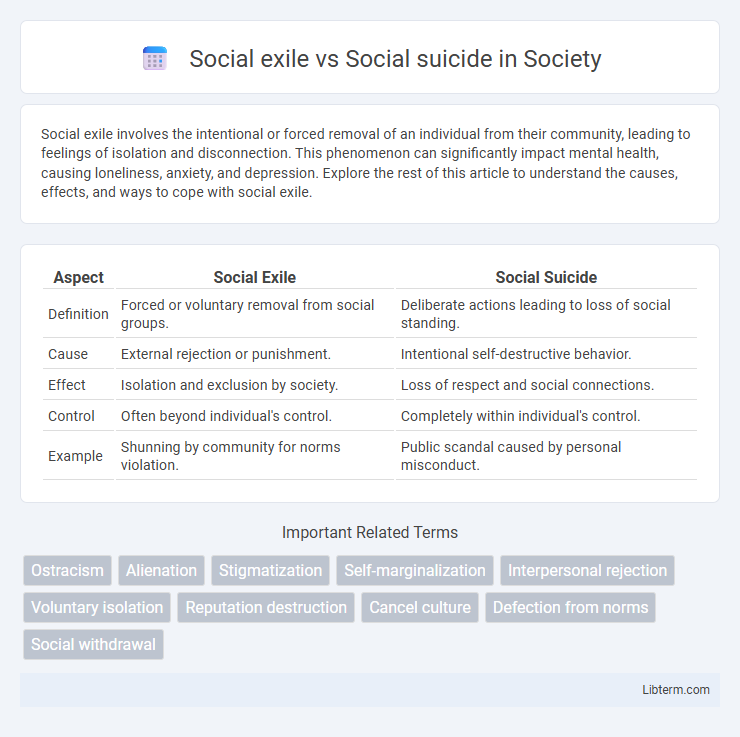
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Exile | Social Suicide |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Forced or voluntary removal from social groups. | Deliberate actions leading to loss of social standing. |
| Cause | External rejection or punishment. | Intentional self-destructive behavior. |
| Effect | Isolation and exclusion by society. | Loss of respect and social connections. |
| Control | Often beyond individual's control. | Completely within individual's control. |
| Example | Shunning by community for norms violation. | Public scandal caused by personal misconduct. |
Understanding Social Exile and Social Suicide
Social exile refers to the involuntary or voluntary removal from social interactions, resulting in isolation and loss of community support, often affecting mental health and social identity. Social suicide involves actions or behaviors that lead an individual to lose social standing or acceptance deliberately, such as public self-sabotage or controversial choices causing rejection. Understanding the distinction between social exile and social suicide is crucial for addressing issues of isolation, stigma, and personal agency in social dynamics.
Defining Social Exile: Key Characteristics
Social exile is characterized by involuntary or voluntary isolation from a community, often involving exclusion, rejection, or abandonment by social groups. Key characteristics include diminished social interactions, loss of support networks, and a persistent sense of loneliness or detachment. This contrasts with social suicide, where individuals deliberately sever social ties, often as a form of self-imposed isolation with varying psychological motivations.
Social Suicide: What Does It Really Mean?
Social suicide refers to actions or behaviors that intentionally or unintentionally lead to severe social rejection or isolation, often damaging personal relationships and reputation beyond repair. This concept involves decisions such as public confessions, controversial statements, or betrayals that cause an individual to lose trust and respect within their community or social circle. Unlike social exile, which may be imposed externally, social suicide stems from one's own choices that result in voluntary or involuntary withdrawal from social acceptance.
Causes Behind Social Exile and Social Suicide
Social exile often results from external factors such as community rejection, stigmatization, or systemic discrimination, causing individuals to face involuntary isolation. Social suicide, in contrast, stems from internal decisions driven by psychological struggles, feelings of hopelessness, or deliberate withdrawal to escape social pressures. Understanding the underlying causes--external exclusion for social exile versus internal despair for social suicide--is crucial for targeted intervention and support.
Psychological Impact of Social Exile
Social exile inflicts profound psychological impacts, including heightened feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression, often leading to diminished self-worth and social identity confusion. This voluntary or imposed isolation disrupts neural pathways linked to social interaction, exacerbating emotional distress and increasing the risk of long-term mental health disorders. Unlike social suicide, which entails actively severing social ties, social exile imposes involuntary social withdrawal, amplifying trauma and hindering recovery from social and emotional deficits.
Emotional Consequences of Social Suicide
Social suicide, unlike social exile, involves a conscious choice to sever ties with one's community, leading to profound emotional consequences such as intense loneliness, depression, and diminished self-worth. The deliberate rejection amplifies feelings of isolation and can result in long-term psychological distress, contrasting with social exile, where disconnection is imposed externally. Understanding these emotional impacts is crucial for mental health interventions targeting individuals experiencing self-imposed social withdrawal.
Social Exile vs Social Suicide: Core Differences
Social exile involves being forcibly removed or isolated from a community, resulting in physical or emotional separation from society, while social suicide is a deliberate act of self-isolation driven by personal decisions to withdraw from social interactions. The core difference lies in agency; social exile is imposed externally, whereas social suicide originates internally through conscious choice. Both impact mental health but differ fundamentally in their causes and implications for social identity.
Coping Mechanisms and Recovery Strategies
Social exile often leads to feelings of isolation and abandonment, requiring coping mechanisms such as building new social networks, engaging in therapy, and practicing mindfulness to restore mental well-being. In contrast, social suicide involves self-imposed withdrawal due to guilt or shame, where recovery strategies emphasize self-compassion, cognitive-behavioral techniques, and gradual reintegration into trusted environments. Both conditions benefit from consistent support systems, resilience training, and addressing underlying emotional traumas to facilitate long-term social recovery.
Real-Life Examples: Stories of Social Exile and Social Suicide
Real-life examples of social exile include Nelson Mandela's imprisonment, where he was physically and socially isolated but maintained a legacy of resilience and eventual reintegration. Social suicide is illustrated by public figures like Anthony Bourdain, whose career successes were overshadowed by personal struggles leading to self-destructive choices that caused social and professional estrangement. These cases highlight the stark difference between enforced isolation and voluntary self-destruction within societal contexts.
Prevention and Support: Building Inclusive Communities
Preventing social exile and social suicide requires fostering inclusive communities that prioritize mental health awareness and empathetic support networks. Implementing peer support programs, accessible counseling services, and community engagement initiatives strengthens social bonds and reduces feelings of isolation. Encouraging open dialogue around mental health challenges and promoting acceptance helps individuals feel valued and connected, mitigating risks.
Social exile Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com