Dominant class location refers to the geographic area where economic and political power is concentrated, often shaping social hierarchies and resources distribution. This location influences access to opportunities, housing, and public services, reinforcing systemic inequalities between social classes. Explore the article further to understand how dominant class location impacts your community and societal dynamics.
Table of Comparison
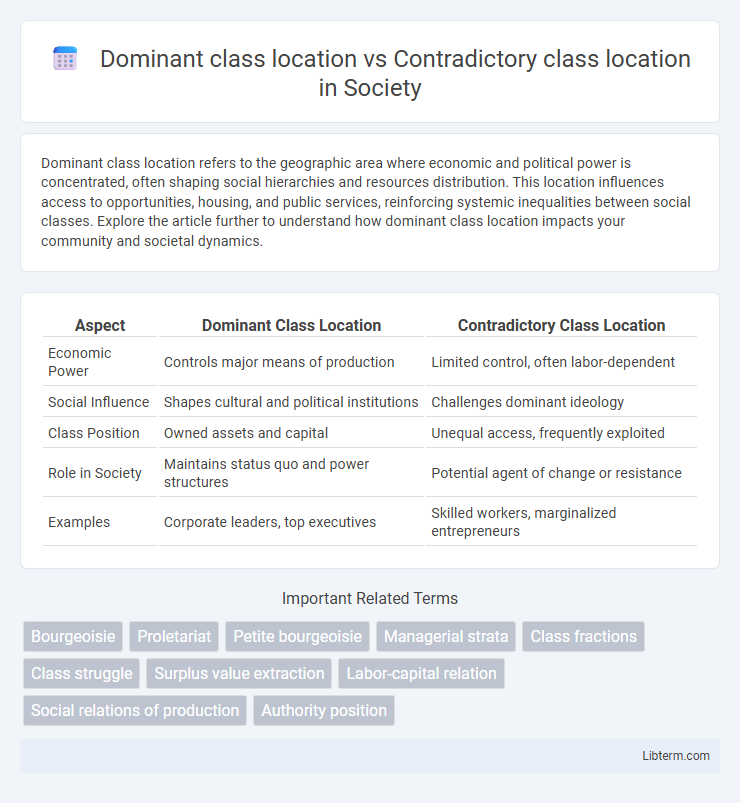
| Aspect | Dominant Class Location | Contradictory Class Location |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Power | Controls major means of production | Limited control, often labor-dependent |
| Social Influence | Shapes cultural and political institutions | Challenges dominant ideology |
| Class Position | Owned assets and capital | Unequal access, frequently exploited |
| Role in Society | Maintains status quo and power structures | Potential agent of change or resistance |
| Examples | Corporate leaders, top executives | Skilled workers, marginalized entrepreneurs |
Understanding Class Locations: Dominant vs Contradictory
Dominant class locations refer to social positions that align with the ruling class interests, typically involving control over capital, institutional power, and cultural influence. Contradictory class locations exist between the dominant and subordinate classes, where individuals or groups experience conflicting interests, such as managers who navigate both labor and capital roles. Understanding these class locations is crucial for analyzing social dynamics, power relations, and class struggles within capitalist societies.
Defining Dominant Class Location
Dominant class location refers to the social and economic position occupied by the ruling or elite class, which controls the means of production and holds significant influence over societal institutions. This location is characterized by ownership and power that shape societal norms, policies, and resource distribution. In contrast, contradictory class locations exist between dominant and subordinate classes, where individuals or groups experience conflicting interests and mixed economic or social positions.
Exploring Contradictory Class Location
Contradictory class location refers to social positions that embody conflicting interests and roles within the economic structure, such as middle managers who simultaneously align with both capital owners and the working class. Exploring contradictory class locations reveals the complexity of class dynamics, challenging traditional binary class models by highlighting how individuals navigate multiple class influences in contemporary labor markets. Understanding these nuanced positions aids in analyzing power relations, workplace authority, and the fragmentation of class solidarity in capitalist societies.
Key Differences Between Dominant and Contradictory Class Locations
Dominant class location refers to the social position that holds the most economic power and control over resources, typically associated with the ruling or capitalist class, while contradictory class location signifies a position that straddles conflicting interests between classes, such as middle managers or small business owners. Key differences include the degree of access to means of production, with dominant classes owning the majority of capital, contrasted by contradictory classes whose roles involve both labor and some control, creating ambivalent class interests. These distinctions impact class consciousness and potential alliances in socio-economic struggles, influencing dynamics in class theory and labor relations.
Historical Development of Class Location Theory
The historical development of class location theory traces back to Karl Marx, who emphasized the dominant class location as those owning the means of production, defining economic power and social status. Contradictory class locations emerged through later scholars like Erik Olin Wright, highlighting groups occupying intermediate positions with conflicting interests between capital and labor. This nuanced analysis advanced class theory by identifying complex social relations and power dynamics beyond a simple binary of owners and workers.
Influential Theorists: Marx, Wright, and Others
Karl Marx's theory centers on the dominant class location in capitalism, emphasizing the bourgeoisie's control over production means, which shapes societal power dynamics. Erik Olin Wright expands this framework by identifying contradictory class locations, highlighting positions such as managers who experience both capitalist authority and worker subordination. Other theorists extend these concepts to contemporary labor structures, illustrating complexity in class relations beyond traditional capitalist-worker dichotomies.
Social Implications of Class Location Categories
Dominant class location refers to the social position holding significant economic power and influence, often linked to elite control over resources and decision-making, which sustains systemic privileges and reinforces social hierarchies. Contradictory class location embodies individuals or groups navigating conflicting class interests, such as managers who share traits of both working and capitalist classes, creating ambiguous social roles and tensions in class solidarity. These class location categories shape social implications by influencing access to opportunities, social mobility, and the dynamics of power, conflict, and identity within socio-economic structures.
Economic Power and Authority in Dominant Class Locations
Dominant class locations wield significant economic power through control of capital, enterprise ownership, and influence over financial markets, which ensures their ability to shape production and wealth distribution. Authority in these positions stems from strategic roles in corporate hierarchies, government policymaking, and institutional governance, reinforcing their capacity to maintain and expand socioeconomic advantages. In contrast, contradictory class locations experience both subordination and authority, often serving as intermediaries but lacking the comprehensive control characteristic of dominant class locations.
Ambiguity and Conflicts in Contradictory Class Locations
Contradictory class locations create ambiguity and conflicts as individuals experience simultaneously opposing class interests, complicating their social roles and economic decisions. This dual positioning generates tension between aligning with dominant class norms and advocating for subordinate group interests, resulting in fluctuating class consciousness. The ambiguity inherent in contradictory class locations challenges clear class identification and often leads to conflicts in political and social behavior.
Relevance of Class Location Concepts in Contemporary Society
Dominant class location refers to social groups that hold significant economic, political, and cultural power, shaping societal norms and resource distribution, while contradictory class location describes groups occupying intermediary positions with conflicting interests, such as managers aligning with both working and owning classes. Understanding these class positions is crucial for analyzing social stratification and power dynamics in contemporary society, as they reveal nuanced class relations beyond simple binary classifications. The relevance of these concepts lies in explaining complex labor markets, social mobility, and ideological conflicts in modern capitalist economies.
Dominant class location Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com