Active nonconformity involves deliberately challenging societal norms and expectations through actions that express individuality and resist conformity. This approach empowers you to assert your identity and encourage change by questioning established rules and behaviors. Discover how embracing active nonconformity can transform your perspective and lifestyle in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
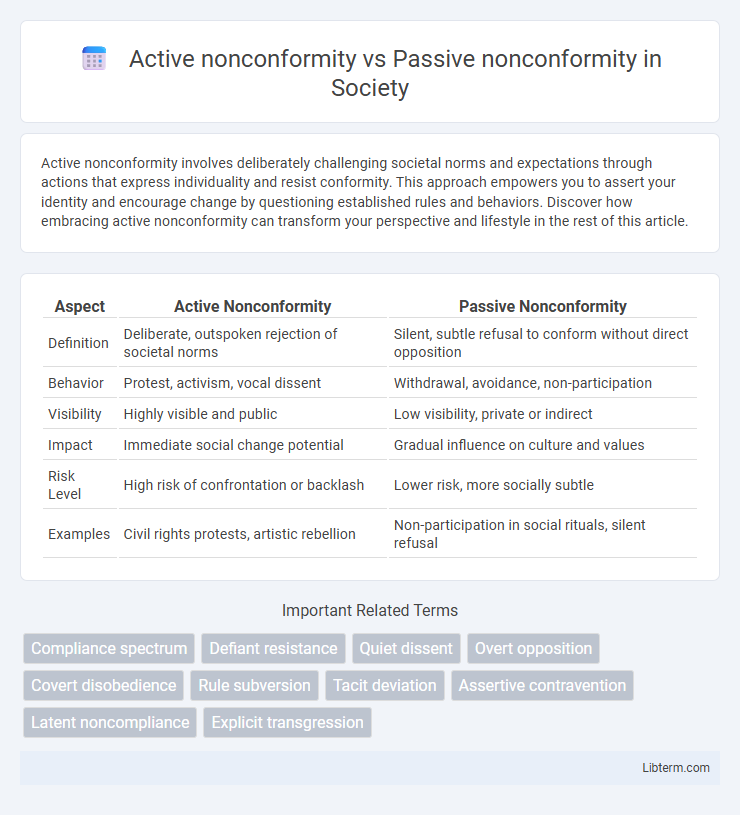
| Aspect | Active Nonconformity | Passive Nonconformity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate, outspoken rejection of societal norms | Silent, subtle refusal to conform without direct opposition |
| Behavior | Protest, activism, vocal dissent | Withdrawal, avoidance, non-participation |
| Visibility | Highly visible and public | Low visibility, private or indirect |
| Impact | Immediate social change potential | Gradual influence on culture and values |
| Risk Level | High risk of confrontation or backlash | Lower risk, more socially subtle |
| Examples | Civil rights protests, artistic rebellion | Non-participation in social rituals, silent refusal |
Understanding Nonconformity: Definitions and Differences
Active nonconformity involves deliberate and overt resistance against established norms or rules, often characterized by outspoken or visible actions. Passive nonconformity, by contrast, entails subtle or indirect defiance, such as ignoring or silently rejecting expectations without explicit confrontation. Understanding these differences highlights how individuals navigate social pressures through either explicit rebellion or quiet dissent, impacting social dynamics and personal identity expression.
The Roots of Active Nonconformity
Active nonconformity stems from deliberate resistance to societal norms through overt actions such as protests, civil disobedience, or vocal opposition, reflecting a conscious effort to challenge and reshape existing systems. Rooted in strong personal conviction and a desire for change, its origins often trace back to critical awareness of injustice and moral disagreement with prevailing standards. This form contrasts with passive nonconformity, where individuals quietly reject conventions by non-participation or subtle dissent without public confrontation.
Exploring Passive Nonconformity
Passive nonconformity involves subtle resistance through omission, avoidance, or silent dissent rather than direct confrontation or overt rebellion. It manifests in behaviors such as deliberately ignoring rules, withholding participation, or quietly rejecting norms without explicit opposition. Exploring passive nonconformity reveals its strategic role in undermining authority while minimizing personal risk in hierarchical or authoritarian environments.
Psychological Motivations Behind Active Nonconformity
Active nonconformity stems from psychological motivations such as the desire for autonomy, assertiveness, and identity expression, driving individuals to consciously challenge societal norms and expectations. It involves deliberate actions and vocal opposition aimed at differentiating oneself and asserting control over personal choices. This behavior contrasts passive nonconformity, which is characterized by subtle, non-disruptive resistance rooted in avoidance or internal disagreement rather than explicit confrontation.
The Social Dynamics of Passive Nonconformity
Passive nonconformity involves subtle, indirect resistance to social norms, often through inaction or minimal compliance rather than overt defiance. This form of nonconformity influences social dynamics by creating ambiguity in group expectations, enabling individuals to express dissent without provoking direct confrontation. Social psychologists highlight that passive nonconformity can undermine authority and prompt gradual social change by collectively signaling dissatisfaction through symbolic gestures and nonverbal cues.
Real-World Examples: Active vs Passive Nonconformists
Active nonconformity is demonstrated by figures like Martin Luther King Jr., who openly challenged segregation laws through protests and speeches, while passive nonconformity is exemplified by those who quietly resist social norms, such as conscientious objectors during wartime refusing to fight without engaging in public demonstrations. In the tech industry, active nonconformists like Elon Musk disrupt markets by launching innovative products aggressively, whereas passive nonconformists might reject mainstream technology subtly by adopting alternative open-source solutions without public campaigns. These examples highlight how active nonconformists engage directly and visibly in change, while passive nonconformists influence through discreet, personal choices.
Impacts on Group Behavior and Social Change
Active nonconformity involves deliberate, visible actions challenging group norms, which can stimulate social change by provoking discussion and encouraging others to reconsider established behaviors. Passive nonconformity, characterized by silent resistance or withdrawal, subtly undermines group cohesion without direct confrontation, often leading to gradual shifts in attitudes over time. Both forms influence group behavior differently: active nonconformity tends to trigger immediate reactions and potential conflict, while passive nonconformity fosters long-term transformation through persistence and non-engagement.
Risks and Rewards: Choosing Active or Passive Nonconformity
Active nonconformity involves openly challenging norms and can lead to significant rewards such as innovation and social change but carries higher risks like social ostracism and professional setbacks. Passive nonconformity, characterized by subtle resistance or non-participation, minimizes conflict and maintains social harmony yet often limits impact and recognition. Choosing between active and passive nonconformity requires weighing the potential for transformative outcomes against the likelihood of personal or professional risk.
Navigating Nonconformity in the Workplace and Society
Active nonconformity involves openly challenging established norms and practices, often leading to innovation and social change by questioning authority and advocating for new ideas. Passive nonconformity, by contrast, manifests as subtle resistance or disengagement, such as quietly ignoring rules or avoiding participation without direct confrontation. Navigating nonconformity in the workplace and society requires understanding the impact of both approaches on collaboration, culture, and progress, balancing assertive change with strategic diplomacy to foster inclusive environments.
Fostering Healthy Nonconformity for Growth and Innovation
Active nonconformity entails deliberate actions challenging established norms to drive innovation and transformational growth, while passive nonconformity involves subtle resistance or non-compliance that may hinder progress. Fostering healthy nonconformity requires cultivating an organizational culture that encourages critical thinking, open dialogue, and risk-taking without fear of reprisal. Companies like Google and 3M demonstrate that empowering employees to voice divergent ideas actively promotes creative problem-solving and sustainable competitive advantages.
Active nonconformity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com