Disenchantment explores the comedic misadventures of Princess Bean in a magical kingdom filled with quirky characters and dark humor. This animated series masterfully blends fantasy and satire to challenge traditional fairy tale tropes. Dive into the article to uncover how disenchantment redefines storytelling with wit and charm.
Table of Comparison
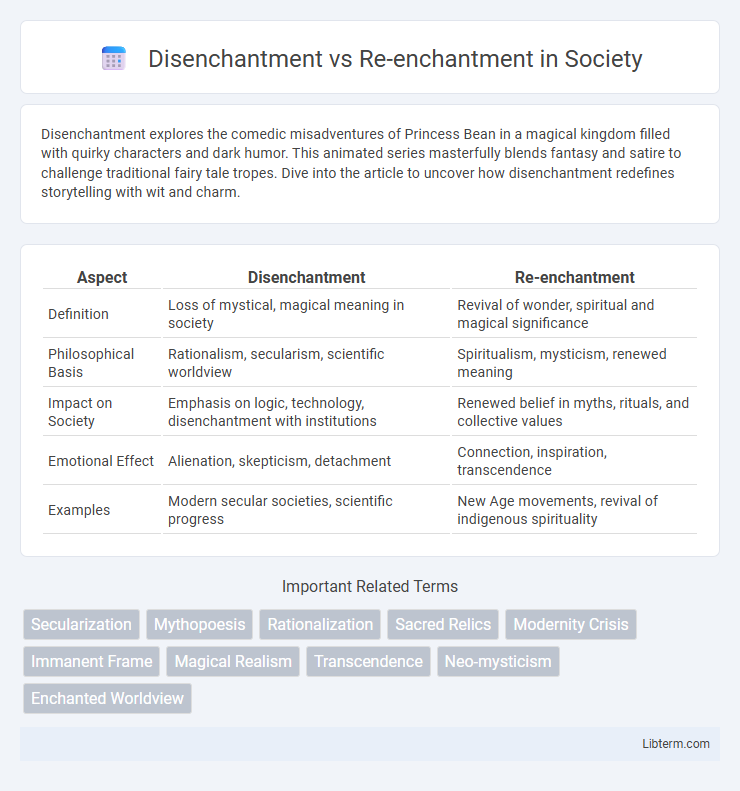
| Aspect | Disenchantment | Re-enchantment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loss of mystical, magical meaning in society | Revival of wonder, spiritual and magical significance |
| Philosophical Basis | Rationalism, secularism, scientific worldview | Spiritualism, mysticism, renewed meaning |
| Impact on Society | Emphasis on logic, technology, disenchantment with institutions | Renewed belief in myths, rituals, and collective values |
| Emotional Effect | Alienation, skepticism, detachment | Connection, inspiration, transcendence |
| Examples | Modern secular societies, scientific progress | New Age movements, revival of indigenous spirituality |
Understanding Disenchantment: Origins and Meaning
Disenchantment refers to the process through which the world is perceived as devoid of magic, mystery, or spiritual significance, largely originating from the rise of rationalism and scientific thinking during the Enlightenment. This concept highlights the transformation from a worldview filled with enchantment, where supernatural and mystical elements explained reality, to one governed by reason, empirical evidence, and secularism. Understanding disenchantment involves exploring its historical roots in Western philosophy and its impact on modern culture, reducing the sense of wonder and symbolic meanings previously embedded in everyday life.
The Rise of Rationalism and Secularization
The rise of rationalism and secularization led to disenchantment by promoting scientific explanations and diminishing mystical or religious interpretations of the world. This intellectual shift emphasized empirical evidence and reason, displacing traditional beliefs and supernatural authority. Despite this, re-enchantment persists through contemporary movements that blend spirituality with modern life, highlighting a complex interplay between rational thought and enduring human quests for meaning.
Symptoms of a Disenchanted World
Disenchantment manifests through widespread feelings of alienation, loss of meaning, and reduced belief in traditional myths or spiritual narratives. Symptoms include societal skepticism, increasing secularization, and a reliance on technological rationality over metaphysical or emotional connection. This shift results in a fragmented worldview where purpose is often questioned and existential anxiety becomes prevalent.
Psychological Impacts of Disenchantment
Disenchantment, characterized by the loss of awe and mystery in everyday life, often leads to feelings of alienation, existential anxiety, and diminished meaning, impacting mental well-being significantly. The psychological effects include increased stress levels, a sense of purposelessness, and difficulty in finding joy or connection with the world. Re-enchantment practices, such as engaging in spirituality, nature, or creative arts, can counteract these effects by restoring a sense of wonder and belonging.
The Call for Re-enchantment: Motivations and Movements
The call for re-enchantment emerges as a response to the disenchantment of modernity, where rationalization and scientific progress have diminished the sense of wonder and meaning in life. Movements advocating re-enchantment emphasize reconnecting with nature, spirituality, and holistic worldviews to restore a deeper existential significance. These motivations reflect a growing desire to integrate mystical and symbolic dimensions into contemporary culture, countering the alienation caused by purely materialistic perspectives.
Spirituality and the Search for Meaning
Disenchantment refers to the modern worldview characterized by rationalization, scientific skepticism, and the decline of mystical or spiritual significance in life. Re-enchantment, in contrast, represents a resurgence of spiritual exploration and the search for deeper meaning through practices like meditation, mysticism, and ecological consciousness. The tension between disenchantment and re-enchantment highlights the evolving human quest for purpose beyond materialism and empirical knowledge.
Re-enchantment through Art and Imagination
Re-enchantment through art and imagination revitalizes a sense of wonder and meaningful connection in contemporary life, counteracting the disenchantment brought by rationalization and secularization. Artistic expression and imaginative narratives foster emotional resonance and invite alternative perspectives, enabling audiences to perceive the world as vibrant and mysterious. This process deepens cultural and spiritual engagement by transforming everyday experiences with symbolism, myth, and creativity.
Technology’s Role in Disenchantment and Re-enchantment
Technology accelerates disenchantment by emphasizing rationality, efficiency, and data-driven decision-making, often reducing the mystical and emotional aspects of human experience. Conversely, technology fosters re-enchantment through virtual reality, augmented reality, and immersive storytelling, creating new spaces for wonder and imaginative engagement. The dual role of technology reshapes cultural perceptions, simultaneously demystifying the world and enabling innovative forms of enchantment.
Case Studies: Societies Rediscovering Wonder
Case studies of societies rediscovering wonder reveal a shift from disenchantment, marked by rationalization and secularization, to re-enchantment through cultural revival and spiritual resurgence. Indigenous communities restoring traditional rituals and urban movements embracing eco-spirituality exemplify how re-enchantment fosters renewed meaning and connection in modern life. These transformations underscore a global trend where re-enchantment counterbalances the alienation caused by scientific rationality.
Disenchantment vs Re-enchantment: Finding a Balance
Disenchantment, characterized by rationalization and loss of mysticism, contrasts sharply with re-enchantment, which restores meaning through symbolism, spirituality, and wonder. Balancing these involves integrating scientific understanding with cultural and emotional significance, fostering both critical thinking and imaginative engagement. This equilibrium supports a holistic worldview that honors empirical knowledge while embracing human creativity and connection.
Disenchantment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com