Endogamy refers to the social practice of marrying within a specific group, community, or social category to preserve cultural, religious, or ethnic identity. This tradition influences social cohesion and can impact genetic diversity within the group. Explore the rest of the article to understand how endogamy shapes societies and affects your community.
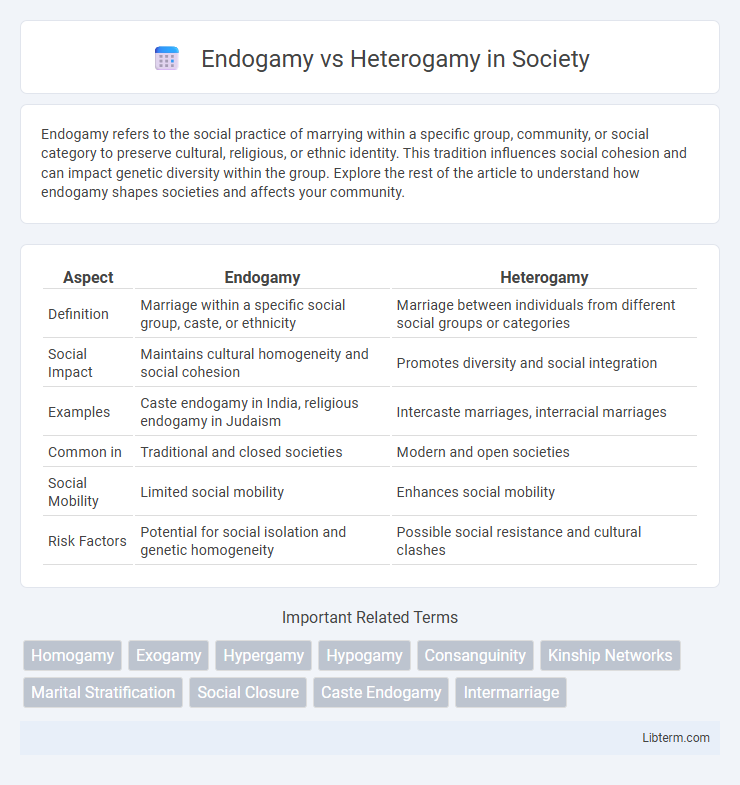
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Endogamy | Heterogamy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marriage within a specific social group, caste, or ethnicity | Marriage between individuals from different social groups or categories |
| Social Impact | Maintains cultural homogeneity and social cohesion | Promotes diversity and social integration |
| Examples | Caste endogamy in India, religious endogamy in Judaism | Intercaste marriages, interracial marriages |
| Common in | Traditional and closed societies | Modern and open societies |
| Social Mobility | Limited social mobility | Enhances social mobility |
| Risk Factors | Potential for social isolation and genetic homogeneity | Possible social resistance and cultural clashes |
Introduction to Endogamy and Heterogamy
Endogamy refers to the social practice of marrying within a specific cultural, ethnic, or social group to maintain group cohesion and heritage. Heterogamy involves marriage between individuals from different social, cultural, or ethnic backgrounds, promoting diversity and social integration. Understanding the distinction between endogamy and heterogamy is crucial for analyzing patterns of social structure and cultural dynamics.
Defining Endogamy: Meaning and Context
Endogamy refers to the social practice of marrying within a specific cultural, ethnic, or social group, reinforcing group identity and cohesion. This custom often preserves heritage and traditions by limiting marital choices to individuals sharing common values, beliefs, and lineage. Endogamy contrasts with heterogamy, where partners come from different social or cultural backgrounds, promoting diversity through marital unions.
Understanding Heterogamy: A Broad Overview
Heterogamy refers to the practice of marrying or forming relationships with individuals from different social, cultural, ethnic, or economic backgrounds, promoting diversity and social integration. This contrasts with endogamy, which involves mating within a specific social group, caste, or community, often preserving cultural or familial boundaries. Understanding heterogamy is crucial for analyzing demographic changes, social mobility, and the blending of cultural identities in increasingly multicultural societies.
Historical Perspectives on Marriage Patterns
Historical perspectives on marriage patterns reveal endogamy as a prevalent practice in many traditional societies, promoting social cohesion by encouraging unions within specific kinship, caste, or ethnic groups. Heterogamy emerged as a contrasting pattern, fostering alliances across different social strata or cultural backgrounds, often driven by economic, political, or social mobility motivations. These marriage patterns reflect underlying societal structures and values, influencing lineage, inheritance, and community stability over time.
Cultural and Religious Significance of Endogamy
Endogamy plays a crucial role in preserving cultural identity and religious traditions by encouraging marriages within specific social, ethnic, or religious groups. This practice helps maintain group cohesion and continuity, reinforcing shared values, rituals, and beliefs across generations. Many communities view endogamous unions as essential to safeguarding heritage and preventing cultural assimilation.
Social Dynamics and Implications of Heterogamy
Heterogamy involves unions between individuals from different social, ethnic, or cultural groups, influencing social dynamics by promoting diversity and challenging traditional norms. This form of partnership can lead to increased social integration and broader acceptance of multicultural values, but may also encounter resistance due to differing social expectations and potential prejudice. The implications of heterogamy extend to weakening rigid social boundaries, fostering inclusivity, and reshaping identity within communities.
Endogamy vs Heterogamy: Key Differences
Endogamy requires marriage within a specific social, cultural, or ethnic group, ensuring cultural continuity and social cohesion, while heterogamy involves marrying outside these groups, promoting diversity and social integration. Endogamous unions typically emphasize shared traditions, values, and social norms, whereas heterogamous marriages often blend different backgrounds, beliefs, and practices. The key differences lie in social boundaries, cultural homogamy, and the implications for social structure and genetic diversity.
Impact on Family Structure and Social Cohesion
Endogamy promotes family structure stability and strengthens social cohesion by encouraging marriages within the same social, ethnic, or cultural group, preserving shared values and traditions. Heterogamy introduces diversity into family units, which can challenge traditional norms but also foster social integration and expanded social networks. The balance between endogamy and heterogamy influences societal harmony, shaping how communities maintain identity while adapting to social change.
Modern Trends and Shifting Preferences
Endogamy, the practice of marrying within a specific social, ethnic, or cultural group, has seen a decline as modern societies embrace heterogamy, which involves unions across diverse backgrounds. Rising globalization, increased urbanization, and evolving social norms promote heterogamy by encouraging intercultural and interethnic relationships, reflecting broader acceptance of diversity. Data from recent sociological studies indicate a significant rise in mixed marriages, highlighting shifting preferences towards personal compatibility and individual choice over traditional group boundaries.
Future Outlook: Endogamy, Heterogamy, and Society
Endogamy, which involves marrying within a specific social group, is increasingly influenced by globalization and digital connectivity, allowing individuals to maintain cultural traditions while adapting to modern social dynamics. Heterogamy, characterized by marrying outside one's social group, reflects growing acceptance of diversity and can drive social integration and innovation by blending distinct cultural perspectives. Future societal trends suggest a complex interplay where endogamy preserves heritage and identity, whereas heterogamy fosters broader social cohesion and adaptability in an interconnected world.
Endogamy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com