Nonconformity challenges established norms and encourages individual thinking that sets you apart from the crowd. Embracing nonconformity can lead to creative breakthroughs and personal growth by resisting societal pressures to conform. Discover how embracing your uniqueness can transform your life in the rest of this article.
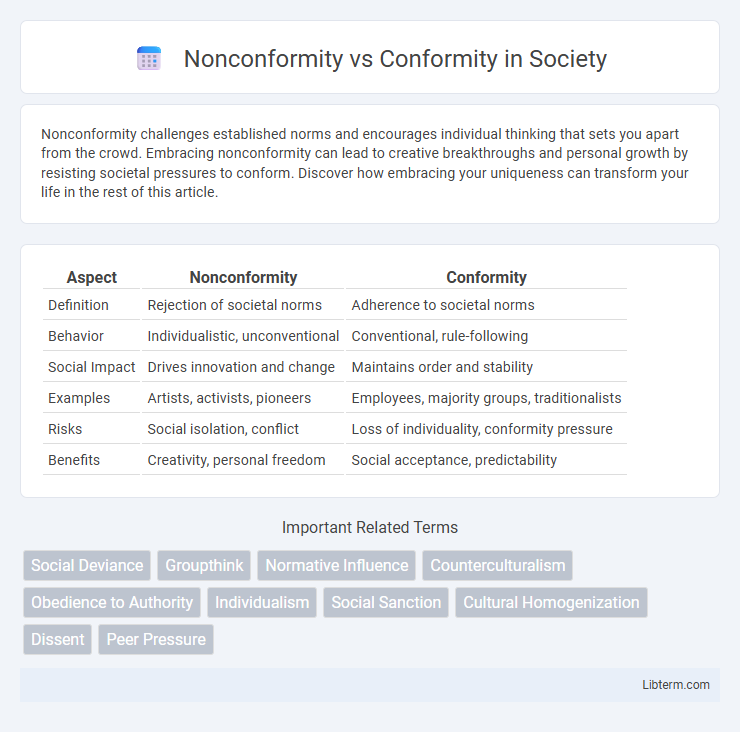
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nonconformity | Conformity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rejection of societal norms | Adherence to societal norms |
| Behavior | Individualistic, unconventional | Conventional, rule-following |
| Social Impact | Drives innovation and change | Maintains order and stability |
| Examples | Artists, activists, pioneers | Employees, majority groups, traditionalists |
| Risks | Social isolation, conflict | Loss of individuality, conformity pressure |
| Benefits | Creativity, personal freedom | Social acceptance, predictability |
Defining Conformity and Nonconformity
Conformity involves aligning attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors with societal norms or group expectations to achieve social acceptance and cohesion. Nonconformity is characterized by the deliberate rejection or deviation from these prevailing social standards, often promoting individuality and innovation. Understanding the dynamics between conformity and nonconformity is crucial in fields such as psychology, sociology, and cultural studies for analyzing social influence and group behavior.
Historical Perspectives on Social Norms
Historical perspectives on social norms reveal how conformity and nonconformity have shaped societies through time, influencing cultural evolution and social order. Conformity has often been linked to the reinforcement of traditional values and collective identity, as seen in the strict social codes of Victorian England and Confucian East Asia. Nonconformity, exemplified by movements such as the Enlightenment and the 1960s counterculture, challenged established norms and promoted individual freedom, driving significant social and political transformations.
Psychological Drivers Behind Conformity
Psychological drivers behind conformity include the innate human desire for social acceptance and fear of rejection, which motivate individuals to align their behavior and beliefs with group norms. Cognitive processes such as informational social influence emerge when people conform to others' actions in ambiguous situations to gain accurate information. Normative social influence also plays a key role, as individuals conform to avoid social disapproval and maintain positive relationships within their social groups.
Motivations for Nonconformist Behavior
Nonconformist behavior is primarily motivated by the desire for self-expression, autonomy, and resistance to perceived social constraints or norms. Individuals often engage in nonconformity to assert identity, challenge authority, or promote innovation and social change. Psychological factors such as a need for uniqueness, personal values, and dissatisfaction with conventional norms significantly drive nonconformist actions.
Benefits of Conforming to Societal Expectations
Conforming to societal expectations fosters social cohesion and facilitates smoother interpersonal relationships by aligning individual behavior with community norms. It enhances trust and predictability within social and professional environments, promoting cooperation and collective stability. Adherence to established rules often leads to increased social acceptance and access to resources or opportunities.
The Risks and Rewards of Nonconformity
Nonconformity often carries the risk of social isolation and professional setbacks as individuals challenge prevailing norms and face resistance from established systems. However, the rewards include fostering innovation, authentic self-expression, and potential leadership in transformative movements that push societal progress. Embracing nonconformity can lead to breakthroughs in creativity and problem-solving, positioning nonconformists as catalysts for change despite initial adversities.
Social Influence: Peer Pressure and Group Dynamics
Nonconformity challenges prevailing social norms by resisting peer pressure and disrupting group dynamics, often driven by a desire for individuality or dissent. Conformity, however, aligns individual behaviors and attitudes with group expectations to maintain social harmony and acceptance. Peer pressure exerts powerful social influence, compelling individuals to conform, while group dynamics can either suppress nonconformity or foster it by creating environments that encourage independent thinking.
Nonconformity in Art, Culture, and Innovation
Nonconformity in art, culture, and innovation drives creative breakthroughs by challenging traditional norms and fostering original expression. Artists like Pablo Picasso and innovators such as Steve Jobs exemplify how rejecting conformity stimulates groundbreaking ideas and transformative movements. This defiance against standard conventions enhances diversity in cultural narratives and accelerates technological advancements.
Conformity in the Workplace and Education
Conformity in the workplace promotes consistency, teamwork, and adherence to organizational policies, which enhances operational efficiency and reduces conflicts among employees. In educational settings, conformity supports standardized testing, uniform curricula, and social cohesion, helping students meet established academic and behavioral expectations. Despite potential limitations on creativity, conformity ensures predictable environments crucial for maintaining order and achieving collective goals.
Striking a Balance: When to Conform and When to Stand Out
Striking a balance between nonconformity and conformity requires understanding situational context and personal values to determine when alignment with social norms fosters cooperation and when individuality drives innovation. Conformity enhances group cohesion and facilitates social acceptance, while nonconformity promotes creativity and challenges outdated paradigms. Effective decision-making involves assessing risks and benefits of each approach to navigate social dynamics without compromising authenticity.
Nonconformity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com