The Singularity refers to a future point when artificial intelligence surpasses human intelligence, leading to rapid and unpredictable technological growth. This moment could dramatically transform every aspect of society, from healthcare to economy, raising important ethical and practical questions. Discover how the Singularity might reshape your world and what to expect in the coming decades by reading on.
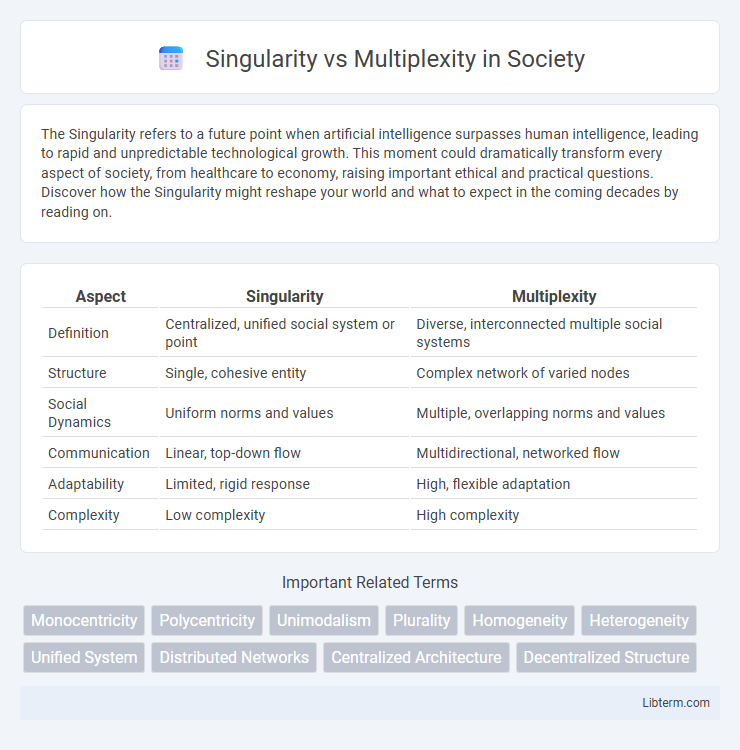
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Singularity | Multiplexity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized, unified social system or point | Diverse, interconnected multiple social systems |
| Structure | Single, cohesive entity | Complex network of varied nodes |
| Social Dynamics | Uniform norms and values | Multiple, overlapping norms and values |
| Communication | Linear, top-down flow | Multidirectional, networked flow |
| Adaptability | Limited, rigid response | High, flexible adaptation |
| Complexity | Low complexity | High complexity |
Understanding Singularity: A Fundamental Overview
Singularity refers to a unique, centralized point or event characterized by unparalleled concentration or unification within a system. It often denotes a moment of transformative change or an essential core that influences the entire structure or process. Understanding singularity involves analyzing its impact on complexity reduction, system behavior, and the potential for exponential growth or disruption.
Defining Multiplexity: Concepts and Contexts
Multiplexity refers to the presence of multiple types of relationships or interactions simultaneously existing within a single social network, emphasizing the complexity and richness of social ties. Unlike singular connections, multiplex ties involve overlapping roles and contexts, such as family, work, and friendship intersecting within individual relationships. Understanding multiplexity is crucial for analyzing social behavior, network dynamics, and how individuals navigate diverse social environments.
Historical Evolution of Singularity and Multiplexity
The historical evolution of singularity traces back to early philosophical and scientific inquiries into the nature of unique events and ultimate points of convergence, such as technological singularity in the 20th century relating to exponential AI growth. Multiplexity emerged from sociological studies in the mid-20th century, emphasizing complex networks and multiple simultaneous social roles or connections within communities. These concepts evolved to contrast singular, transformative phenomena with the layered, interconnected dynamics of social and technological systems.
Key Differences: Singularity vs Multiplexity
Singularity refers to a state where a system or concept is unified and operates as a single entity, often emphasizing simplicity and coherence. Multiplexity, in contrast, describes the presence of multiple, interconnected layers or dimensions within a system, highlighting complexity and diverse interactions. Key differences include singularity's focus on unity and coherence versus multiplexity's emphasis on dimensionality and relational richness across various components.
Technological Impact of Singularity and Multiplexity
Technological singularity refers to a hypothetical point where artificial intelligence exceeds human intelligence, driving exponential advancements in technology that transform industries and society beyond current comprehension. Multiplexity emphasizes the simultaneous interaction of multiple technologies and systems, resulting in complex, interconnected infrastructures that enhance adaptability and resilience across sectors. Both singularity and multiplexity significantly influence innovation trajectories, but singularity accelerates disruptive change, while multiplexity fosters integrated, multifaceted technological ecosystems.
Applications in Artificial Intelligence
Singularity in Artificial Intelligence refers to a future point where AI surpasses human intelligence in all aspects, enabling autonomous learning and decision-making across diverse domains. Multiplexity emphasizes the integration of multiple AI models or systems working synergistically to handle complex tasks with increased flexibility and robustness. Applications leveraging multiplexity enhance natural language processing, computer vision, and autonomous systems by combining specialized algorithms, while singularity-driven AI strives for universal adaptability and continuous self-improvement.
Psychological and Social Dimensions
Singularity emphasizes a unified psychological identity, fostering clear self-concept and consistent social roles, which can lead to stable interpersonal relationships and predictable social interactions. Multiplexity involves multiple, overlapping social ties and psychological identities, enhancing social support networks and adaptability but potentially causing internal conflict and role strain. Balancing singularity and multiplexity influences mental health outcomes and social integration, reflecting complexity in human behavior and community dynamics.
Real-World Case Studies: Singularity vs Multiplexity
Real-world case studies comparing singularity and multiplexity reveal significant differences in network dynamics and resilience. For instance, the spread of information in social media platforms often exemplifies multiplexity, where multiple channels and relationships create robust, interconnected networks that enhance diffusion efficiency. In contrast, singularity-centered models, such as centralized communication hubs in emergency response systems, highlight vulnerabilities due to dependency on single nodes, making them prone to failure under stress.
Future Implications and Emerging Trends
Singularity, characterized by a unified intelligence or system, promises streamlined decision-making and unprecedented efficiency in AI-driven environments, potentially transforming industries like healthcare and finance by enabling rapid innovation and adaptive learning. Multiplexity emphasizes interconnected, diverse systems operating simultaneously, fostering resilience and flexibility through complex networked interactions, which supports scalable solutions in smart cities and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). Emerging trends suggest a convergence where hybrid models balance singular powerful systems with multiplex frameworks, enhancing transparency, robustness, and ethical AI deployment in the future technological landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
Singularity in technology centers on creating highly advanced, autonomous systems, posing challenges such as ethical dilemmas, control risks, and potential job displacement. Multiplexity emphasizes interconnected, multi-layered infrastructures, offering opportunities for robust data integration, enhanced collaborative networks, and resilient system designs. Navigating the balance between singular autonomous intelligence and complex multiplex networks is crucial for sustainable innovation and societal benefit.
Singularity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com