Recognition plays a crucial role in motivating individuals and enhancing overall performance by acknowledging achievements and efforts. It fosters a positive environment that encourages continuous growth and commitment. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective strategies for implementing recognition in your organization.
Table of Comparison
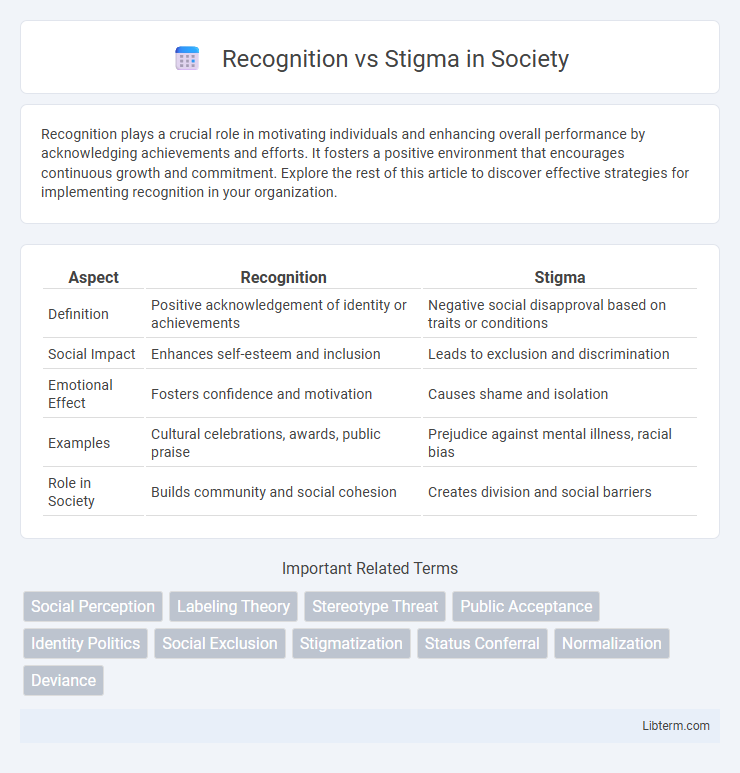
| Aspect | Recognition | Stigma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Positive acknowledgement of identity or achievements | Negative social disapproval based on traits or conditions |
| Social Impact | Enhances self-esteem and inclusion | Leads to exclusion and discrimination |
| Emotional Effect | Fosters confidence and motivation | Causes shame and isolation |
| Examples | Cultural celebrations, awards, public praise | Prejudice against mental illness, racial bias |
| Role in Society | Builds community and social cohesion | Creates division and social barriers |
Understanding Recognition and Stigma
Recognition involves acknowledging and valuing individual identities, achievements, or conditions, fostering social acceptance and inclusion. Stigma refers to negative labeling or stereotyping that leads to discrimination, social rejection, and psychological harm. Understanding both concepts is crucial for promoting mental health awareness and implementing effective social policies.
The Psychology Behind Social Recognition
Social recognition activates reward centers in the brain, releasing dopamine and reinforcing positive behaviors that enhance self-esteem and motivation. Conversely, stigma triggers negative emotional responses such as shame and social withdrawal, often activating the amygdala and increasing stress hormones like cortisol. Understanding these psychological mechanisms highlights the critical role of social validation in mental health and the detrimental impact of stigmatization on individual well-being.
How Stigma Shapes Perceptions
Stigma significantly shapes perceptions by creating negative stereotypes and social disapproval around certain conditions or identities, which leads to marginalization and discrimination. This distorted view limits individuals' access to resources, support, and opportunities, reinforcing fears and misconceptions within communities. Understanding the dynamics of stigma is crucial for developing effective recognition and acceptance strategies that promote inclusion and mental health awareness.
Societal Impacts of Recognition vs Stigma
Recognition fosters social inclusion, enhances self-esteem, and promotes mental well-being by affirming individual identities and contributions within the community. Stigma leads to social exclusion, discrimination, and marginalization, which contribute to increased stress, reduced access to resources, and poor health outcomes. Societal impacts reveal that recognition strengthens social cohesion and equity, while stigma perpetuates inequality and hinders collective progress.
Factors Influencing Recognition and Stigma
Factors influencing recognition and stigma include cultural beliefs, social norms, and media representation, which shape public perceptions and attitudes toward mental health conditions. Education level and personal experiences with mental illness often affect individuals' ability to recognize symptoms and reduce stigmatizing beliefs. Accessibility to accurate information and community support networks also play critical roles in promoting recognition and mitigating stigma.
Breaking Down Barriers: Reducing Stigma
Breaking down barriers to reduce stigma involves fostering awareness and education to challenge misconceptions about mental health. Promoting open conversations and sharing personal stories encourages recognition of mental health conditions as common and treatable. Creating supportive environments in schools, workplaces, and communities helps dismantle prejudices and facilitates access to necessary resources.
The Role of Media in Recognition and Stigma
Media plays a pivotal role in shaping public perception by influencing recognition and stigma around various social issues. Positive media representation fosters recognition, increasing awareness and empathy, while negative portrayals can reinforce stigma and marginalize affected groups. The framing, language, and frequency of media coverage significantly impact societal attitudes, making media a powerful tool in either combating or perpetuating stigma.
Personal Stories: From Stigma to Acceptance
Personal stories highlight the powerful journey from stigma to acceptance by showcasing ordinary individuals overcoming societal prejudices related to mental health, illness, or identity. These narratives emphasize the importance of recognition in validating personal experiences and fostering empathy, which in turn challenges harmful stereotypes and reduces discrimination. By sharing authentic accounts, communities create safe spaces that promote understanding and support for those previously marginalized or misunderstood.
Strategies to Promote Positive Recognition
Promoting positive recognition involves implementing educational programs that increase awareness and understanding of mental health conditions, reducing misconceptions and fostering empathy. Creating supportive environments through peer support groups and inclusive policies encourages open dialogue and acceptance, mitigating stigma. Media campaigns highlighting personal stories and achievements help reshape public perceptions, emphasizing strengths rather than limitations.
Building a Culture of Support and Understanding
Recognition of mental health challenges fosters a culture of support by validating individual experiences and encouraging open dialogue within communities. Reducing stigma requires education and empathy, which promote acceptance and create safe spaces for seeking help. Building understanding through awareness campaigns strengthens social bonds and empowers individuals to access necessary resources without fear of judgment.
Recognition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com