Hypogamy refers to the practice of marrying someone from a lower social or economic status. This concept often challenges traditional social hierarchies and can influence cultural and familial dynamics. Explore the full article to understand how hypogamy impacts relationships and societal structures.
Table of Comparison
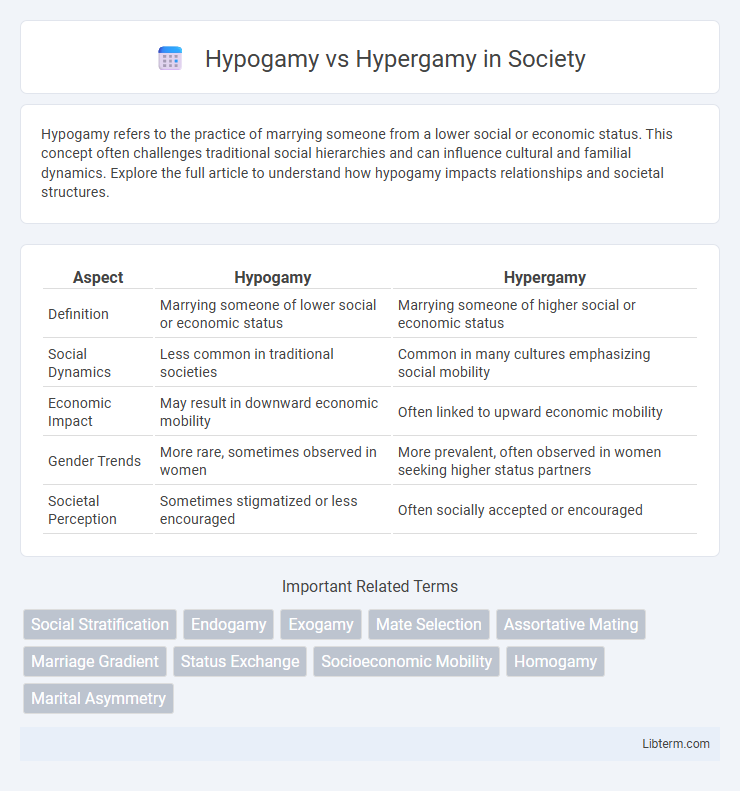
| Aspect | Hypogamy | Hypergamy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marrying someone of lower social or economic status | Marrying someone of higher social or economic status |
| Social Dynamics | Less common in traditional societies | Common in many cultures emphasizing social mobility |
| Economic Impact | May result in downward economic mobility | Often linked to upward economic mobility |
| Gender Trends | More rare, sometimes observed in women | More prevalent, often observed in women seeking higher status partners |
| Societal Perception | Sometimes stigmatized or less encouraged | Often socially accepted or encouraged |
Understanding Hypogamy and Hypergamy
Hypogamy refers to the practice of marrying someone of lower social or economic status, while hypergamy involves marrying someone of higher status. Understanding hypogamy and hypergamy is essential for analyzing social mobility patterns and relationship dynamics in various cultures. These concepts influence mate selection by reflecting societal values related to status, wealth, and gender roles.
The Historical Context of Marital Choices
Historical marital choices reveal a complex interplay between hypogamy and hypergamy shaped by social hierarchies and economic imperatives. Hypogamy, marrying into a lower social or economic status, often occurred under constraints such as limited social mobility or cultural norms promoting family alliances. Hypergamy, the practice of marrying "up," historically provided women with economic security and enhanced social standing, reinforcing class stratifications through strategic matrimonial alliances.
Social and Cultural Influences on Partner Selection
Hypogamy and hypergamy reflect social and cultural influences on partner selection by shaping preferences based on socioeconomic status and cultural norms. In many societies, hypergamy--marrying up in social or economic status--is encouraged to enhance family prestige and economic stability, while hypogamy may be less socially accepted due to traditional views on gender roles and status hierarchies. These patterns are reinforced through socialization, media representations, and community expectations, highlighting the persistent impact of cultural values on mate choice.
Economic Impacts on Hypogamy and Hypergamy
Hypogamy, where individuals marry into lower economic status, can lead to financial strain and decreased household wealth, affecting social mobility negatively. Hypergamy, marrying into a higher economic status, often results in increased resource accumulation, improved living standards, and enhanced socio-economic opportunities. These marriage patterns significantly influence income distribution, asset growth, and intergenerational economic disparities within societies.
Gender Roles and Power Dynamics
Hypogamy and hypergamy shape gender roles by influencing mate selection preferences where hypergamy often involves women seeking partners with higher socioeconomic status, reinforcing traditional power dynamics favoring male economic dominance. Hypogamy, less commonly studied, can invert these roles, with men choosing partners of lower status, challenging conventional gender norms. These patterns reveal how societal structures and cultural expectations intertwine with personal relationships, perpetuating or contesting gender-based power hierarchies.
Modern Trends in Relationship Patterns
Modern relationship patterns reveal a shift in traditional hypogamy and hypergamy trends, with increasing acceptance of couples where individuals marry outside conventional socioeconomic or educational hierarchies. Data from recent social studies show a rise in hypogamous unions, where individuals partner with those of higher socioeconomic status, challenging historic hypergamous norms that favored upward mobility for women. Changing cultural values, greater gender equality, and economic factors contribute to these evolving trends in partner selection across diverse societies.
Challenges and Benefits of Hypogamous Relationships
Hypogamous relationships, where an individual partners with someone of lower social or economic status, often face societal stigma and pressure due to traditional norms favoring upward social mobility. Challenges include overcoming external judgment and potential disparities in educational or income levels, which can affect power dynamics. Benefits of hypogamous relationships include increased emotional intimacy, reduced competition, and breaking of conventional class barriers, fostering personal growth and resilience.
The Appeal and Criticisms of Hypergamy
Hypergamy, the practice of marrying or forming a relationship with a partner of higher socioeconomic status, appeals to many due to its perceived benefits in social mobility, enhanced financial stability, and improved lifestyle opportunities. Critics argue that hypergamy reinforces class divisions, perpetuates gender inequality, and can promote materialism over emotional compatibility in relationships. The debate often centers on how hypergamy shapes social norms around marriage and influences individual partner choices in contemporary society.
Media Representation and Stereotypes
Media representation often portrays hypogamy as less desirable, reinforcing stereotypes that women should seek partners with equal or higher socioeconomic status, typical of hypergamy. Hypergamy is frequently idealized in films and advertising, perpetuating traditional gender roles and expectations about upward social mobility through marriage. These portrayals contribute to societal pressures and misconceptions, influencing real-life relationship dynamics and perpetuating gender-based inequalities.
Future Perspectives on Love, Marriage, and Societal Evolution
Hypogamy and hypergamy, defined as marrying downward or upward in social status respectively, are shifting due to evolving gender roles and economic factors. Future perspectives on love and marriage predict a decline in traditional status-based unions as digital connectivity and individualism promote more diverse partner choices. Societal evolution increasingly values emotional compatibility and personal fulfillment over rigid class structures, reshaping norms around hypogamous and hypergamous relationships.
Hypogamy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com