Information accessibility ensures that content is easily obtainable and understandable for all users, including those with disabilities or limited technical skills. By prioritizing clear navigation, readable text, and adaptive technologies, organizations enhance user experience and promote inclusivity. Discover how improving your information accessibility can transform engagement and broaden your audience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
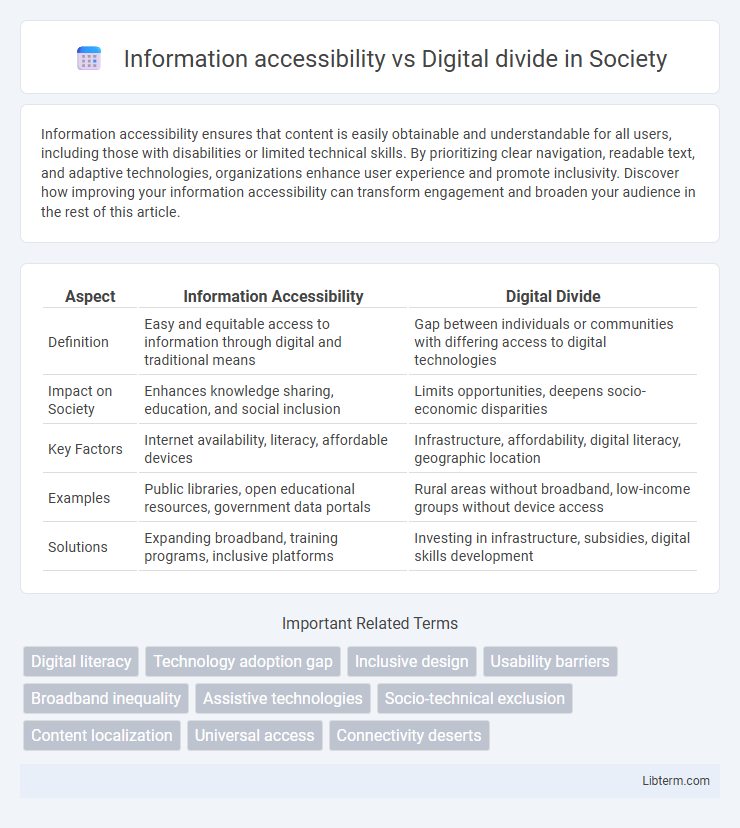
| Aspect | Information Accessibility | Digital Divide |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Easy and equitable access to information through digital and traditional means | Gap between individuals or communities with differing access to digital technologies |
| Impact on Society | Enhances knowledge sharing, education, and social inclusion | Limits opportunities, deepens socio-economic disparities |
| Key Factors | Internet availability, literacy, affordable devices | Infrastructure, affordability, digital literacy, geographic location |
| Examples | Public libraries, open educational resources, government data portals | Rural areas without broadband, low-income groups without device access |
| Solutions | Expanding broadband, training programs, inclusive platforms | Investing in infrastructure, subsidies, digital skills development |
Understanding Information Accessibility
Information accessibility ensures that all individuals, including those with disabilities, can easily access, understand, and use digital content and services, promoting inclusive communication and equal opportunities. It involves designing websites, applications, and digital tools following standards like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) to remove barriers caused by sensory, cognitive, or physical impairments. Bridging information accessibility gaps directly reduces the digital divide by enabling underserved populations to participate fully in the digital economy and society.
Defining the Digital Divide
The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals and communities that have access to modern information and communication technologies versus those who lack such access. This divide impacts information accessibility by limiting the ability of underprivileged groups to participate fully in the digital economy, education, and social services. Factors such as socioeconomic status, geographic location, and technological infrastructure contribute to the persistence of the digital divide worldwide.
Key Factors Influencing Information Access
Key factors influencing information access include internet infrastructure, digital literacy, and socioeconomic status, which collectively shape the digital divide. Unequal distribution of broadband connectivity limits access to information for rural and low-income communities, exacerbating disparities. Furthermore, variations in educational opportunities and device availability critically affect online information accessibility and engagement.
Socioeconomic Impacts on Digital Inclusion
Socioeconomic disparities significantly influence information accessibility, creating a digital divide that limits digital inclusion for marginalized communities. Lower-income individuals often lack affordable access to high-speed internet and digital devices, restricting their ability to benefit from online education, healthcare, and job opportunities. Bridging this gap requires targeted investments in infrastructure, digital literacy programs, and affordable technology to ensure equitable participation in the digital economy.
The Role of Technology in Bridging Gaps
Technology plays a pivotal role in bridging the digital divide by enhancing information accessibility through affordable internet services, mobile devices, and educational platforms. Innovative tools like low-cost smartphones and community Wi-Fi initiatives facilitate digital inclusion for underserved populations, enabling equitable access to knowledge and resources. Investments in digital literacy programs empower users to effectively navigate technology, minimizing disparities in information access across socio-economic and geographic boundaries.
Barriers to Equitable Information Access
Barriers to equitable information access stem from limited internet infrastructure, socioeconomic disparities, and inadequate digital literacy skills, which collectively deepen the digital divide. Marginalized communities often face restricted access to reliable technology and quality educational resources, hindering their ability to participate fully in the digital economy. Addressing these obstacles requires targeted investments in broadband expansion, affordable devices, and comprehensive digital education programs to ensure inclusive information accessibility.
Digital Literacy and Its Importance
Digital literacy is a critical factor in bridging the digital divide, as it empowers individuals to effectively access, understand, and utilize digital information and technologies. Enhanced digital skills improve access to educational resources, job opportunities, and essential services, reducing information accessibility gaps across different socioeconomic groups. Promoting digital literacy initiatives leads to greater inclusion and equity in the digital landscape, fostering economic growth and social participation.
Government Policies and Global Initiatives
Government policies aimed at enhancing information accessibility prioritize expanding broadband infrastructure, digital literacy programs, and affordable internet access to bridge the digital divide. Global initiatives such as the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals and the World Bank's Digital Economy for Africa project drive investments in connectivity and digital skills across underserved regions. These efforts collectively address disparities by promoting inclusive access to information and digital technologies worldwide.
Innovations Reducing the Digital Divide
Innovations reducing the digital divide focus on enhancing information accessibility through affordable internet solutions, widespread distribution of low-cost smart devices, and deployment of community-based digital literacy programs. Initiatives like satellite internet services and mesh networks enable remote and underserved areas to gain reliable connectivity, bridging gaps in digital access. These advancements empower marginalized populations to participate in the digital economy, improving education, healthcare, and social inclusion.
Future Prospects for Inclusive Information Access
Expanding information accessibility necessitates bridging the digital divide through investments in affordable internet infrastructure, digital literacy programs, and inclusive technology design. Emerging innovations such as 5G networks, AI-powered accessibility tools, and low-cost devices promise broader reach to underserved populations. Ensuring equitable access to information resources will foster social inclusion, economic opportunities, and global knowledge sharing in the future.
Information accessibility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com