Assimilation is the process by which individuals or groups adopt the culture, language, and norms of another group, often leading to the blending or loss of original cultural identities. It plays a crucial role in social integration and can impact your sense of belonging and cultural heritage. Explore this article to understand the complexities and effects of assimilation in diverse societies.
Table of Comparison
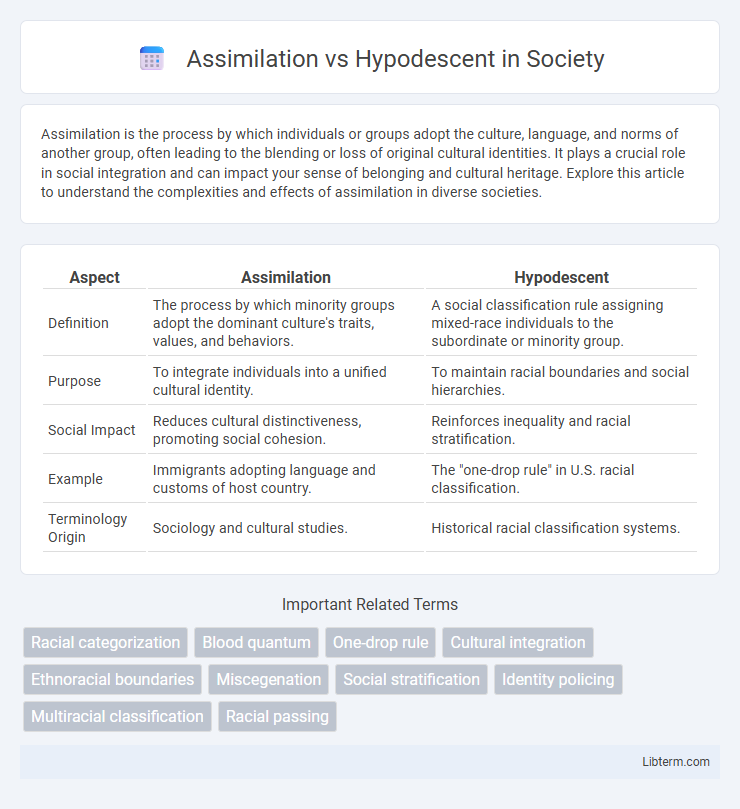
| Aspect | Assimilation | Hypodescent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process by which minority groups adopt the dominant culture's traits, values, and behaviors. | A social classification rule assigning mixed-race individuals to the subordinate or minority group. |
| Purpose | To integrate individuals into a unified cultural identity. | To maintain racial boundaries and social hierarchies. |
| Social Impact | Reduces cultural distinctiveness, promoting social cohesion. | Reinforces inequality and racial stratification. |
| Example | Immigrants adopting language and customs of host country. | The "one-drop rule" in U.S. racial classification. |
| Terminology Origin | Sociology and cultural studies. | Historical racial classification systems. |
Understanding Assimilation: Definition and Historical Context
Assimilation refers to the process by which individuals or groups adopt cultural traits or social patterns of another group, often leading to the blending or absorption of minority populations into a dominant culture. Historically, assimilation policies have been implemented in various societies to integrate immigrants or indigenous peoples, sometimes causing the erosion of original cultural identities. Understanding assimilation involves examining its role in social cohesion, identity formation, and the complexities of cultural loss and adaptation.
What is Hypodescent? Origins and Meaning
Hypodescent is a social classification principle assigning mixed-race individuals to the racial group with lower social status, often referred to as the "one-drop rule" in the United States. Its origins stem from historical racial hierarchies and legal frameworks during slavery and segregation, designed to maintain racial boundaries and reinforce white supremacy. Hypodescent serves as a mechanism to preserve social stratification by socially and legally categorizing individuals based on ancestry rather than cultural assimilation.
Key Differences Between Assimilation and Hypodescent
Assimilation involves the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits of another group, often leading to blending or integration within a dominant society. Hypodescent, by contrast, is a social classification rule that assigns a person of mixed racial heritage to the racial group perceived as subordinate or minority. The key difference lies in assimilation being a dynamic cultural adaptation, while hypodescent is a rigid, inherited social categorization based on lineage.
Historical Examples of Assimilation Policies
Historical examples of assimilation policies include the Indian Boarding Schools in the United States, where Native American children were forced to abandon their languages and cultures to adopt Euro-American customs. The Australian government implemented the Stolen Generations policy, removing Aboriginal children from their families to integrate them into white society. Canada's residential school system similarly aimed to erase Indigenous identities by imposing European cultural norms and values on Indigenous youth.
Hypodescent in Racial Classification Systems
Hypodescent is a racial classification system that assigns children of mixed-race unions to the socially subordinate group, reinforcing racial boundaries and maintaining systemic racial hierarchies. This principle is widely observed in societies with a history of strict racial stratification, such as the United States, where individuals with any identifiable minority ancestry are categorized as belonging to that minority group. Hypodescent serves as a mechanism to perpetuate racial inequality by legally and socially defining group membership based on ancestry rather than cultural assimilation or individual identity.
Social and Cultural Impacts of Assimilation
Assimilation influences social cohesion by encouraging minority groups to adopt the dominant culture's language, norms, and values, which can lead to the erosion of original cultural identities and traditions. This process often results in increased social integration but may also generate identity conflicts and loss of heritage among assimilated individuals. The cultural impacts of assimilation include diminished linguistic diversity and the homogenization of cultural expressions, affecting community solidarity and intergenerational cultural transmission.
The Role of Hypodescent in Identity Formation
Hypodescent plays a critical role in identity formation by legally and socially classifying individuals with mixed racial heritage into the subordinate or marginalized group, which influences their social experiences and self-identification. This system perpetuates racial boundaries by enforcing a rigid hierarchy that impacts access to resources, group membership, and cultural belonging. Understanding hypodescent reveals how societal constructs of race shape personal identity and community dynamics beyond mere phenotypic traits.
Controversies and Criticisms Surrounding Assimilation
Assimilation faces criticism for promoting cultural erasure by encouraging minority groups to abandon their distinct identities to conform to dominant societal norms. Critics argue it perpetuates power imbalances, masking systemic inequalities under the guise of social unity. These controversies highlight the tension between assimilation policies and multiculturalism, where preserving diverse heritages challenges the notion of a homogeneous national identity.
Contemporary Relevance of Hypodescent
Hypodescent, the practice of categorizing mixed-race individuals into the socially subordinate group, remains relevant in contemporary society as it influences identity formation and social dynamics, particularly among multiracial populations in the United States. This racial classification system perpetuates systemic inequalities by reinforcing hierarchical racial structures despite increasing racial diversity and multiculturalism. Understanding hypodescent is critical for addressing ongoing racial discrimination and promoting more inclusive definitions of identity in social policy and cultural discourse.
Future Implications: Assimilation vs Hypodescent in a Multicultural Society
Assimilation promotes cultural blending, potentially fostering social cohesion but risking the erosion of unique ethnic identities within a multicultural society. Hypodescent, by maintaining rigid racial or ethnic classifications, may reinforce social divisions and limit opportunities for inclusive identity formation. Future implications hinge on balancing integration with respect for diversity to achieve social equity and collective harmony.
Assimilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com