Multiculturalism embraces the coexistence of diverse cultures within a society, promoting inclusion, respect, and equal opportunities for all groups. It enriches social interactions, drives innovation through varied perspectives, and strengthens community cohesion. Discover how multiculturalism shapes modern society and what it means for Your community in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
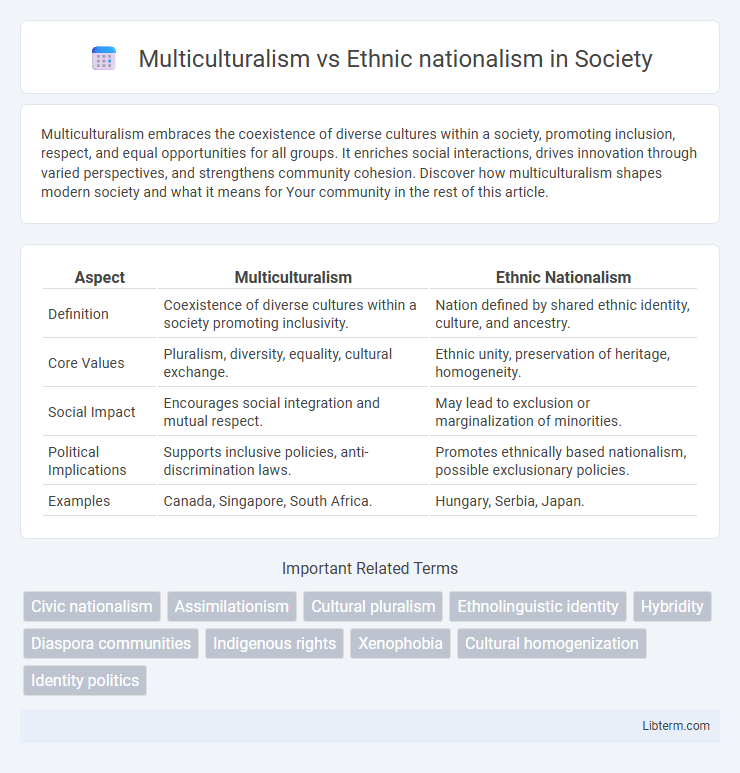
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Ethnic Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures within a society promoting inclusivity. | Nation defined by shared ethnic identity, culture, and ancestry. |
| Core Values | Pluralism, diversity, equality, cultural exchange. | Ethnic unity, preservation of heritage, homogeneity. |
| Social Impact | Encourages social integration and mutual respect. | May lead to exclusion or marginalization of minorities. |
| Political Implications | Supports inclusive policies, anti-discrimination laws. | Promotes ethnically based nationalism, possible exclusionary policies. |
| Examples | Canada, Singapore, South Africa. | Hungary, Serbia, Japan. |
Introduction to Multiculturalism and Ethnic Nationalism
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a single society, emphasizing inclusivity, equal rights, and cultural recognition. Ethnic nationalism prioritizes a shared heritage, language, and ancestry, advocating for political sovereignty based on ethnic identity. These contrasting frameworks shape social policies and national unity by either embracing diversity or reinforcing ethnocultural homogeneity.
Historical Roots of Multiculturalism
Multiculturalism emerged historically as a response to increasing migration and cultural diversity within nation-states, particularly after World War II, promoting social integration and acceptance of multiple cultural identities. This framework contrasts with ethnic nationalism, which is rooted in the 19th and early 20th centuries' emphasis on ethnolinguistic homogeneity and the idea of a nation-state based on shared ancestry and heritage. The historical roots of multiculturalism are closely linked to postcolonial immigration patterns and human rights movements advocating for equality and cultural pluralism in diverse societies.
Origins and Evolution of Ethnic Nationalism
Ethnic nationalism originated in the 19th century during the rise of Romantic nationalism, emphasizing a shared heritage, language, and culture as the basis for nationhood, contrasting sharply with civic nationalism's inclusive ideals. Its evolution is marked by movements aiming to preserve or revive ethnic identity, often in reaction to globalization and multicultural policies perceived as threats to homogeneity. This form of nationalism sometimes fuels conflicts and exclusionary practices, underscoring tensions with multiculturalism, which promotes diversity and equal rights across cultural groups.
Core Values: Inclusion vs. Exclusivity
Multiculturalism emphasizes inclusion by promoting diversity and equal respect for all cultural identities within a society, fostering social cohesion through acceptance and mutual understanding. Ethnic nationalism centers on exclusivity, prioritizing the interests and values of a specific ethnic group, often leading to rigid boundaries and exclusion of others. The core tension lies in multiculturalism's commitment to collective pluralism versus ethnic nationalism's focus on homogeneous identity preservation.
Social Cohesion and Community Bonds
Multiculturalism fosters social cohesion by promoting inclusive community bonds that respect diverse cultural identities, enhancing mutual understanding and cooperation among different ethnic groups. Ethnic nationalism, however, often prioritizes a singular cultural identity, which can strengthen in-group solidarity but risks marginalizing minorities and fracturing broader societal unity. Balancing these approaches is crucial for sustainable social cohesion in increasingly diverse societies.
Policy Approaches and Government Strategies
Multiculturalism promotes inclusive policy approaches that recognize and support diverse cultural identities through anti-discrimination laws, education reform, and equitable resource distribution. Ethnic nationalism prioritizes government strategies aimed at preserving the dominant ethnic group's culture, often involving restrictive immigration policies and emphasis on national unity rooted in shared heritage. These contrasting frameworks shape social cohesion and political integration, influencing legislation on minority rights and public representation.
Cultural Identity and National Narratives
Multiculturalism fosters inclusive national narratives by recognizing and celebrating diverse cultural identities, promoting social cohesion through mutual respect and shared values. Ethnic nationalism emphasizes a singular cultural identity rooted in ancestry and heritage, often shaping national narratives that prioritize one ethnic group's history and traditions over others. The tension between these approaches influences policy-making, social integration, and the construction of collective memory within modern nation-states.
Economic Impacts and Opportunities
Multiculturalism fosters economic growth by promoting diversity, innovation, and a broader range of skills in the workforce, which enhances productivity and global competitiveness. Ethnic nationalism can constrain economic opportunities by prioritizing homogeneity, potentially leading to social exclusion, reduced labor mobility, and limited market expansion. Studies show that inclusive multicultural policies attract international investment and talent, driving economic dynamism and sustainable development.
Challenges and Conflicts in Diverse Societies
Multiculturalism in diverse societies often faces challenges such as social fragmentation, identity clashes, and unequal access to resources, which can lead to tensions between different cultural groups. Ethnic nationalism intensifies conflicts by emphasizing exclusive group identities and promoting policies that marginalize minorities, resulting in heightened ethnic polarization and potential violence. Both approaches can complicate efforts to achieve social cohesion and equitable governance in multi-ethnic nations.
Future Perspectives: Navigating National Identity
Future perspectives on national identity emphasize balancing multiculturalism's inclusive approach with the preservation goals of ethnic nationalism, seeking models that foster social cohesion while respecting cultural heritage. Emerging policies leverage intercultural dialogue and legal frameworks to accommodate diverse identities within unified political structures, promoting resilience in increasingly globalized societies. Technological advancements and demographic shifts will further influence how nations negotiate identity politics, with hybrid identities and transnational affiliations becoming more prominent in defining future nationhood.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com