Organizational deviance refers to behaviors within a workplace that violate established norms or policies, negatively impacting productivity and morale. These actions can range from minor rule-breaking to serious infractions such as fraud or sabotage, undermining trust and organizational cohesion. Explore the rest of this article to understand the types, causes, and strategies to address organizational deviance effectively.
Table of Comparison
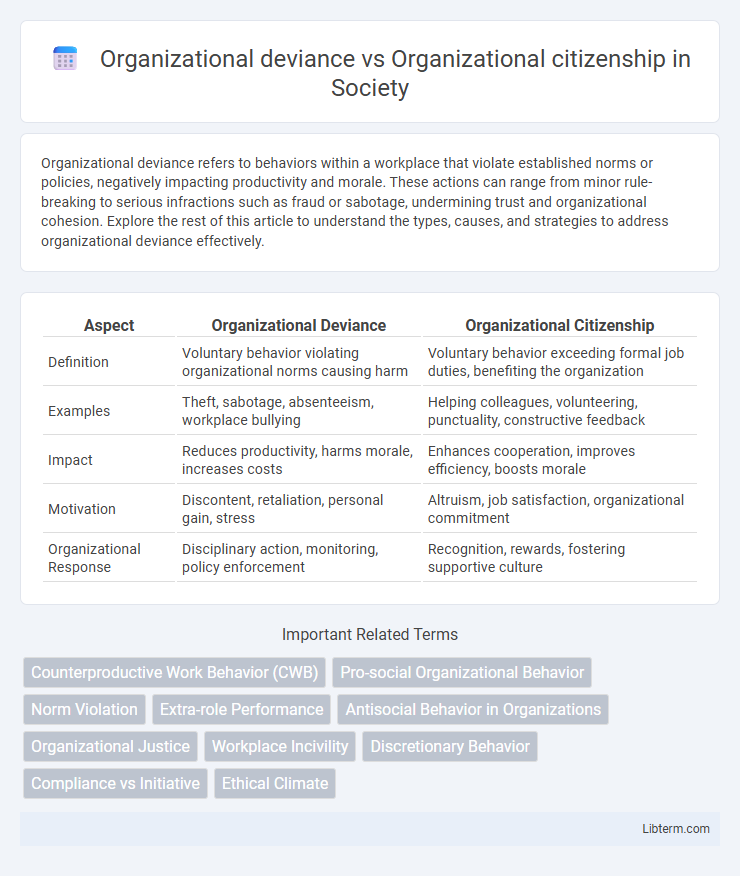
| Aspect | Organizational Deviance | Organizational Citizenship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary behavior violating organizational norms causing harm | Voluntary behavior exceeding formal job duties, benefiting the organization |
| Examples | Theft, sabotage, absenteeism, workplace bullying | Helping colleagues, volunteering, punctuality, constructive feedback |
| Impact | Reduces productivity, harms morale, increases costs | Enhances cooperation, improves efficiency, boosts morale |
| Motivation | Discontent, retaliation, personal gain, stress | Altruism, job satisfaction, organizational commitment |
| Organizational Response | Disciplinary action, monitoring, policy enforcement | Recognition, rewards, fostering supportive culture |
Understanding Organizational Deviance: Definition and Concepts
Organizational deviance refers to voluntary behaviors that violate significant organizational norms, potentially harming the organization or its members, such as theft or sabotage. In contrast, organizational citizenship involves discretionary behaviors that contribute positively to the organization's efficiency and social environment, like helping colleagues or volunteering for extra tasks. Understanding organizational deviance requires recognizing its various forms, including interpersonal and organizational, and the psychological, social, and environmental factors that drive employees to engage in such counterproductive actions.
Defining Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB)
Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) refers to voluntary, discretionary actions by employees that are not formally rewarded but contribute to organizational effectiveness and a positive work environment. OCB includes behaviors such as helping colleagues, adhering to informal norms, and showing initiative beyond job requirements, which enhance teamwork and organizational functioning. Unlike organizational deviance, which involves harmful or counterproductive actions, OCB fosters cooperation and organizational commitment.
Core Differences Between Deviance and Citizenship in Organizations
Organizational deviance involves behaviors that violate formal norms and harm the organization, such as theft, sabotage, or absenteeism, while organizational citizenship refers to voluntary, discretionary actions that promote organizational effectiveness, like helping colleagues or volunteering for extra tasks. Deviance typically results in negative consequences and is punished, whereas citizenship behaviors are positively recognized and often go beyond formal job requirements. The core difference lies in the intent and impact: deviance undermines organizational goals, whereas citizenship supports and enhances them.
Types of Organizational Deviance: Key Examples
Organizational deviance includes behaviors such as production deviance, property deviance, political deviance, and personal aggression, each negatively impacting workplace efficiency and morale. Production deviance involves intentional reduction in work output or quality, while property deviance includes theft, sabotage, or misuse of resources. Political deviance encompasses favoritism, gossip, or manipulation, and personal aggression refers to harassment or verbal abuse, contrasting with organizational citizenship that promotes voluntary, constructive behaviors supporting organizational effectiveness.
Dimensions of Organizational Citizenship: Altruism, Sportsmanship, and More
Organizational citizenship encompasses behaviors that exceed formal job requirements, enhancing workplace environment and efficiency; key dimensions include altruism, which involves voluntary assistance to colleagues, and sportsmanship, reflecting tolerance of inconveniences without complaint. Other dimensions such as conscientiousness, civic virtue, and courtesy further promote collaboration and organizational effectiveness. Contrastingly, organizational deviance entails behaviors that harm organizational functioning, highlighting the importance of fostering positive citizenship behaviors for sustained success.
Root Causes of Deviant and Citizenship Behaviors in the Workplace
Organizational deviance often stems from factors such as job dissatisfaction, perceived unfairness, lack of trust in management, and poor communication, which lead employees to engage in counterproductive behaviors like absenteeism or theft. Conversely, organizational citizenship behaviors originate from positive workplace conditions, including supportive leadership, recognition, strong organizational commitment, and intrinsic motivation, encouraging voluntary actions that benefit the organization. Understanding these root causes is essential for fostering a culture that minimizes deviance while promoting proactive, citizenship-oriented employee conduct.
Impacts of Organizational Deviance on Performance and Culture
Organizational deviance significantly undermines overall performance by fostering decreased productivity, higher absenteeism, and increased turnover rates, ultimately disrupting workflow and resource allocation. The prevalence of deviant behaviors such as sabotage, theft, or misuse of information erodes trust among employees and management, leading to a toxic workplace culture characterized by low morale and diminished cooperation. In contrast, a culture plagued by organizational deviance diminishes innovation and knowledge sharing, impairing long-term competitiveness and organizational sustainability.
Benefits of Organizational Citizenship for Company Success
Organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) enhances company success by fostering a cooperative work environment, boosting employee morale, and increasing overall productivity. Unlike organizational deviance, which undermines trust and operational efficiency, OCB promotes proactive support beyond formal job requirements, leading to improved team cohesion and customer satisfaction. Companies that cultivate OCB experience lower turnover rates, higher innovation, and sustained competitive advantage in their industries.
Strategies to Reduce Deviance and Promote Citizenship Behaviors
Implementing clear organizational policies and fostering transparent communication significantly reduce organizational deviance by setting explicit behavioral expectations. Encouraging recognition programs, job enrichment, and leadership support cultivates organizational citizenship behaviors, enhancing employee engagement and collaboration. Regular training sessions emphasizing ethical conduct and teamwork further strengthen a culture of positive workplace behaviors.
Building a Positive Organizational Environment: Balancing Deviance and Citizenship
Balancing organizational deviance and organizational citizenship is essential for building a positive organizational environment, where employees engage in constructive behaviors that encourage innovation without undermining corporate values. Organizational deviance, when managed, can challenge dysfunctional norms and stimulate improvement, while organizational citizenship behaviors promote cooperation, commitment, and enhanced team performance. Effective leadership strategies harness the productive aspects of deviance and nurture citizenship behaviors through clear communication, recognition, and supportive workplace culture to optimize overall organizational effectiveness.
Organizational deviance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com