Charitable organizations play a vital role in addressing social issues by providing resources and support to those in need. These organizations often rely on donations, volunteers, and community engagement to maximize their impact. Discover how your involvement can make a difference by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
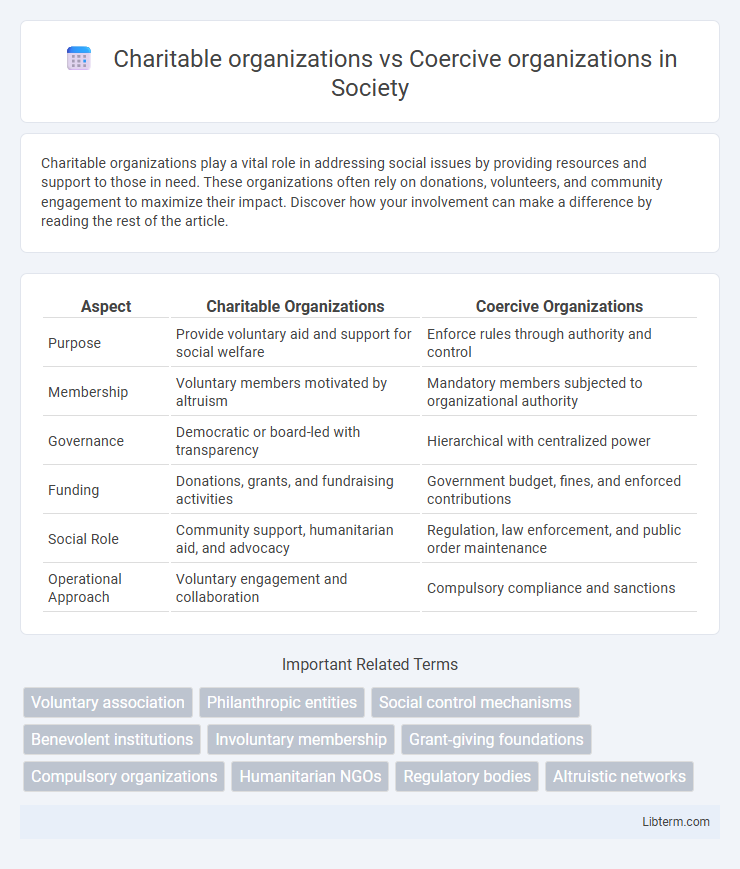
| Aspect | Charitable Organizations | Coercive Organizations |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provide voluntary aid and support for social welfare | Enforce rules through authority and control |
| Membership | Voluntary members motivated by altruism | Mandatory members subjected to organizational authority |
| Governance | Democratic or board-led with transparency | Hierarchical with centralized power |
| Funding | Donations, grants, and fundraising activities | Government budget, fines, and enforced contributions |
| Social Role | Community support, humanitarian aid, and advocacy | Regulation, law enforcement, and public order maintenance |
| Operational Approach | Voluntary engagement and collaboration | Compulsory compliance and sanctions |
Understanding Charitable Organizations
Charitable organizations operate primarily to provide public benefits through voluntary contributions and services, emphasizing philanthropy and community support. They are typically governed by nonprofit laws, ensuring transparency, accountability, and the allocation of resources toward social causes without profit motives. Understanding charitable organizations involves recognizing their reliance on donor trust, mission-driven activities, and regulatory compliance to maintain tax-exempt status and maximize social impact.
Defining Coercive Organizations
Coercive organizations are defined by their use of force or pressure to achieve compliance and control over members or external entities, often operating under strict hierarchical structures and enforced rules. Unlike charitable organizations that rely on voluntary participation and altruistic motives, coercive organizations maintain authority through sanctions, threats, or legal mandates. Examples include penal institutions, military units, and detention centers where obedience and control are paramount for organizational functioning.
Core Differences Between Charitable and Coercive Organizations
Charitable organizations prioritize voluntary support and aid, driven by altruistic missions to address social needs without expecting direct returns. Coercive organizations operate through force or authority, compelling participation or compliance to maintain control or enforce rules. The core difference lies in motivation and method: charitable groups rely on voluntary engagement and goodwill, while coercive groups depend on power and obligation.
Mission and Purpose: Altruism vs. Control
Charitable organizations prioritize altruism by focusing on humanitarian missions aimed at improving societal welfare through voluntary support and resource distribution. Coercive organizations emphasize control, often enforcing compliance through hierarchical authority and regulatory measures to achieve organizational goals. The core purpose of charitable entities revolves around voluntary altruistic actions, whereas coercive organizations operate on structured dominance and mandated obedience.
Funding Sources and Financial Models
Charitable organizations primarily rely on donations, grants, and fundraising events as their funding sources, emphasizing voluntary contributions from individuals, corporations, and philanthropic entities. Their financial models often include unrestricted funds and dedicated endowments that support mission-driven activities with transparency and accountability. In contrast, coercive organizations depend largely on compulsory funding mechanisms such as taxes, fees, or fines imposed by governing authorities, operating under budgets allocated through legal mandates and regulatory frameworks.
Membership and Participation Criteria
Charitable organizations typically have open membership policies, allowing individuals to join based on shared values and voluntary participation in philanthropic activities. Coercive organizations enforce strict membership criteria through compulsory compliance, often using authoritarian measures to ensure conformity and participation. While charitable groups prioritize altruism and inclusion, coercive entities demand obedience and restrict voluntary engagement.
Social Impact and Public Perception
Charitable organizations generate positive social impact by addressing community needs through voluntary contributions and transparent operations, which enhance public trust and support. Coercive organizations, often perceived as authoritative or controlling, may achieve compliance but risk damaging their public image due to perceived insensitivity or lack of autonomy. The contrast in social impact and public perception highlights the effectiveness of voluntary engagement over enforced adherence in fostering sustainable social change.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Charitable organizations operate under strict legal frameworks that emphasize transparency, donor intent, and non-profit status to ensure ethical fundraising and resource allocation. Coercive organizations often face legal scrutiny due to practices involving manipulation or forced compliance, raising significant ethical concerns about autonomy and consent. Compliance with local and international laws, including regulations on financial reporting and human rights, is critical to distinguishing ethical charitable endeavors from coercive activities.
Case Studies: Successful Charitable and Coercive Organizations
Charitable organizations like the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation demonstrate success through philanthropic initiatives targeting global health and education, effectively mobilizing extensive donor networks and transparent impact reporting. In contrast, coercive organizations such as the U.S. military exemplify operational success by enforcing strategic objectives through structured hierarchy and command, ensuring compliance and discipline in mission-critical environments. Case studies reveal that while charitable organizations thrive on voluntary support and societal goodwill, coercive organizations rely on authority and control to achieve their goals efficiently.
Future Trends and Challenges for Both Organization Types
Charitable organizations are increasingly leveraging technology and data analytics to enhance donor engagement and impact measurement, facing challenges in maintaining transparency and adapting to shifting regulatory landscapes. Coercive organizations confront growing scrutiny from human rights groups and governments, requiring strategic shifts toward ethical practices and compliance to sustain operations amid rising societal demands for accountability. Both entity types must navigate digital transformation, increased public awareness, and evolving governance standards to remain effective and legitimate in the future.
Charitable organizations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com