Social participation plays a crucial role in enhancing mental well-being, fostering a sense of belonging, and building strong community connections. Engaging in group activities and community events promotes personal growth and helps develop valuable communication skills. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical ways to boost your social participation and enrich your life.
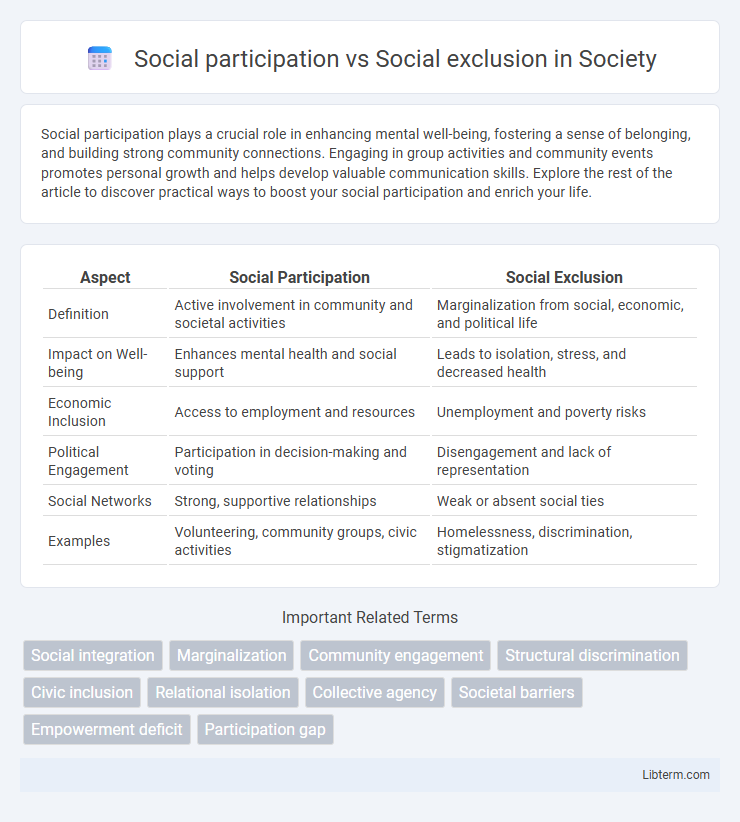
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Participation | Social Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active involvement in community and societal activities | Marginalization from social, economic, and political life |
| Impact on Well-being | Enhances mental health and social support | Leads to isolation, stress, and decreased health |
| Economic Inclusion | Access to employment and resources | Unemployment and poverty risks |
| Political Engagement | Participation in decision-making and voting | Disengagement and lack of representation |
| Social Networks | Strong, supportive relationships | Weak or absent social ties |
| Examples | Volunteering, community groups, civic activities | Homelessness, discrimination, stigmatization |
Understanding Social Participation
Social participation refers to the active engagement of individuals in community activities, fostering inclusion, well-being, and social cohesion. It enhances mental health, builds social networks, and promotes access to resources, contrasting sharply with social exclusion, which isolates individuals or groups from these benefits. Understanding social participation involves recognizing its role in empowering marginalized populations and reducing inequalities in society.
Defining Social Exclusion
Social exclusion refers to the process through which individuals or groups are systematically blocked from various rights, opportunities, and resources that are normally available to members of society. This phenomenon results in limited access to essential services such as education, employment, healthcare, and social networks, leading to marginalization and diminished social participation. Understanding social exclusion is crucial for developing policies aimed at fostering inclusive communities and promoting equal participation across diverse social groups.
Factors Influencing Social Participation
Factors influencing social participation include socioeconomic status, education level, and access to community resources, which significantly determine an individual's ability to engage in social activities. Social networks, cultural norms, and physical or mental health also play crucial roles in either facilitating or hindering participation. Conversely, social exclusion often results from barriers such as discrimination, poverty, and lack of infrastructure, limiting opportunities for meaningful social involvement.
Causes and Consequences of Social Exclusion
Social exclusion stems from factors such as poverty, discrimination, limited access to education, and social stigma, which marginalize individuals or groups from mainstream societal activities. This exclusion leads to significant consequences including increased unemployment rates, poor mental and physical health, reduced social cohesion, and limited opportunities for personal and economic development. Addressing root causes like inequality and enhancing inclusive policies can mitigate these detrimental effects and promote social participation.
The Role of Community in Social Inclusion
Community plays a critical role in fostering social participation by creating supportive environments that encourage engagement and collaboration among diverse groups. Effective community programs promote social inclusion by addressing barriers such as poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to resources, thereby reducing social exclusion. Strong social networks within communities enhance individual well-being and collective resilience, reinforcing a sense of belonging and participation.
Impact of Social Exclusion on Mental Health
Social exclusion significantly impacts mental health by increasing risks of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem, leading to feelings of isolation and hopelessness. Research shows that excluded individuals experience heightened stress levels, which disrupt brain function and emotional regulation. Enhancing social participation fosters resilience and emotional well-being, mitigating the adverse effects associated with social exclusion.
Benefits of Fostering Social Participation
Fostering social participation enhances community cohesion, improves mental health, and promotes economic inclusion, reducing the risk of social exclusion. Active engagement in social networks increases access to resources, support systems, and opportunities for personal development. Encouraging diverse social participation builds resilience and empowers marginalized groups, fostering more equitable societies.
Strategies to Combat Social Exclusion
Strategies to combat social exclusion focus on enhancing social participation through inclusive education, equitable employment opportunities, and community engagement programs. Targeted policies addressing discrimination, poverty alleviation, and accessible public services foster a more inclusive society. Empowering marginalized groups with resources and social networks strengthens their integration and reduces social isolation.
Measuring Social Participation and Exclusion
Measuring social participation involves assessing individuals' involvement in community activities, social networks, and access to resources through surveys, participation indices, and social capital metrics. Social exclusion is quantified by evaluating barriers to social integration, including economic deprivation, limited access to education, healthcare, and discrimination using multidimensional deprivation indices and exclusion scales. Combining quantitative data from national censuses and qualitative insights from ethnographic studies enhances the accuracy of social participation and exclusion measurements.
Building Inclusive Societies for the Future
Social participation empowers individuals by fostering community engagement, which strengthens social cohesion and reduces inequalities. Social exclusion, characterized by barriers such as poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to education or employment, undermines social stability and perpetuates marginalization. Building inclusive societies requires policies promoting equitable access to resources, inclusive governance, and supportive social networks to ensure all members can contribute to and benefit from collective progress.
Social participation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com