Building a strong community fosters connection, support, and shared purpose among its members. Engaging actively with your community enhances collaboration and drives positive impact. Discover practical ways to strengthen your community by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
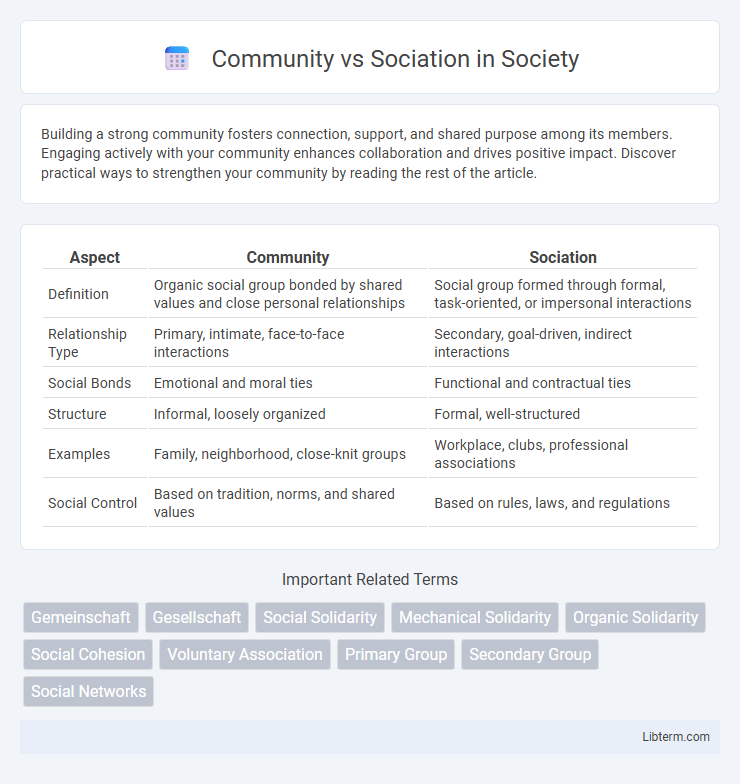
| Aspect | Community | Sociation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organic social group bonded by shared values and close personal relationships | Social group formed through formal, task-oriented, or impersonal interactions |
| Relationship Type | Primary, intimate, face-to-face interactions | Secondary, goal-driven, indirect interactions |
| Social Bonds | Emotional and moral ties | Functional and contractual ties |
| Structure | Informal, loosely organized | Formal, well-structured |
| Examples | Family, neighborhood, close-knit groups | Workplace, clubs, professional associations |
| Social Control | Based on tradition, norms, and shared values | Based on rules, laws, and regulations |
Definition of Community and Sociation
Community refers to a social group characterized by close, personal relationships, shared values, and a strong sense of belonging among its members. Sociation describes formal, impersonal social associations or interactions based on roles, rules, and structured relationships rather than emotional bonds. Understanding these definitions highlights the contrast between emotionally connected communities and organized social arrangements in sociology.
Historical Evolution of Social Groups
The historical evolution of social groups reveals a transition from communities characterized by close, personal relationships and shared traditions to sociations defined by formal, indirect interactions within organized institutions. Early human societies were predominantly community-based, emphasizing kinship, mutual dependence, and collective identity, while modern social structures evolved toward sociations with contractual ties and role-based associations. This shift reflects broader societal changes including urbanization, industrialization, and the rise of complex bureaucratic systems that prioritize efficiency and individualism over communal bonds.
Key Differences Between Community and Sociation
Community is characterized by close-knit relationships, shared values, and strong social bonds often found in small, homogenous groups, whereas sociation involves more formal, impersonal associations typically based on individual roles or interests within larger, diverse populations. The key difference lies in emotional connectedness; communities emphasize collective identity and mutual support, while sociations prioritize functional cooperation and goal-oriented interactions. Furthermore, communities tend to be enduring with intrinsic social cohesion, whereas sociations are often temporary and task-specific with more flexible social ties.
Social Bonds: Emotional vs Rational Connections
Community forms social bonds primarily through emotional connections characterized by shared values, traditions, and a deep sense of belonging, fostering strong interpersonal relationships. Sociation relies on rational connections based on formal roles, contractual obligations, and functional interactions, emphasizing practical cooperation rather than emotional closeness. These distinctions shape the nature of social cohesion, with communities promoting solidarity and sociations facilitating structured social organization.
Examples of Community in Modern Society
Communities in modern society manifest through neighborhood associations, online interest groups, and cultural organizations that foster shared identities and mutual support. Examples include local farmers' markets where residents connect over sustainable food practices, social media platforms like Facebook groups centered on hobbies or activism, and religious congregations that provide spiritual and social cohesion. These community forms emphasize close-knit relationships and collective values distinct from the more individualistic and goal-oriented nature of sociation.
Sociation in Contemporary Social Structures
Sociation in contemporary social structures refers to the dynamic and fluid interactions among individuals and groups characterized by impersonal, goal-oriented relationships rather than close emotional bonds present in communities. Modern societies emphasize roles, statuses, and institutional frameworks that facilitate cooperation and coordination across diverse social networks and organizations. This shift towards sociation reflects increased specialization, mobility, and complexity in social arrangements, enabling efficient functioning within urban, professional, and digital environments.
The Role of Tradition in Community Building
Tradition serves as a foundational pillar in community building, reinforcing shared values and collective identity that strengthen social bonds. It facilitates continuity by preserving cultural practices and norms, which foster trust and cooperation among members. In contrast, sociation emphasizes individual roles and formal associations, where tradition has a limited influence compared to structured interactions and functional objectives.
Impact of Globalization on Community and Sociation
Globalization intensifies the interaction between traditional communities and modern sociations by expanding cross-cultural connections and economic networks. Communities rooted in local traditions face challenges preserving social cohesion as global influences introduce diverse values and lifestyles, altering identity and social bonds. Sociations, structured around formal institutions and specialized roles, become more complex and interconnected due to transnational organizations and digital communication, reshaping social integration on a global scale.
Challenges in Maintaining Social Cohesion
Maintaining social cohesion in communities faces challenges such as balancing individual autonomy with collective interests and managing conflicts arising from diverse values and norms. In sociation, the complexity of relationships and institutional roles can lead to fragmentation and weakened social bonds. Effective communication and inclusive participation are critical to overcoming these obstacles and fostering unity.
Future Trends: Blurring Lines Between Community and Sociation
Emerging technologies and digital platforms are reshaping the boundaries between community and sociation, fostering hybrid social structures that combine close-knit relationships with more impersonal, role-based interactions. Virtual reality, social media, and online collaboration tools enable dynamic, fluid connections that challenge traditional distinctions by integrating emotional bonds with instrumental ties. These future trends suggest increasingly interconnected social networks where community warmth coexists with sociation efficiency, reflecting evolving human social behavior in a digitized world.
Community Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com