Integration streamlines processes by connecting disparate systems and data sources, enhancing efficiency and accuracy across your operations. Seamless integration supports real-time data flow, reducing manual effort and errors while improving overall decision-making. Discover how effective integration can transform your workflow by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
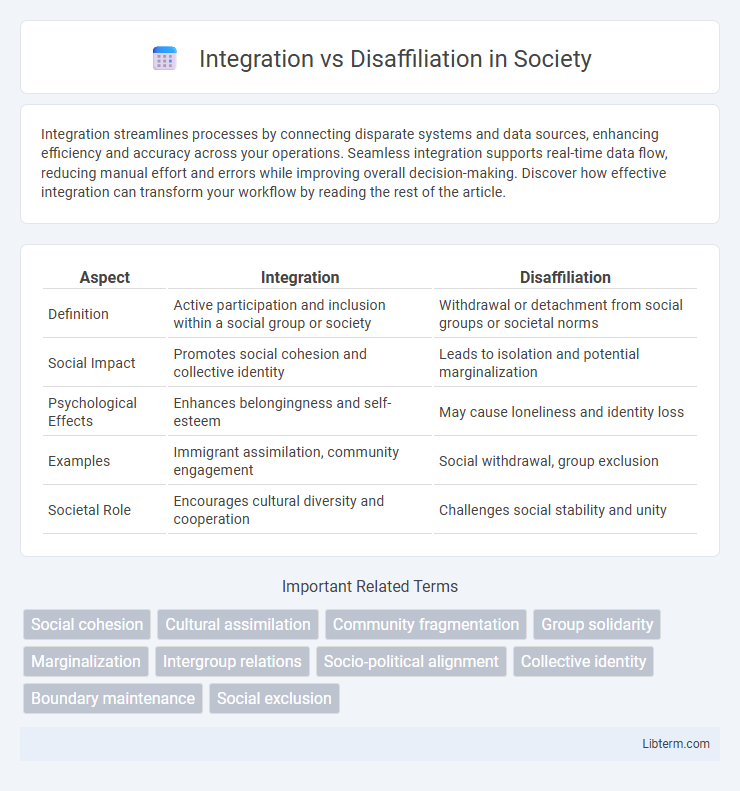
| Aspect | Integration | Disaffiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation and inclusion within a social group or society | Withdrawal or detachment from social groups or societal norms |
| Social Impact | Promotes social cohesion and collective identity | Leads to isolation and potential marginalization |
| Psychological Effects | Enhances belongingness and self-esteem | May cause loneliness and identity loss |
| Examples | Immigrant assimilation, community engagement | Social withdrawal, group exclusion |
| Societal Role | Encourages cultural diversity and cooperation | Challenges social stability and unity |
Understanding Integration and Disaffiliation
Integration refers to the process by which individuals or groups become part of a larger social, cultural, or organizational system, fostering inclusion and unity. Disaffiliation involves the deliberate separation or withdrawal from such systems, often to maintain distinct identity or autonomy. Understanding integration and disaffiliation requires examining motivations behind belonging or distancing, such as social acceptance, identity preservation, and cultural adaptation.
Historical Context: Roots of Integration and Disaffiliation
The historical roots of integration trace back to early immigration waves and civil rights movements aiming to incorporate diverse groups into mainstream society, emphasizing social cohesion and equal opportunities. Disaffiliation emerged from contexts of systemic exclusion, cultural preservation, and political resistance, where marginalized communities sought independence from dominant institutions. These contrasting origins reveal deep societal dynamics influencing group identities and collective actions over time.
Key Differences Between Integration and Disaffiliation
Integration involves incorporating individuals or groups into a larger system or community, promoting cohesion and access to shared resources. Disaffiliation refers to the process of withdrawing or separating oneself from an established group or organization, often leading to loss of support and identity within that network. Key differences include the direction of social connection--joining versus leaving--the impact on social identity, and the access to collective benefits or resources.
Motivations Behind Pursuing Integration
Motivations behind pursuing integration often include the desire for increased economic growth, access to larger markets, and enhanced political cooperation. Countries seek integration to improve trade efficiency, attract foreign investment, and foster regional stability through collaborative policies. Economic interdependence and shared strategic interests drive nations to commit to deeper integration rather than pursue disaffiliation.
Factors Driving Disaffiliation Decisions
Disaffiliation decisions are primarily driven by ideological misalignment, perceived lack of representation, and dissatisfaction with organizational policies or leadership. Socioeconomic factors, cultural shifts, and changes in community needs also significantly influence individuals' or groups' choices to separate from established institutions. Trust erosion due to transparency issues or conflict further exacerbates the push towards disaffiliation over integration.
Impact on Organizational Structure and Culture
Integration fosters a unified organizational structure by aligning departments and processes, promoting cohesive culture through shared values and collaborative practices. Disaffiliation often leads to decentralization, creating fragmented units with distinct subcultures and potential challenges in maintaining consistent communication and strategic alignment. The structural centralization in integration enhances adaptability, whereas disaffiliation may result in increased autonomy but risks cultural divergence.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Case studies on integration versus disaffiliation reveal varied outcomes influenced by organizational culture and stakeholder alignment. Successful integration, as seen in mergers like Disney and Pixar, leverages complementary strengths and shared visions to drive innovation and growth. Conversely, disaffiliation cases such as the Yahoo and Alibaba separation highlight challenges in autonomy loss and strategic misalignment, leading to operational inefficiencies and market share decline.
Challenges and Risks of Integration vs Disaffiliation
Integration poses challenges such as cultural clashes, loss of organizational identity, and operational disruptions that can lead to decreased employee morale and productivity. Disaffiliation risks include isolation from key resources, reduced brand recognition, and potential financial instability due to loss of shared services and economies of scale. Both strategies require careful risk management to balance short-term disruptions with long-term strategic goals.
Future Trends: Integration and Disaffiliation in Modern Contexts
Future trends indicate rising complexities in integration and disaffiliation, driven by globalization, digital connectivity, and shifting social identities. Integration involves merging diverse communities and systems to foster inclusivity, while disaffiliation reflects growing detachment from traditional institutions and group identities. Emerging patterns suggest hybrid models combining selective integration with personalized disaffiliation, reshaping sociocultural dynamics and organizational structures.
Strategic Considerations for Decision-Makers
Decision-makers must evaluate integration and disaffiliation by analyzing potential impacts on operational control, resource allocation, and market positioning. Integration often enhances synergies and competitive advantage through shared assets and unified strategies, whereas disaffiliation enables agility, focused specialization, and reduced complexity. Assessing organizational culture alignment, financial health, and long-term strategic goals is critical to making informed decisions that balance risk and opportunity.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com